12.02.2022
ESA selects payloads for Ariane 6 first flight

ESA in close collaboration with ArianeGroup and Arianespace has selected payloads which best fit the profile of the first mission of its new generation Ariane 6 launch vehicle from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana.
This selection follows ESA’s announcement of opportunity in November 2021, which offered a launch to low Earth orbit for experiments up to a total mass of 80 kg and release of payloads with a combined mass of up to 800 kg. They will be hosted on a ‘mass dummy’ featuring a large platform, inside the 14 m long version of the fairing on an Ariane 6 fitted with two strap-on boosters (A62 version).
This demonstration flight will contribute to the qualification of the Ariane 6 launch system as part of the transition from its highly reliable and successful predecessor, Ariane 5. This launch is an important step in the preparation for future institutional missions planned for Ariane 6, such as Galileo.
For this flight, ESA is responsible for operations from the launch campaign to the payload separation, and then disposal of the upper stage through burn-up during reentry.
“I’m glad that ESA can use the very first Ariane 6 flight as a platform for launching these fantastic payloads, some of which will enable European start-ups to validate their systems and provide future commercial services. The Ariane 6 inaugural launch is a key step towards full qualification of the Ariane 6 launch system,” said Daniel Neuenschwander, ESA Director of Space Transportation.
Experiments on board
Four experiments, ranging in mass from 0.15–12 kg, will be fixed to the platform on top of the mass dummy. These experiments will return valuable data up to the end of the mission when the upper stage reenters Earth’s atmosphere.
| Organisation | Country | Payload | Description | Mass |
| Garef Aerospatial | France | PariSat | Thermal equilibrium of an array to confirm black-body radiation theory | ≤12 |
| Sint-Pieterscollege | Belgium | Peregrinus | Dual sensor magnetic field | ≤ 0.5 |
| Libre Space | Greece | SIDLOC | In-orbit demonstrator Radio Frequency beacon | ≤ 0.15 |
| ESA | – | ESA YPSat – Eye2Sky | Photo and video footage | < 3 |
Ridesharing payloads
ESA has also selected the candidate payloads listed below as part of the baseline for this Ariane 6 flight. Negotiations can now start for the corresponding launch service.
| Organisation | Country | Payload | Description | Mass (kg) |
| PTS | Germany | CuriumOne | with a duplicate ASTRIS Engineering Qualification Model PCB as primary payload |
≤ 24.5 (AstroFein deployer: 6.5) |
| TU Berlin | Germany | OOV-Cube | Microsatellite – IoT agriculture use case demo |
≤ 17 (AstroFein deployer: 7) |
| ESA Education Office / University of Catalunya | Spain | 3Cat4 | 1U CubeSat – Techno demo Flexible Microwave Payload | 1.3 |
| ESA Education Office / University of Lisbon | Potugal | ISTSAT | 1U CubeSat – Characterisation of aircraft’s ‘cone of silence’ and in-flight performances of a custom-made Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) system | 1.3 |
| Spacemanic | Slovakia | GRBBeta | 1U CubeSat – Gamma Ray Burst detection | 1.3 |
| ArianeGroup | France | SpaceCase SC-X01 | Test platform for reentry technologies such as new-generation ablative materials for thermal protection systems |
≤ 43 (separated: 40) |
| The Exploration Company | France, Germany | Bikini Demo | First passive, small-scale demonstrator of a reentry capsule |
≤ 26 (separated: 20) |
Deployers
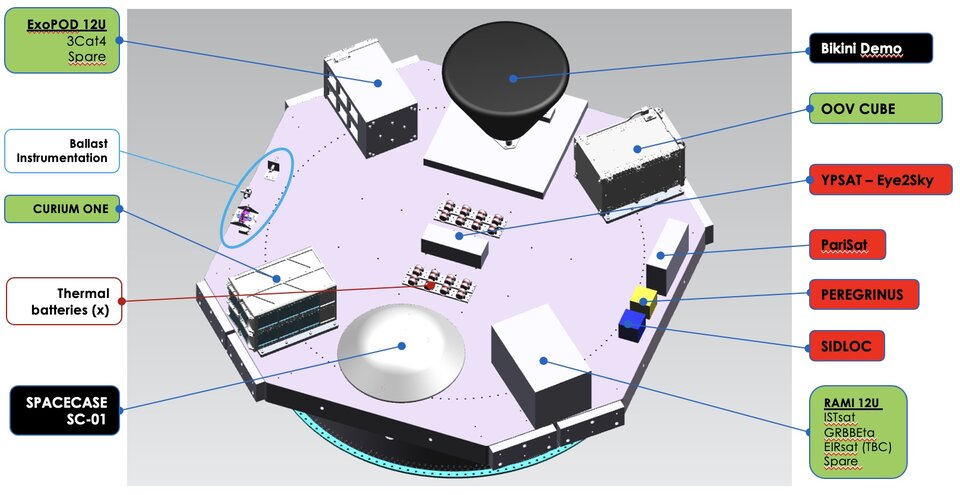
Two deployers will be arranged on board and will accommodate CubeSats. The RAMI deployer is built by Spain’s UARX Space, and the ExoPOD is built by ExoLaunch in Germany.
With some spaces for CubeSats still available, ESA may add to this collection closer to launch.
Ariane 6 is a modular launch vehicle using two or four P120C strap-on boosters to achieve the required performance. The reignitable Vinci engine powers the upper stage which allows Ariane 6 to reach a range of orbits to deliver more payloads on a single launch. The upper stage engine will typically burn one, two or more times to reach the required orbits. After payload separation a final burn deorbits the upper stage to mitigate space debris.
Ariane 6 is a project managed and funded by the European Space Agency. ArianeGroup is design authority and industrial prime contractor for the launcher system. The French space agency CNES is prime contractor for the development of the Ariane 6 launch base at Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana. Arianespace is the launch service provider of Ariane 6.


Access the video
Ariane 6 takes next step to first flight with upper stage hot fire tests

ESA’s flagship Ariane 6 launch vehicle programme has taken a dramatic step towards first flight with the start of a series of hot fire tests of the rocket’s upper stage and its all-new Vinci engine.
These tests, which began on 5 October 2022, represent a significant step forward thanks to the specially-built P5.2 test bench at Germany’s DLR centre for engine and stage testing in Lampoldshausen. The P5.2 test bench subjects the entire upper stage to operating conditions representative of a flight from Europe's Spaceport in French Guiana, with the exception of vacuum and microgravity.
Vinci, the upper stage engine of Ariane 6 fed by liquid hydrogen and oxygen, can be stopped and restarted multiple times – a critical capability for the complex missions demanded by launch customers today: placing several satellites into different orbits and de-orbiting the upper stage, to leave an absolute minimum of hazardous debris in space.
In addition to restart capabilities and endurance in space, Vinci has been developed for reliability, simplicity and lower costs
This test series is a critical milestone on a development path that will soon see Ariane 6 replace Ariane 5 as ESA’s heavy launcher. For more than a quarter century, Ariane 5 has been a reliable partner for commercial, institutional and scientific clients – one of its most notable missions was the 25 December 2021 flight that carried the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope to its operational outpost in deep space. But Ariane 6 will be an even more versatile vehicle, further strengthening Europe’s autonomy in accessing space.
COMPLEX TESTING

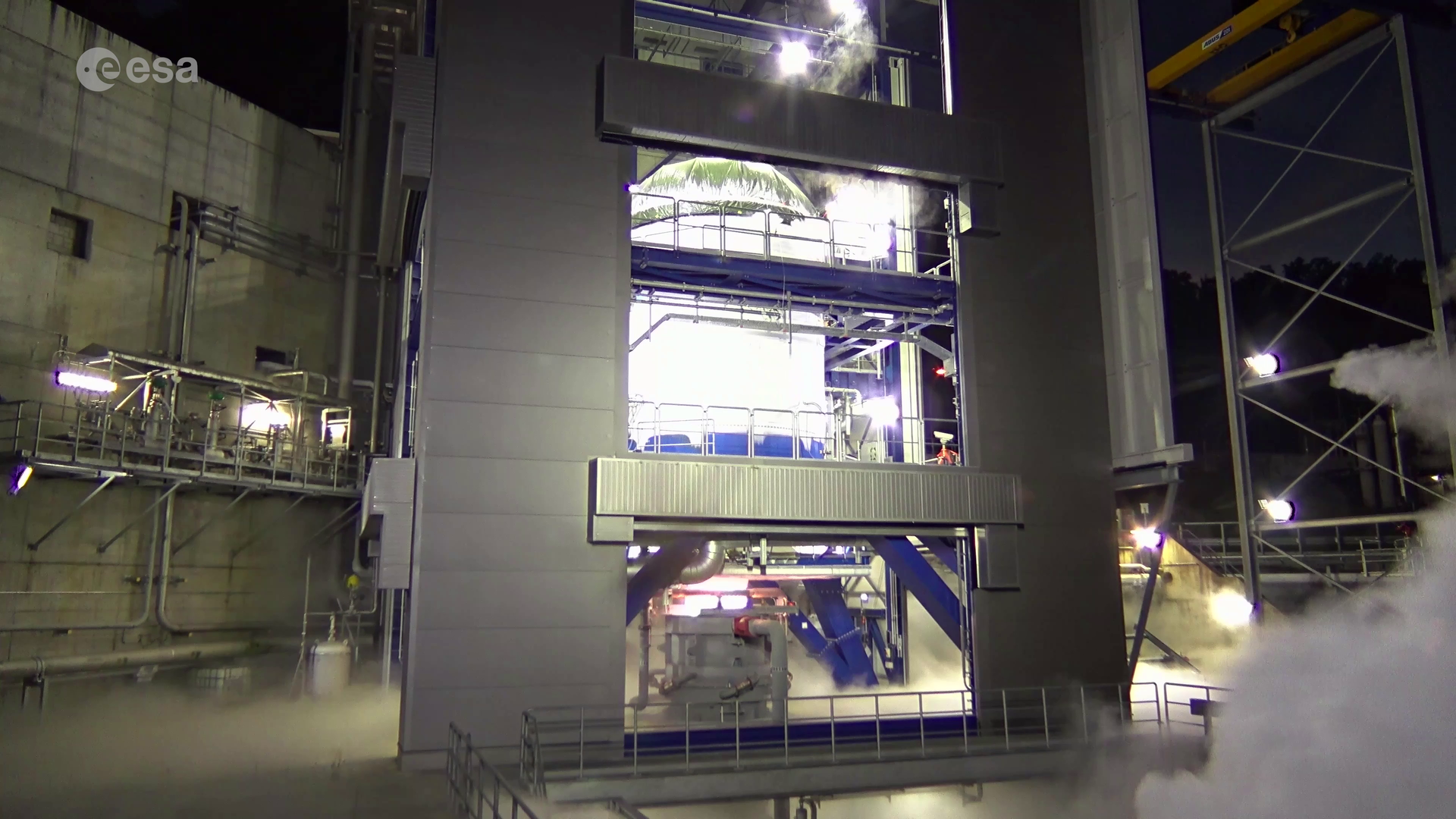
Access the video
The tests being run at Lampoldshausen are also evaluating an innovative Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) which works in tandem with the Vinci engine and is instrumental to Ariane 6 upper stage performance. In order to restart in space, earlier engines relied on large quantities of tanked helium to generate the necessary pressure and temperature in the propellant tanks and to ensure there are no bubbles in the fuel lines. But the APU delivers these conditions using only small amounts of the cryogenic hydrogen and oxygen already carried in the main tanks.
This test series is being run by DLR and ArianeGroup, the Ariane 6 launcher prime contractor. When the test series is complete, this upper stage – integrated by ArianeGroup at its facility in Bremen, Germany – will be shipped to ESA’s ESTEC technical centre in the Netherlands for stage separation and acoustic tests.
Ultimately, the Lampoldshausen tests will investigate hardware behaviour and system function of the complete stage with its tanks, engines and avionics. “The preparation for these hot firing tests is even more complex than for an actual launch,” says Ariane 6 launcher programme manager Guy Pilchen, noting that: “Our colleagues in Lampoldshausen have decades of experience in rocket propulsion with extremely advanced test facilities. With ArianeGroup colleagues to control the upper stage and DLR people operating the test bench, we couldn’t ask for a better team.”
ESA Director of Space Transportation Daniel Neuenschwander adds that this new engine and the upper stage it powers are indispensable components of Ariane 6 and its objective – to guarantee that Europe maintains independent, competitive and sustainable access to space:
“It’s a fact in the 21st century that Europeans depend on space for safety, prosperity and security. Europe needs to work toward complete autonomy in accessing and operating in space. Ariane 6 is key to this and we are eager to see the liftoff from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana.”
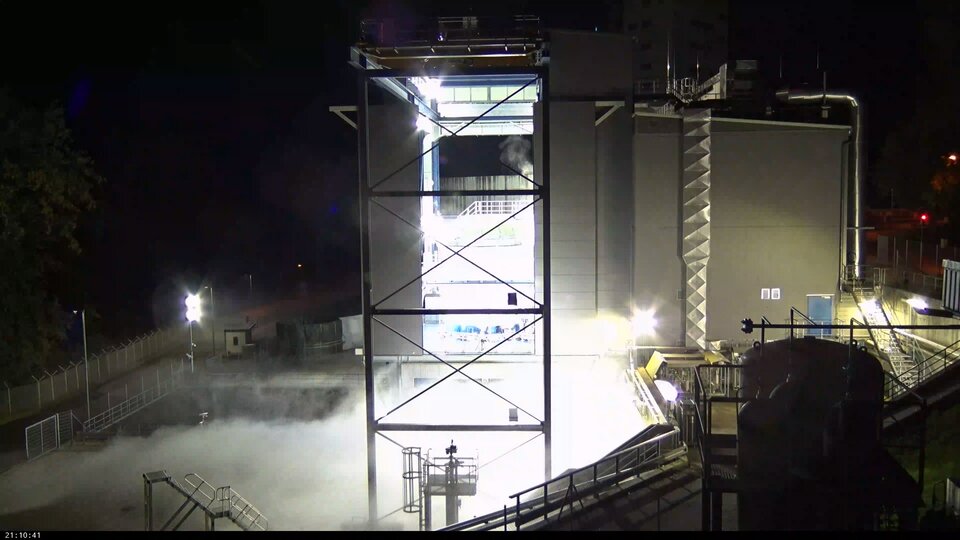

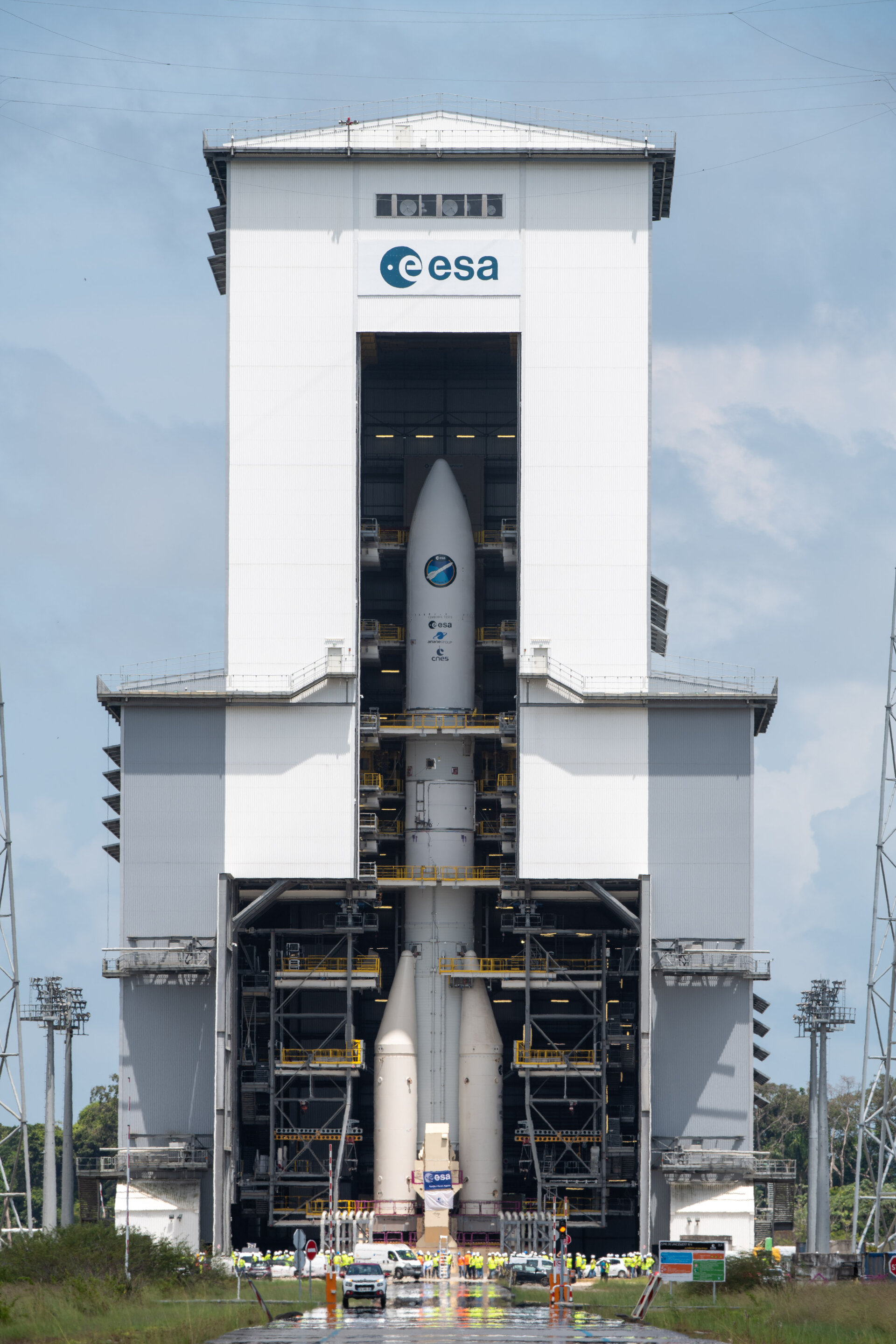
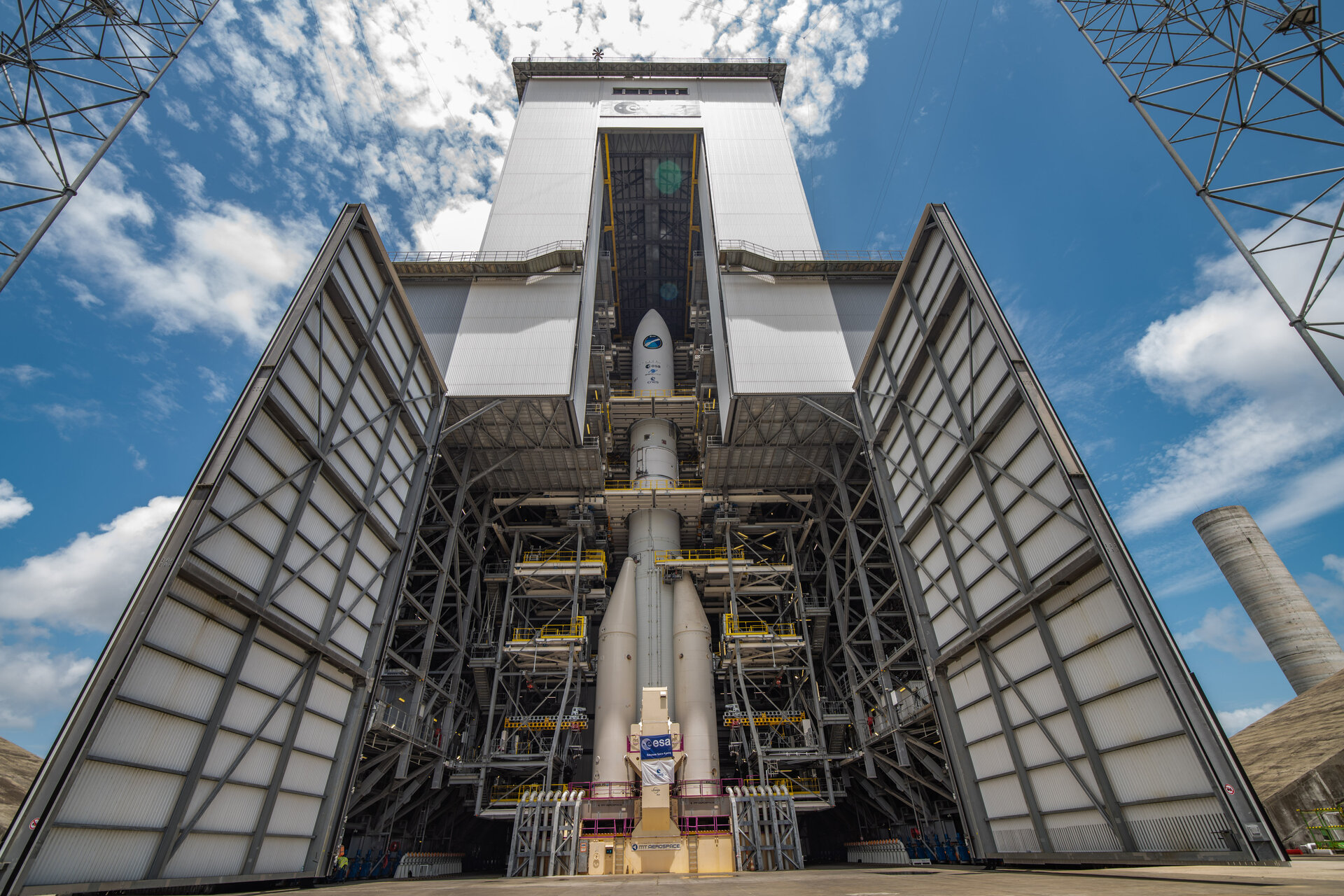
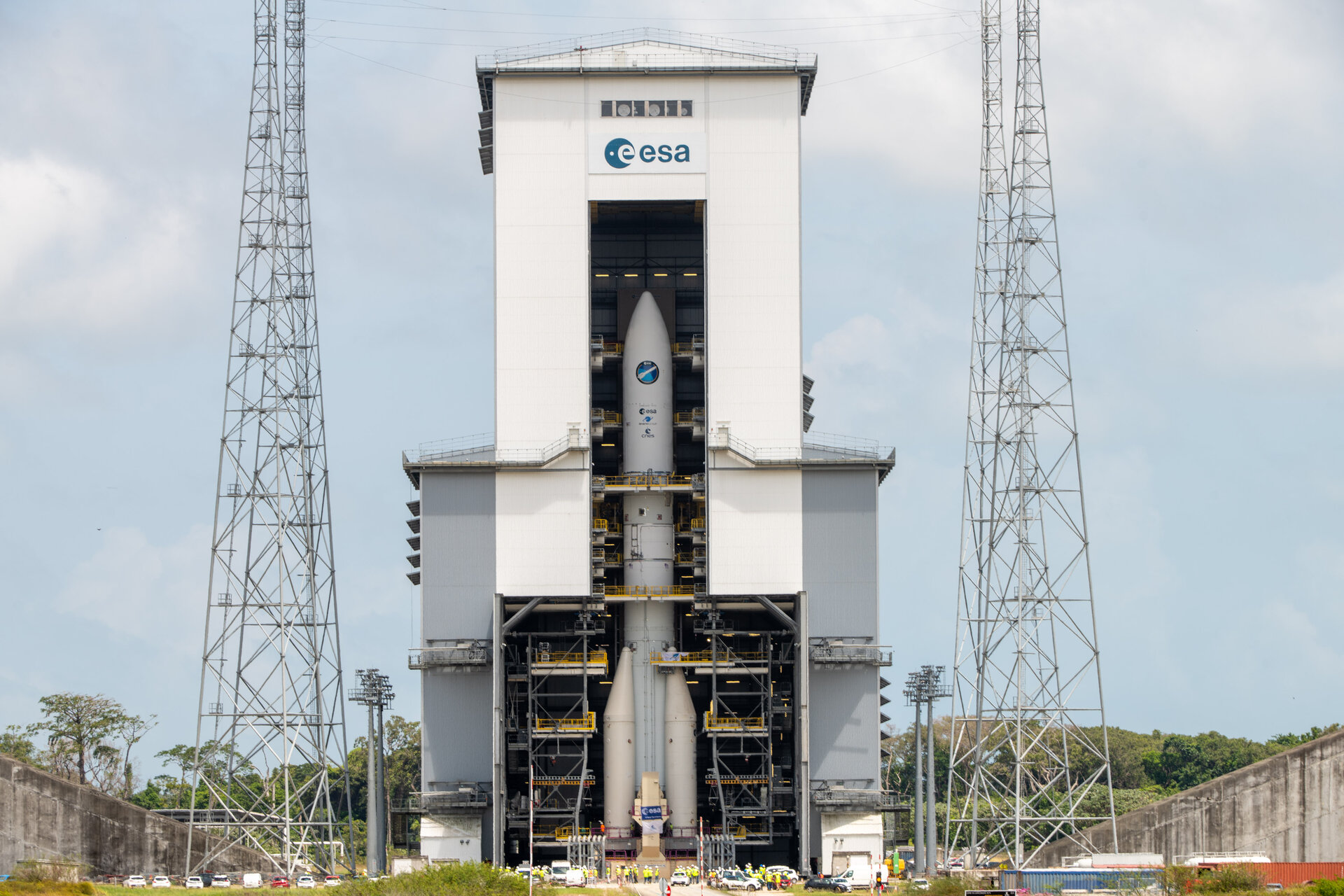
Ariane 6 stands tall on its launch pad
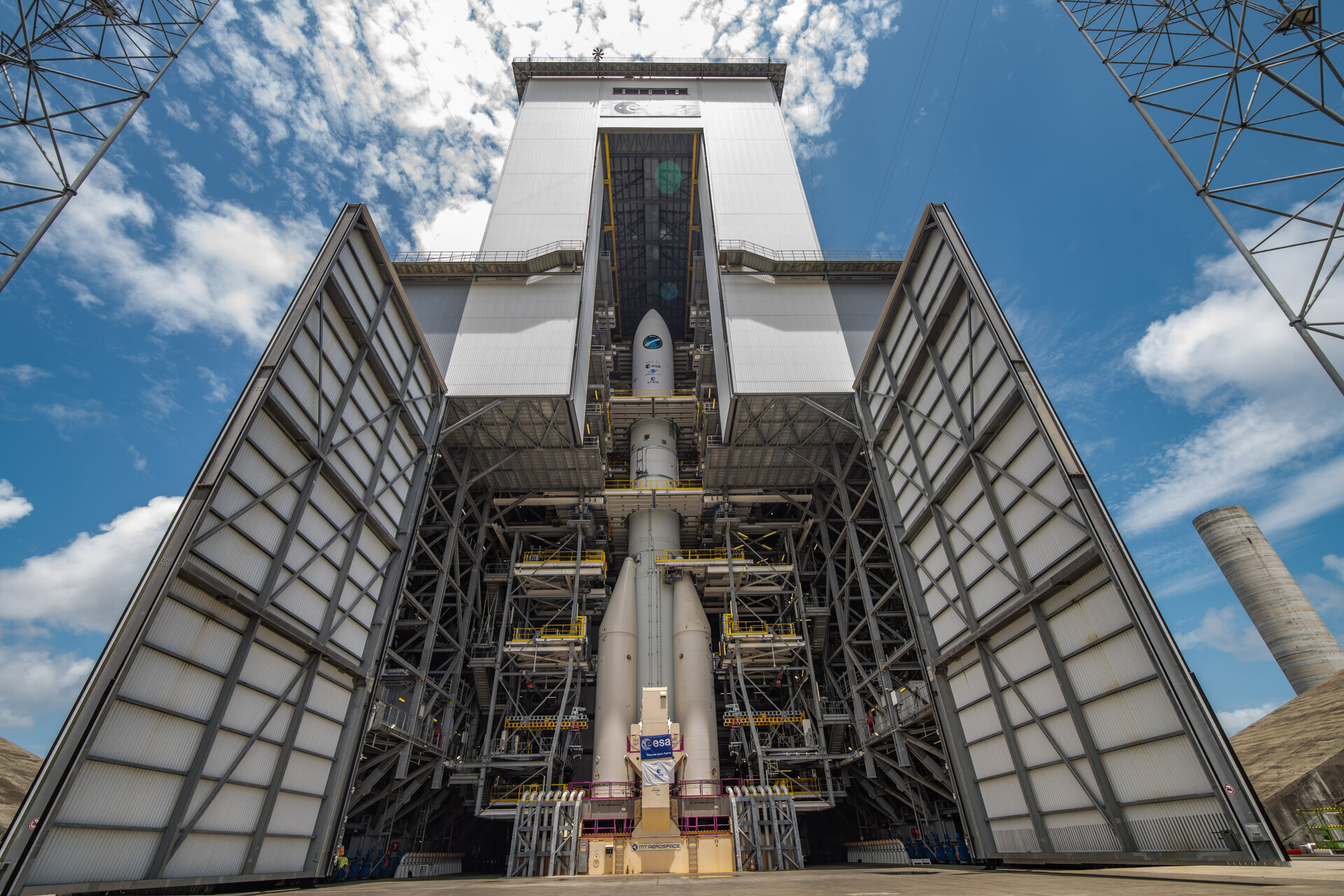

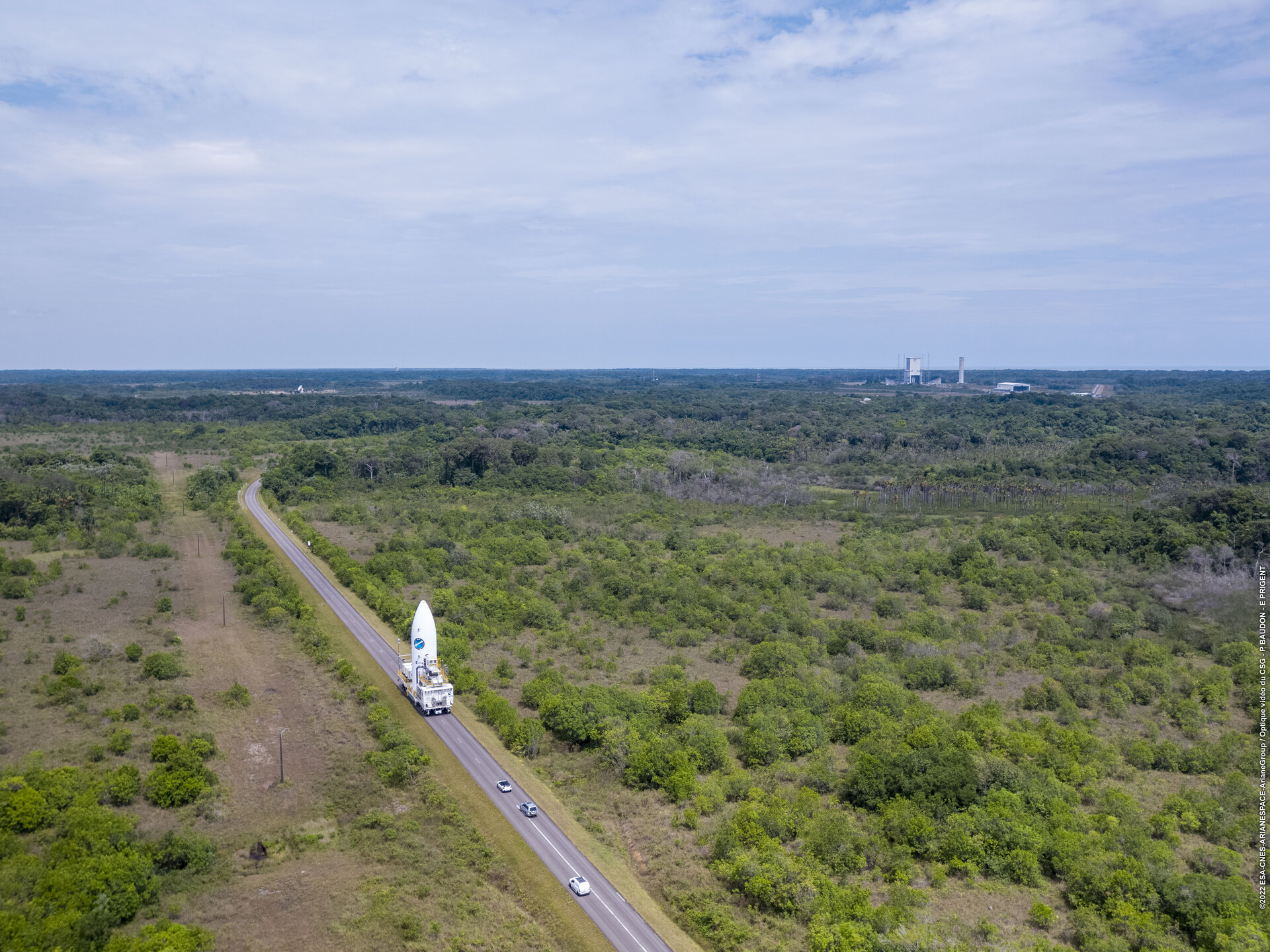
The Ariane 6 launch pad at Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana now hosts for the first time a fully assembled example of ESA’s new heavy-lift rocket, following the addition of an upper composite to the core stage and four boosters already in place. The upper composite – consisting of two half-fairings and a payload mock-up with the structural adapter needed to join it to the core stage – made the 10 km trip from the encapsulation building to launch pad on 12 October.
Assembly, transfer and installation of an upper composite validates the Ariane 6 assembly process. Now, over the next several weeks, teams from ESA, ArianeGroup and French space agency CNES will make the mechanical, electrical and fluid connections which join this test model of the Ariane 64 configuration to the launch pad.
With Ariane 6 fully integrated with the pad, so-called combined tests will validate the rocket, launch pad and shared electrical, fluid and mechanical systems as a complete system. The combined tests include tank filling and drainage operations which guarantee smooth-running of a launch sequence. Flight and control bench software will also be tested.
Then, the launch pad will serve as a test bed for static hot-fire tests of the Vulcain 2.1 core stage engine, including aborted firings and long firings with disconnection. Vulcain 2.1 is derived from Ariane 5’s Vulcain 2.
Separately, static hot-fire tests of the Ariane 6 upper stage and its all-new Vinci engine began in October on a purpose-built test bed at Germany’s DLR centre for engine and stage testing at Lampoldshausen.
The reignitable Vinci engine allows Ariane 6 to deliver multiple payloads to different orbits on a single launch. After payload separation a final engine burn deorbits the upper stage so that it does not become a debris threat in space.
ESA Director of Space Transportation Daniel Neuenschwander underscores the importance of Ariane 6 as a successor to Ariane 5, which for more than a quarter century has provided Europe with reliable access to space: “Innovation is the key to maintaining Europe’s capacity to reach space with a fully independent launch system that is competitive and versatile.”
“With Ariane 6 we have Europe’s best engineers developing new technologies and manufacturing methods to build on the success of one of the world’s most reliable launch systems.”
On Wednesday 19 October 2022, a media briefing will be held in Paris at 1700 to detail Ariane 6 progress. Media can attend in person or by Webex; for details and registration here. The briefing will be broadcast to all interested viewers on ESA Web TV. Taking part will be ESA and its Ariane 6 partners: prime contractor ArianeGroup, launch operator Arianespace and French space agency CNES, which operates Europe’s Spaceport and is delivering Ariane 6 ground infrastructure.
Ariane 6 is a modular launch vehicle using either two or four P120C strap-on boosters, depending on mission requirements. The P120C engine does double duty, also serving as the first stage of ESA’s new Vega-C rocket.
Ariane 6 is project-managed and funded by ESA, which also acts as launch system architect. ArianeGroup is design authority and industrial prime contractor for the launcher system and CNES is prime contractor for the Ariane 6 launch base at Europe’s Spaceport. Arianespace is the launch service provider of Ariane 6.
Quelle: ESA
----
Update: 24.11.2022
.
France, Germany and Italy sign agreement on launch vehicle development
PARIS — An agreement among three European countries could help secure near-term funding for launch vehicle development but have a bigger effect in the long term on how future projects are financed.
The governments of France, Germany and Italy announced Nov. 22 they signed an agreement on “the future of launcher exploitation in Europe” intended, they said, to enhance competitiveness of European vehicles while also ensuring independent European access to space.
The agreement includes a timetable that, by June 2024, calls for a new framework to be in place for public financing of vehicles such as the Ariane 6 and Vega C. That includes “a mechanism incentivizing cost reduction” with funding “commensurate to the commercial risks taken” and ability to achieve target prices.
The agreement also endorses having new small launch vehicles under development by several European companies be able to compete for European Space Agency missions. That’s considered a priority for Germany in particular, which has supported development of commercial small launch vehicles.
The agreement coincides with the ongoing ESA ministerial meeting where member states will allocate funding for projects, including launch vehicle development. ESA is seeking a little more than 3 billion euros ($3.1 billion) for space transportation overall, including 600 million euros for an Ariane 6 “transition program” as the long-delayed rocket, whose first flight has slipped to at least late 2023, enters service.
The program has secured two-thirds of its funding going into the ministerial, but faced a gap of 195 million euros as the meeting started. ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher, speaking to reporters at the end of the first day of the ministerial council meeting Nov. 22, said he was optimistic the agreement announced by France, Germany and Italy would help close that gap.
“This was quite important because this political understanding and agreement unblocks other discussions that then have an influence on subscriptions,” he said. “That was quite important and significant, and opened the door for a discussion later on.”
However, as of late Nov. 22 that funding gap was not yet closed, according to a source familiar with the negotiations. That was, the source added, to be expected given the nature of negotiations, including the iterative process where countries revise their funding commitments over several rounds.
The agreement will help close that funding gap, the source said, because it united France, Germany and Italy around support for both Ariane 6 and Vega C as well as future launch systems, creating interdependence among the countries given differing priorities. Any long-term agreement requires success in securing funding for launch programs at the ministerial.
However, the agreement appeared to open the door to revisit a long-standing ESA principle of “georeturn,” or apportioning contracts based on the share each country contributes to agency programs. Some larger countries have been critical of georeturn, arguing it makes programs less efficient.
The document stated that, as part of the new launcher framework, “such exercise would involve starting a reflection with concerned states on the conditions for the industrial and geographical distribution of work in exploitation.”
A statement from the French economic ministry was more blunt, stating that competitiveness would be achieved in part by a change in the rules for geographic return.
Any change, an agency source said, would be a long-term effort, and require the approval of ESA’s 22 member states, which would not be easy. The rules for Ariane 6 and Vega C in particular were set at the beginning of those programs year ago, although the source said that the georeturn issue could be examined for future launch vehicle development projects.
There is other pressure on ESA to reform its support of launch vehicle development. “There is no European space policy without autonomous access to space,” said Thierry Breton, European Union commissioner for the internal market, in comments at the opening session of the ministerial meeting Nov. 22.
“The shortage of autonomous launch capacity in the E.U. has a direct impact on the deployment of E.U. space programs like Galileo,” he said, referring to the ongoing pause in launching Galileo satellites because the Soyuz rocket is no longer available and Ariane 6 is delayed. “The situation is not sustainable for long, and there is an urgent need to remedy the situation through a truly European approach to have a fully autonomous, reliable and cost-effective E.U. launch solution, including, of course, backups covering all ranges of launchers.”
Breton said he expected ESA member states to back “sustained financing” of Ariane 6 and Vega C and work on future launch systems. The E.U., he said, “is definitely ready to support all these efforts, and it will.”
Quelle: SN
----
Update: 29.11.2022
.
Airbus and ArianeGroup sign Ariane 6 transition batch contract in Spain
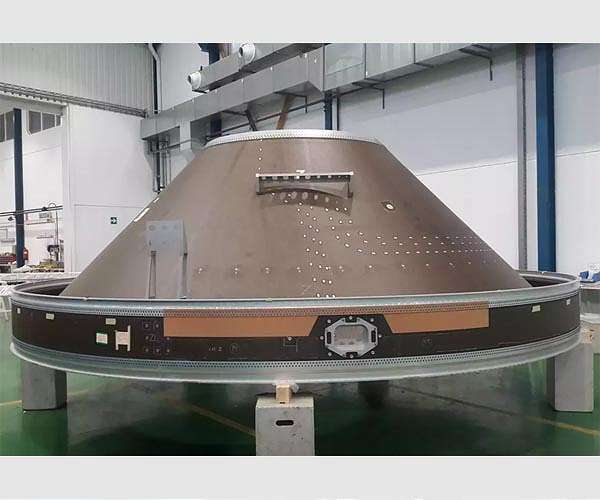

The Interface Structure (upper and lower) is the largest space carbon fibre structure ever produced in Europe. The other structures include the Launch Vehicle Adapter, for the upper stage; and the Equipped Solid Rocket upper part of each rocket booster.
Airbus and ArianeGroup have signed a contract for the next transition batch of Ariane 6 large carbon fibre structures. The contract includes the manufacturing and supply of innovative, large, lightweight structures for the next fourteen Ariane 6 launchers, to be manufactured until 2025. The contract will support ArianeGroup's ramp up to full production rate by then.
Airbus builds up to four carbon fibre structures for each Ariane launcher at its Getafe site, near Madrid. The new state-of-the-art 4.0 industrial facility includes a dedicated manufacturing and assembly line for the Ariane 6 launcher structures. The latest technology innovations have resulted in a reduced mass while delivering a stronger structure in a single piece at a lower cost.
The Interface Structure (upper and lower) is the largest space carbon fibre structure ever produced in Europe. The other structures include the Launch Vehicle Adapter, for the upper stage; and the Equipped Solid Rocket upper part of each rocket booster.
"Signing this contract is a significant step forward, not only for Airbus and its launcher activities in Spain, but for the overall Ariane 6 programme," said Luis Guerra, head of Space Systems in Airbus in Spain. "It demonstrates that Spanish participation is key to the future of Ariane 6 and what is next in space for Europe."
"Following the signature of the exploitation contracts with Sabca, Europropulsion, Avio and MTAerospace, this contract with Airbus is a new and key step towards a strong Ariane 6 European team" said Stephane Nogatchewsky, Head of Procurement of ArianeGroup.
Quelle: SD




