.

Mission: Long Duration Exposure Facility deploy, first on-orbit spacecraft repair
Space Shuttle: Challenger
Launch Pad: 39A
Launch Weight: 254,254 pounds
Launched: April 6, 1984 at 8:58:00 a.m. EST
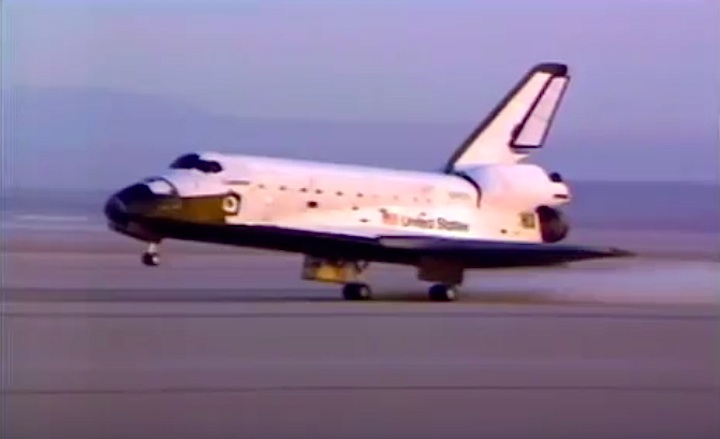
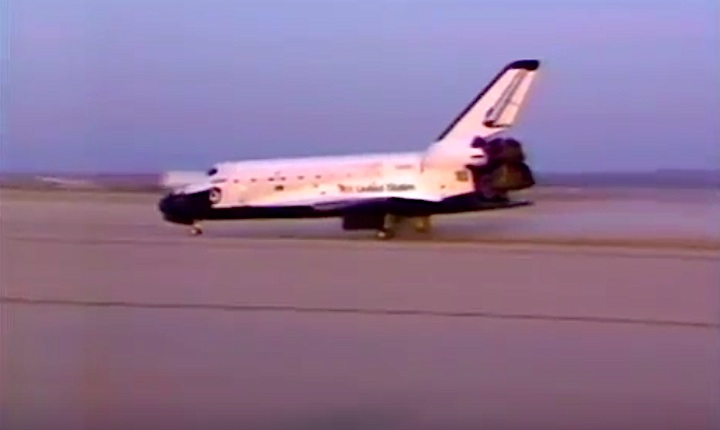
Landing Site: Edwards Air Force Base, Calif.
Landing: April 13, 1984 at 5:38:07 a.m. PST
Landing Weight: 196,975 pounds
Runway: 17
Rollout Distance: 8,716 feet
Rollout Time: 49 seconds
Revolution: 108
Mission Duration: 6 days, 23 hours, 40 minutes, 7 seconds
Orbit Altitude: 313 nautical miles
Orbit Inclination: 28.5 degrees
Miles Traveled: 2.9 million
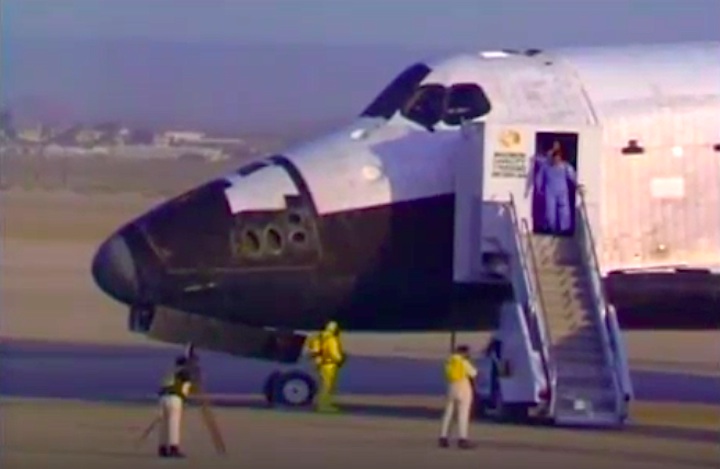
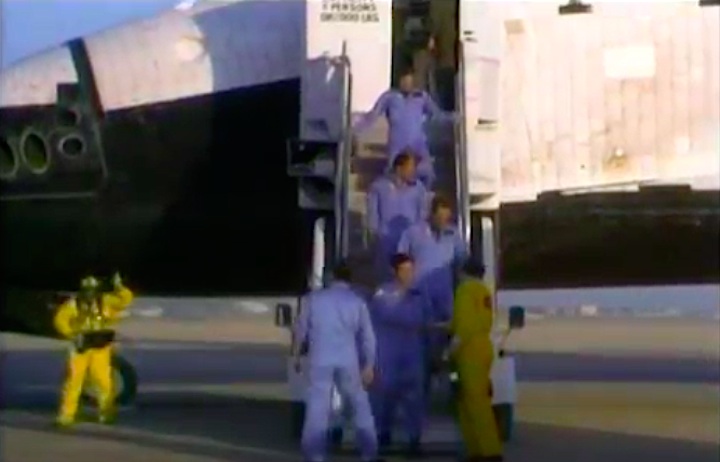
Crew Members

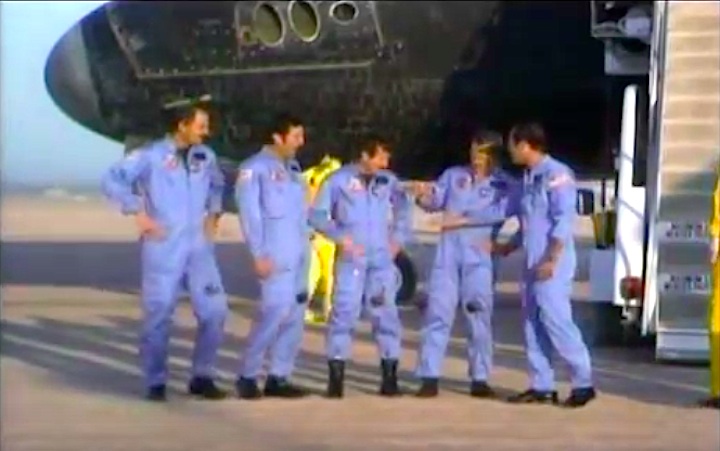
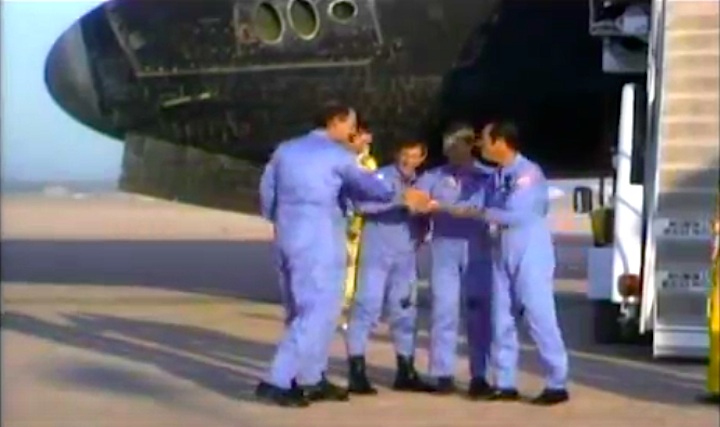
Image above: STS-41C Crew photo with Commander Robert L. Crippen, Pilot Francis R. Scobee, Mission Specialists Geroge D. Nelson, James D. A. Van Hoften and Terry J. Hart. Image Credit: NASA
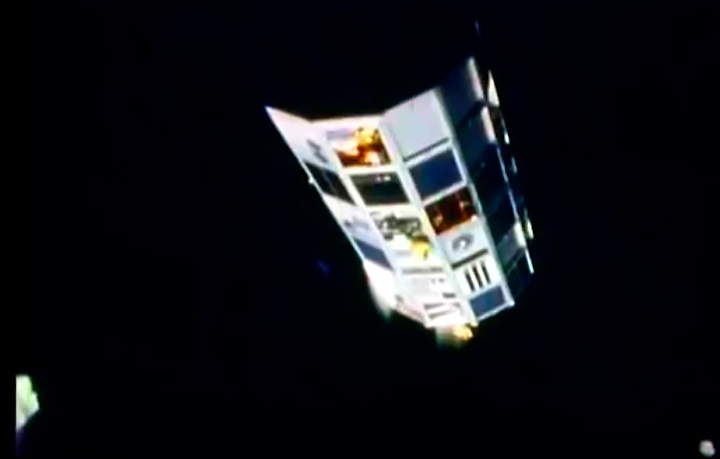
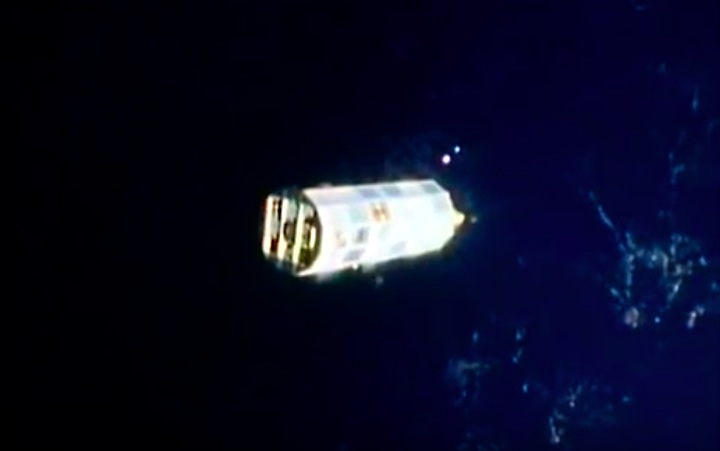
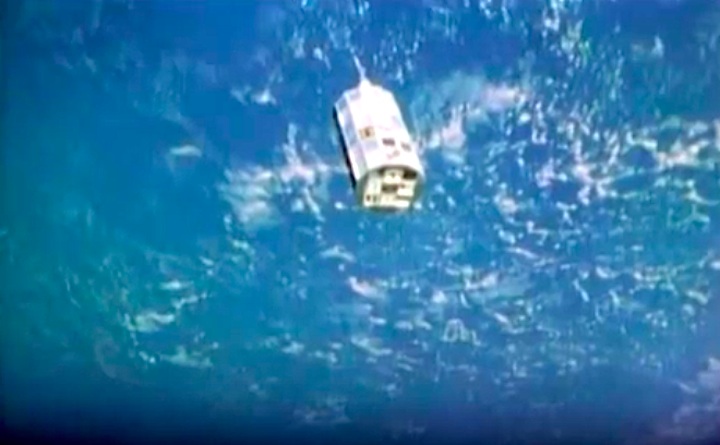
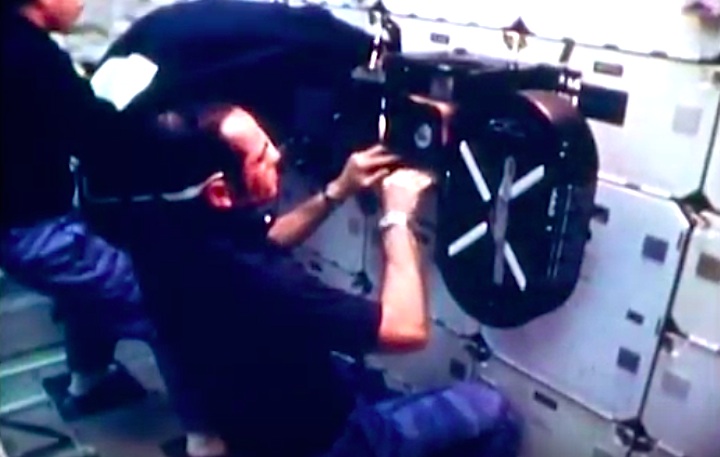
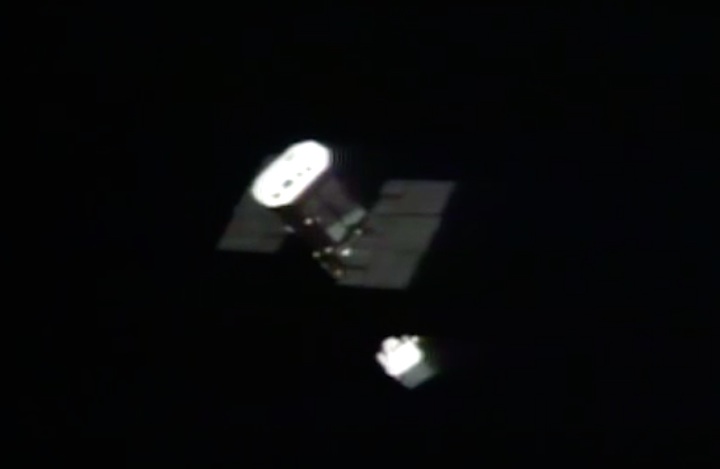
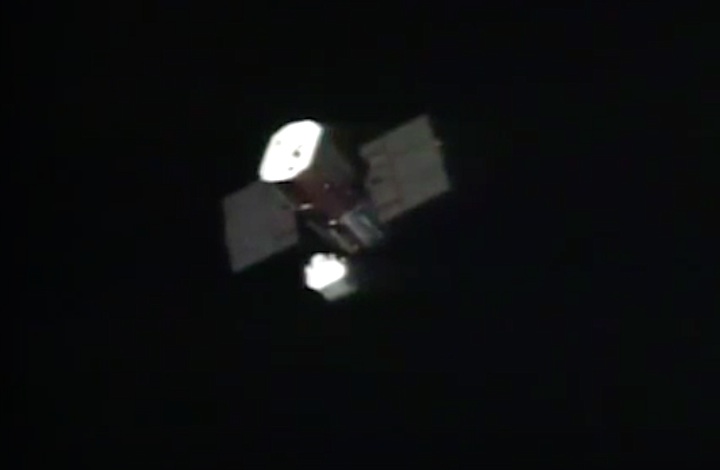
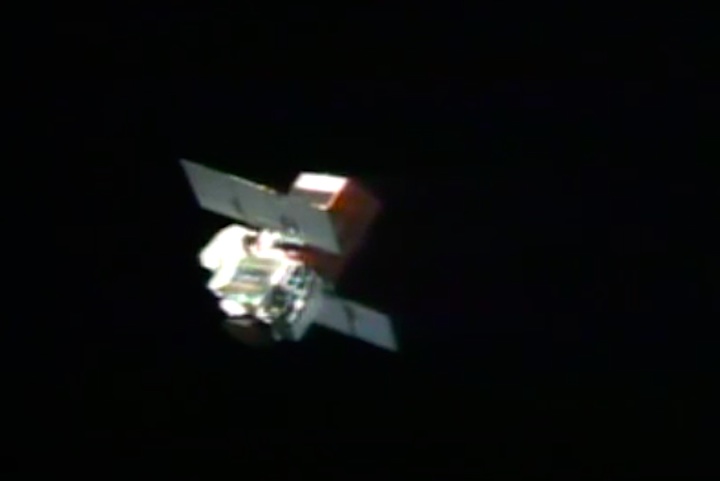
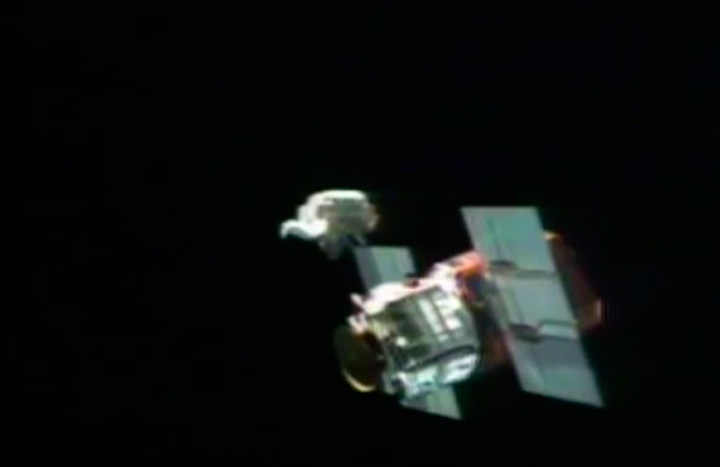
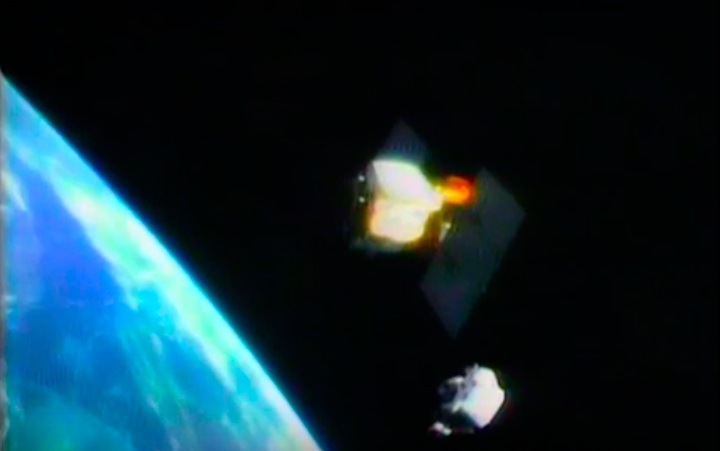
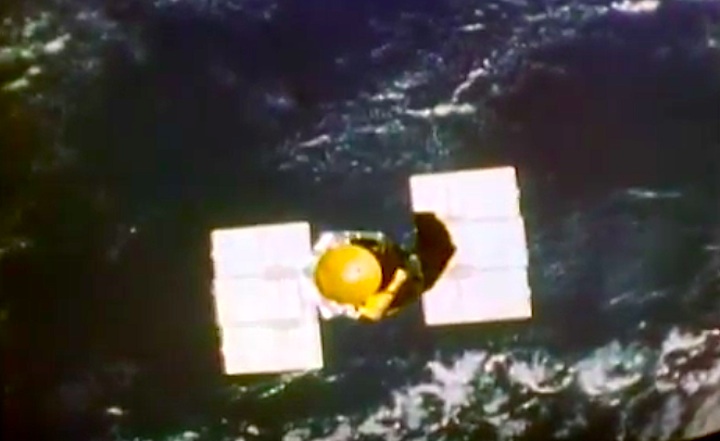
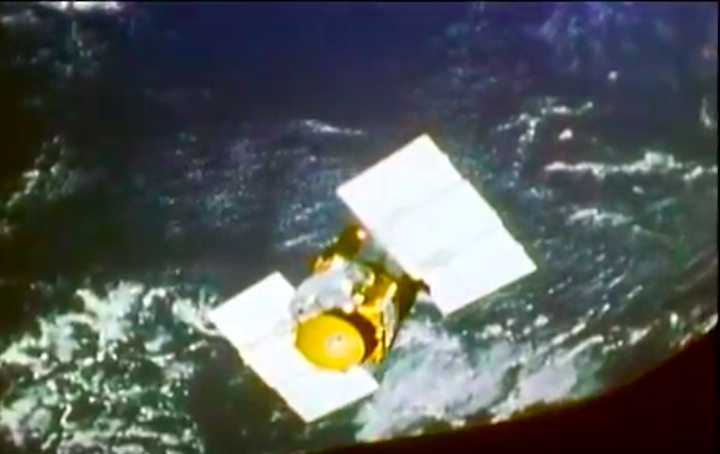
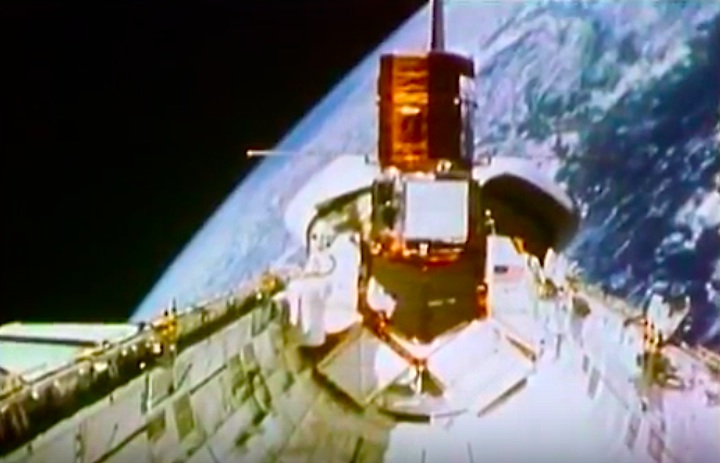
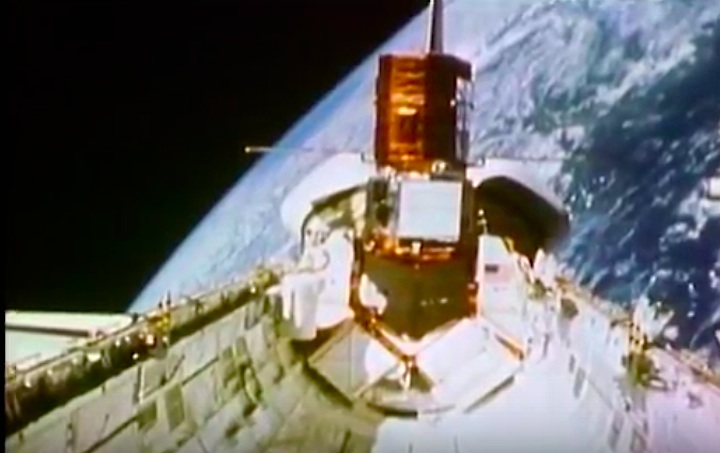
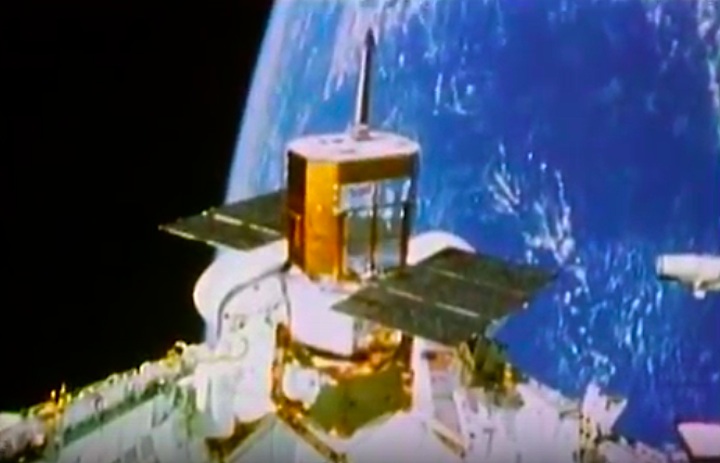
Mission Highlights The first direct ascent trajectory for space shuttle. Using the manned maneuvering unit, astronauts replaced the altitude control system and coronagraph/polarimeter electronics box in the Solar Max satellite while it remained in orbit. The Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) was deployed, carrying 57 experiments which were left on orbit with an intention of retrieving them during a later mission. Other payloads on this mission were: IMAX camera; Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME); Cinema 360; Shuttle Student Involvement Program (SSlP) experiment.
The first direct ascent trajectory for space shuttle. Using the manned maneuvering unit, astronauts replaced the altitude control system and coronagraph/polarimeter electronics box in the Solar Max satellite while it remained in orbit. The Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) was deployed, carrying 57 experiments which were left on orbit with an intention of retrieving them during a later mission. Other payloads on this mission were: IMAX camera; Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME); Cinema 360; Shuttle Student Involvement Program (SSlP) experiment.
---
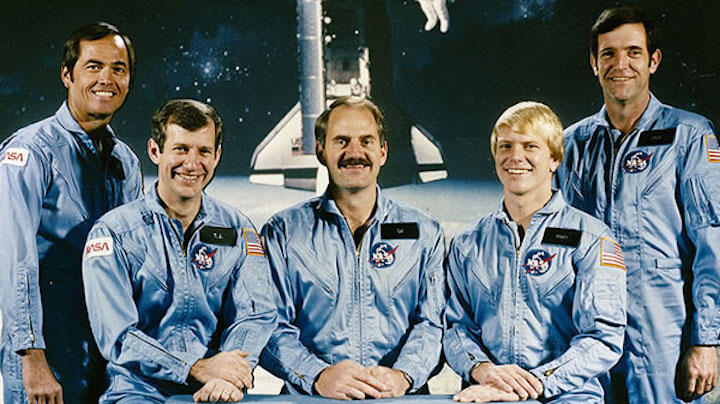

STS-41-C | Shuttle: Challenger | Launch: April 6, 1984
From left to right: Robert L. Crippen (commander), Terry J. Hart (mission specialist), James D. Van-Hoften(mission specialist), George D. Nelson (mission specialist), Francis R. (Dick) Scobee (pilot)
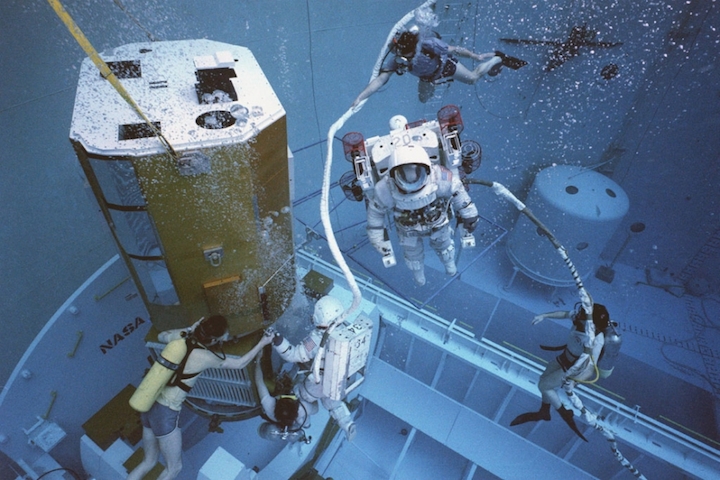
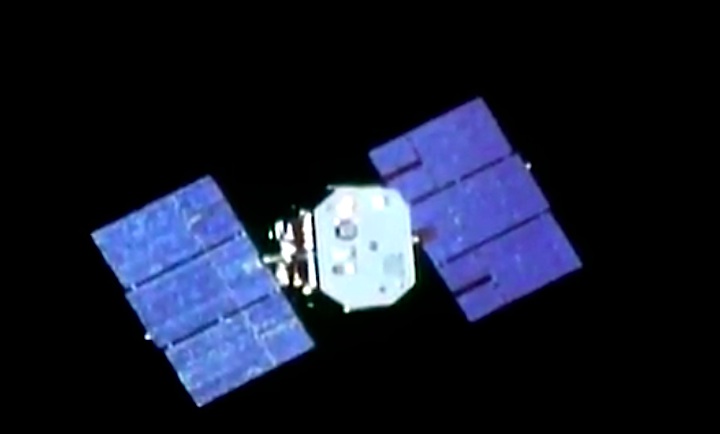
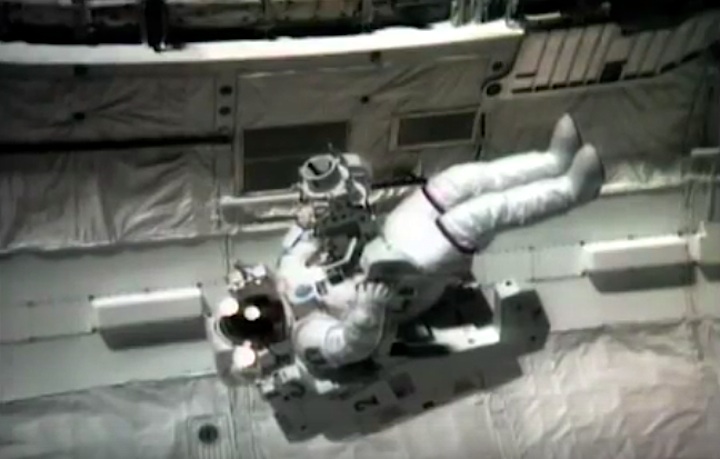
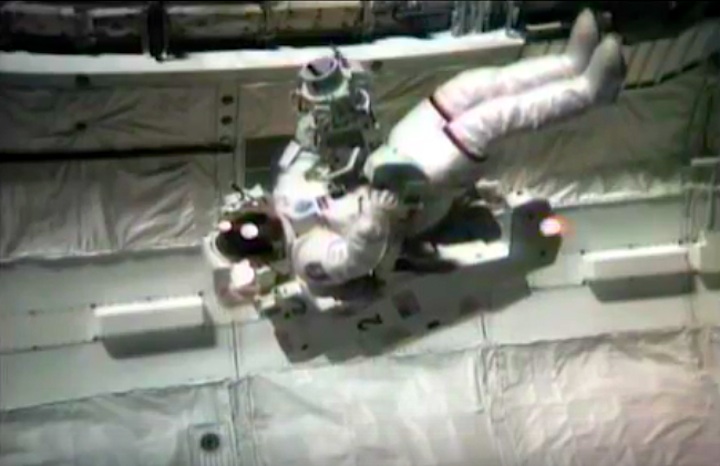
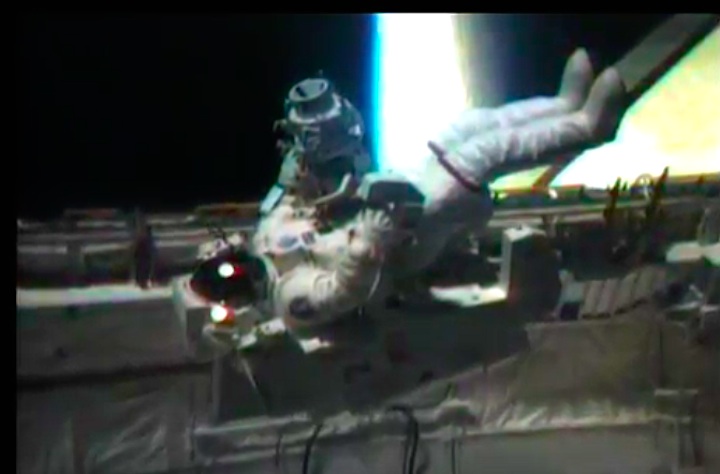
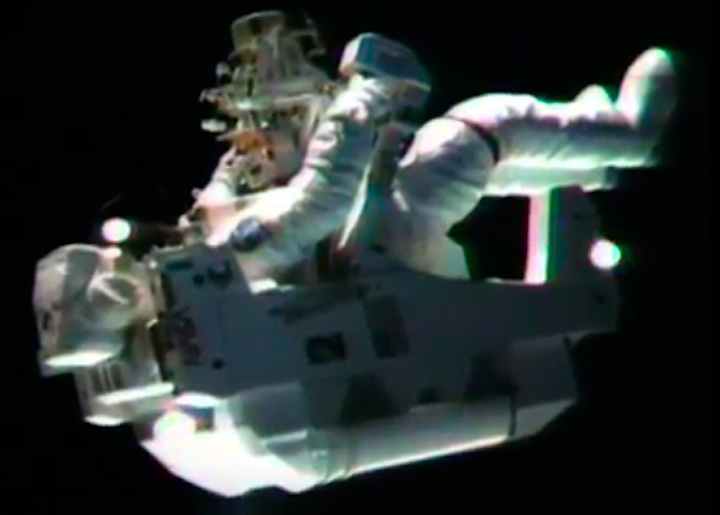
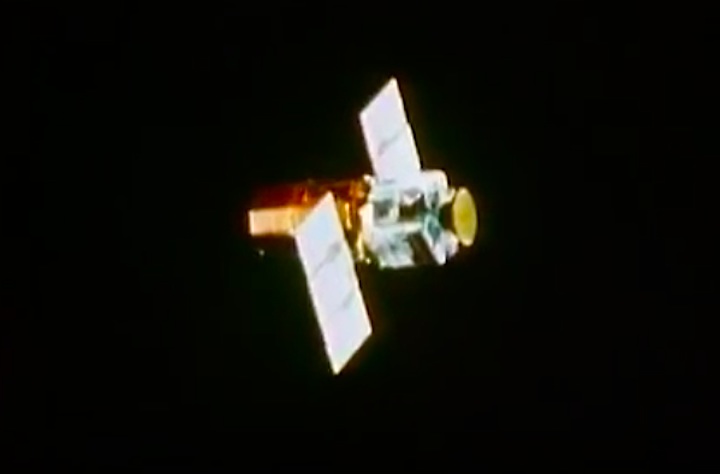
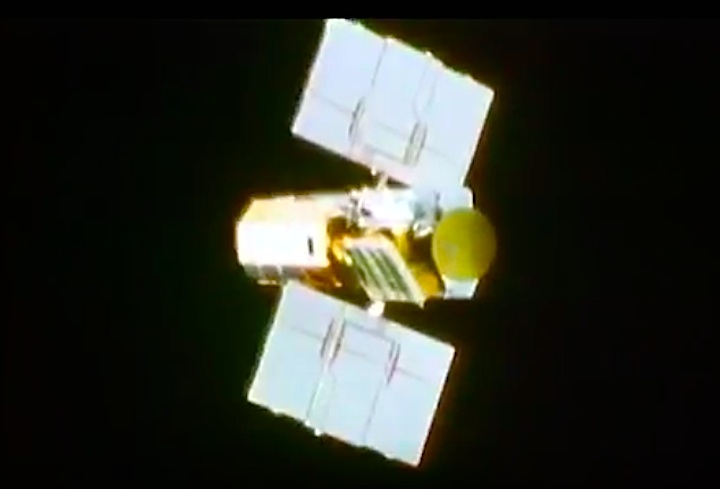
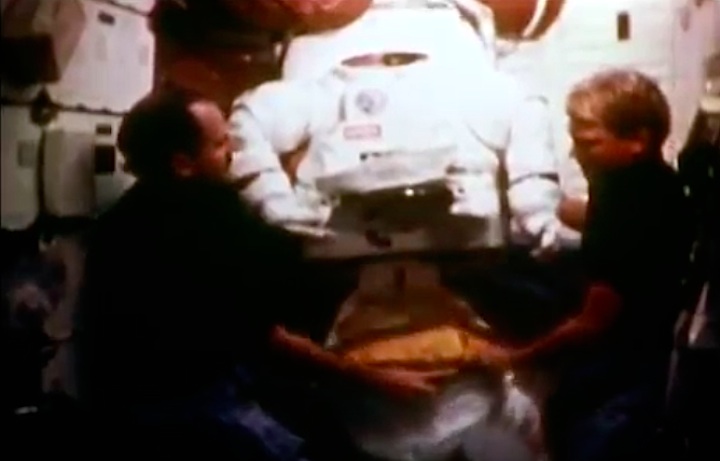
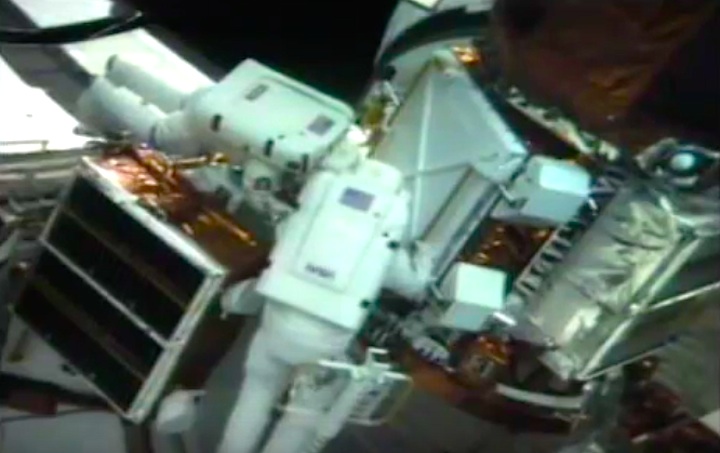
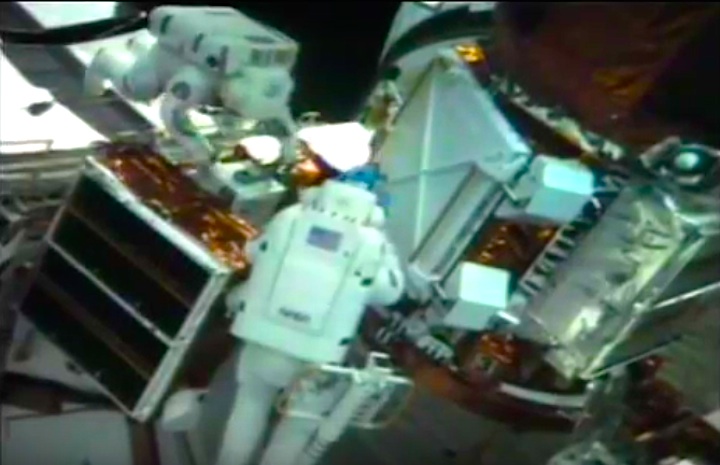
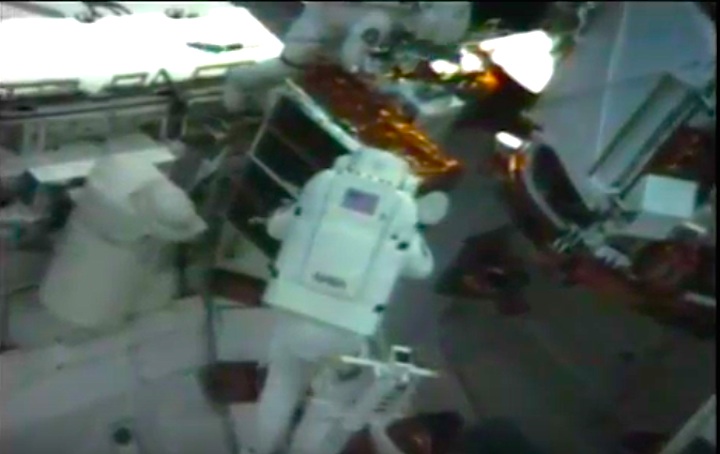
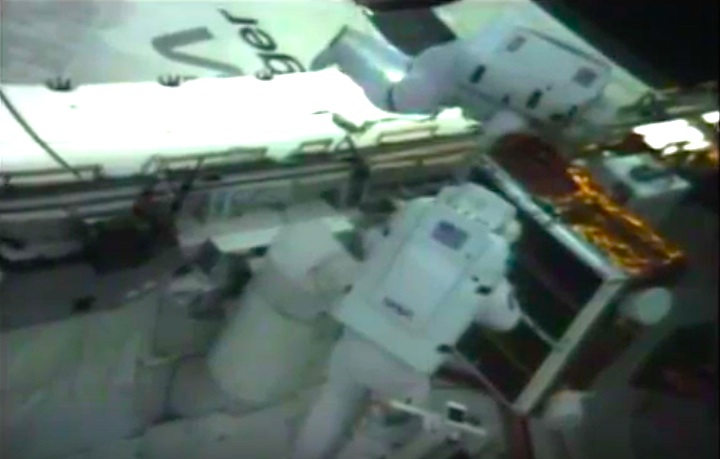
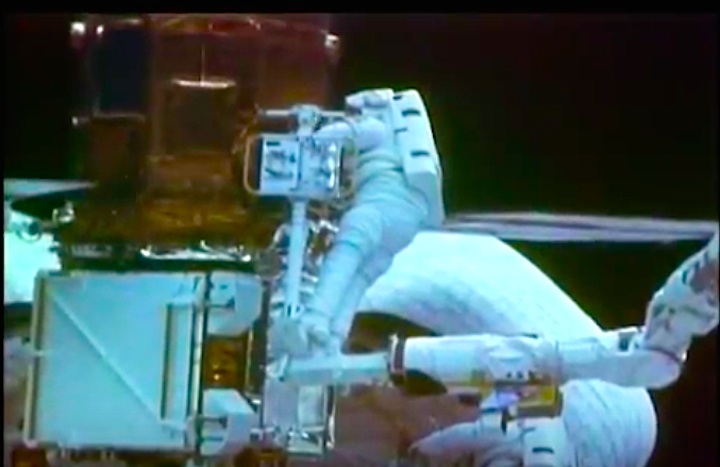
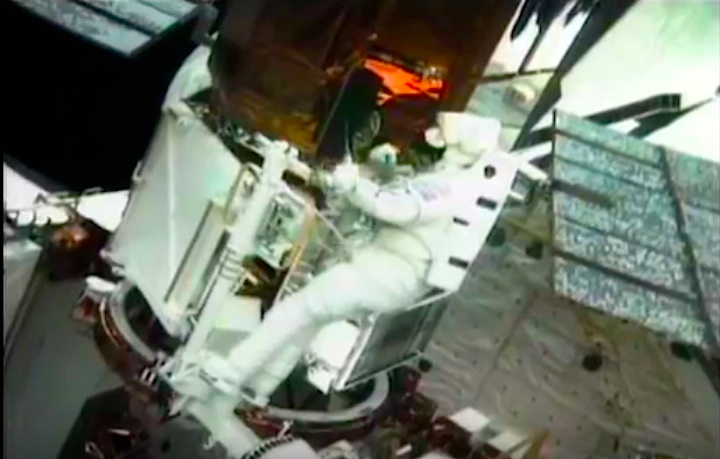
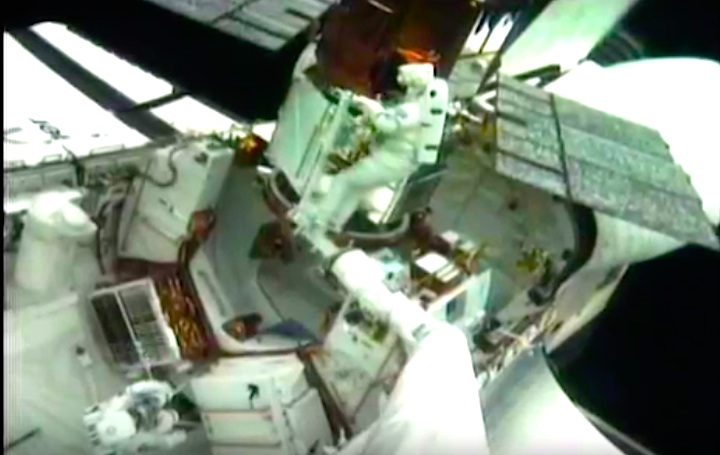
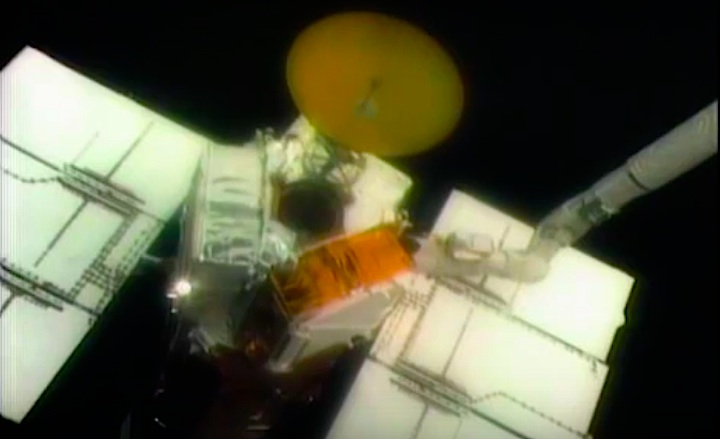
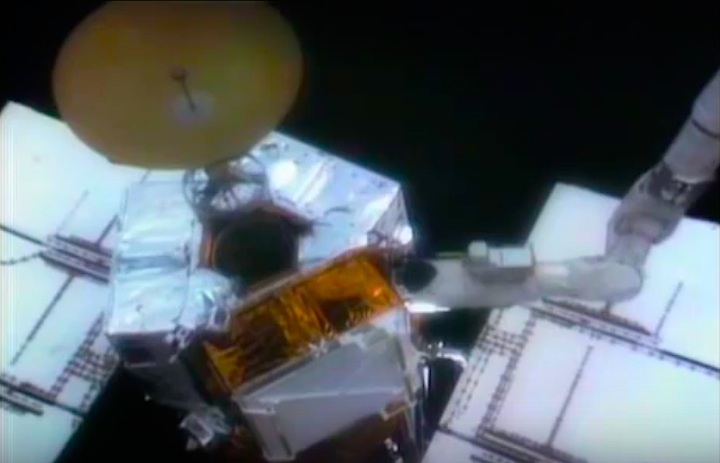
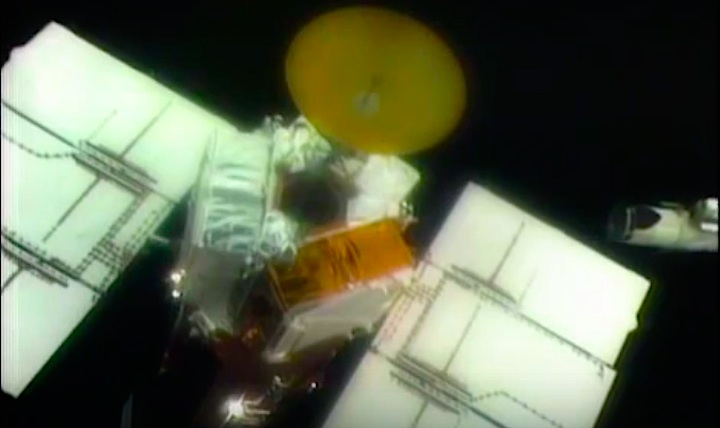
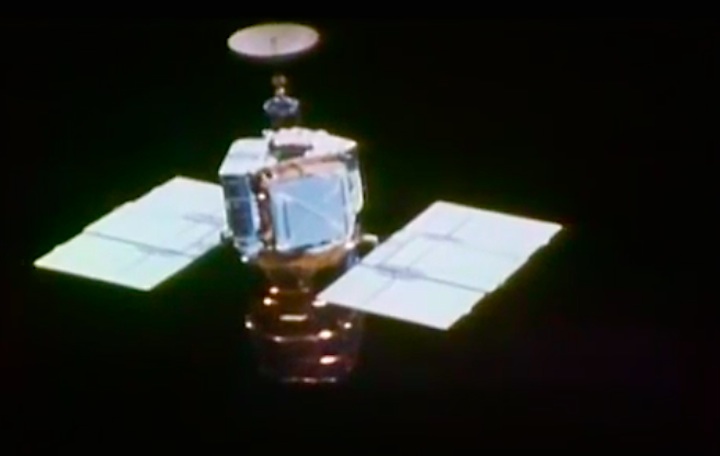
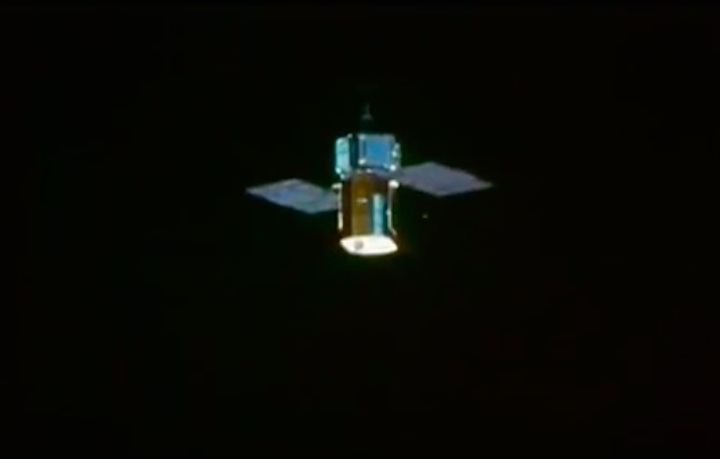
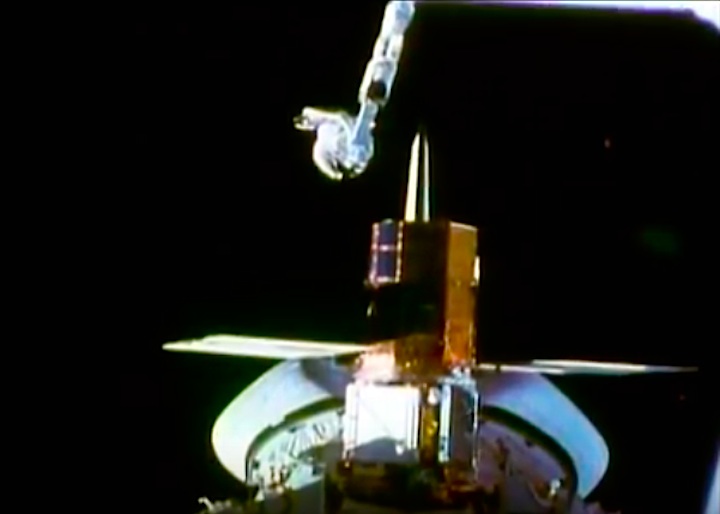
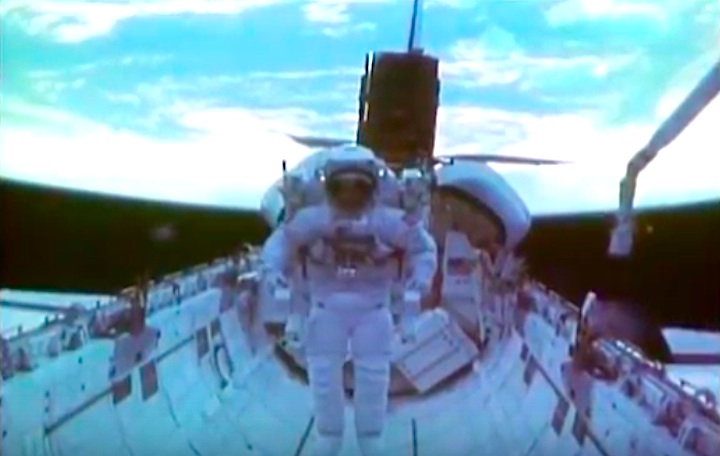
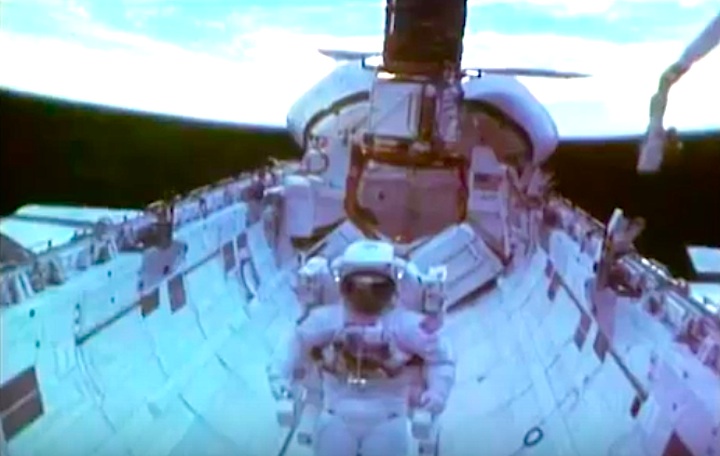
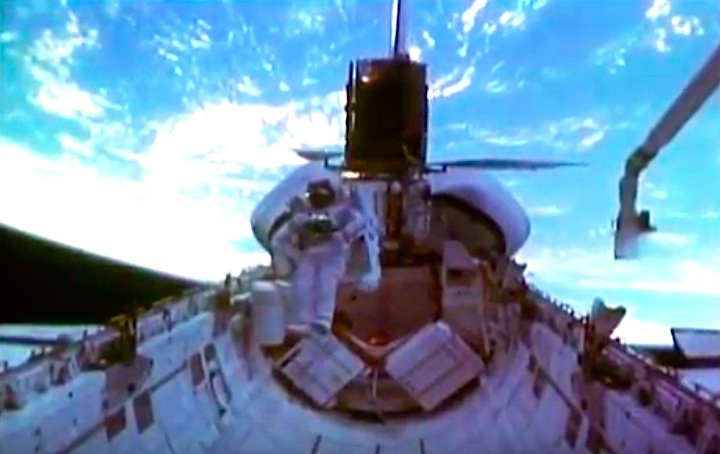
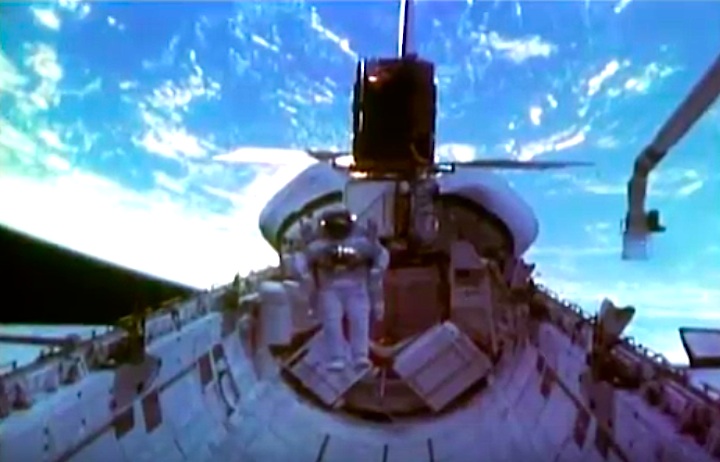
On April 1, 1983, divers and astronauts at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala., prepared for the first satellite repair mission in space. Before the repair, the crew of Space Shuttle Challenger mission STS-41-C spent months at the Marshall Center Neutral Buoyancy Simulator, an underwater training facility that is now a historic landmark. They used a mockup of the Solar Maximum satellite to practice retrieving the satellite and piloting a new Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), which allowed astronauts to travel in space without being tethered to the shuttle. On April 6, 1984, Space Shuttle Challenger (STS-41C) traveled to the satellite, which was designed to study the sun but had a systems failure about a year after it was launched. The crew initiated a series of firsts for NASA: the first satellite retrieval, the first service use of a MMU and the Remote Manipulator System, and the Space Shuttle Challenger's first space flight. The crew retrieved Solar Max, repaired it, and placing it back in service. The Solar Maximum Repair mission provided engineers with valuable data that helped them design the Hubble Space Telescope for on-orbit repair and maintenance.
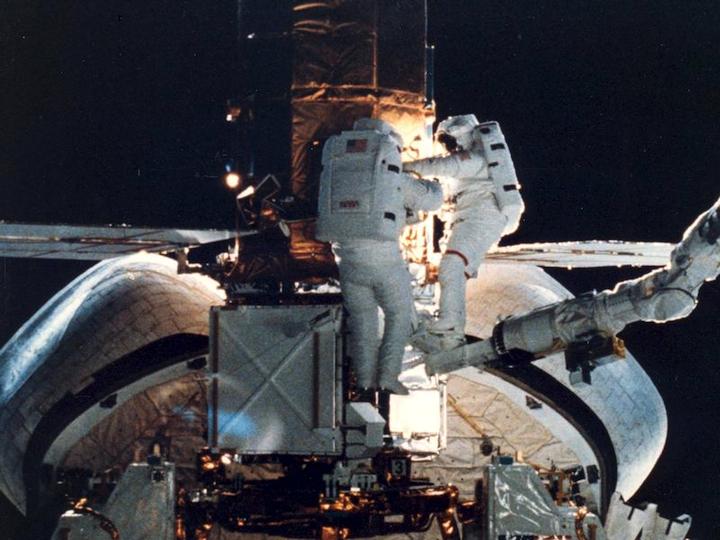

Solar Max Under Repair
Astronauts George "Pinky" Nelson and James van Hoften repair the Solar Max satellite in the cargo bay of Challenger before returning the research spacecraft to operate on its own. The work was done during STS-41C.
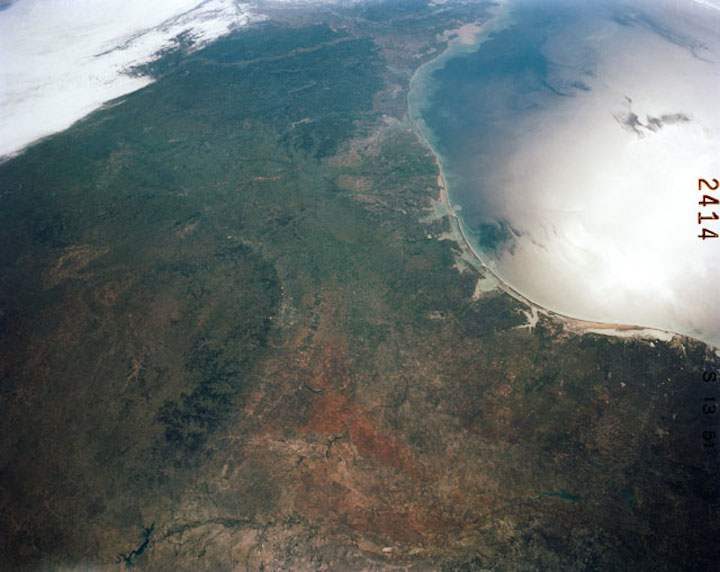

41C-51-2414 (6-13 April 1984) --- The entire Texas portion of the Gulf Coast and part of Louisiana's shoreline are visible in this frame, photographed on 4"x5" roll film using a large format camera aboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger. Coastal bays and other geographic features from the Boca Chica (mouth of Rio Grande), to the mouth of the Mississippi are included in the frame, photographed from approximately 285 nautical miles above Earth. Inland cities that can be easily delineated are San Antonio, Austin, College Station, Del Rio and Lufkin. Easily pinpointed coastal cities include Houston, Galveston and Corpus Christi. The 41-C crew members used this frame as one of the visuals for their post-flight press conference on April 24, 1984.
---
Frams von STS-41C Challenger Mission NASA-Video:
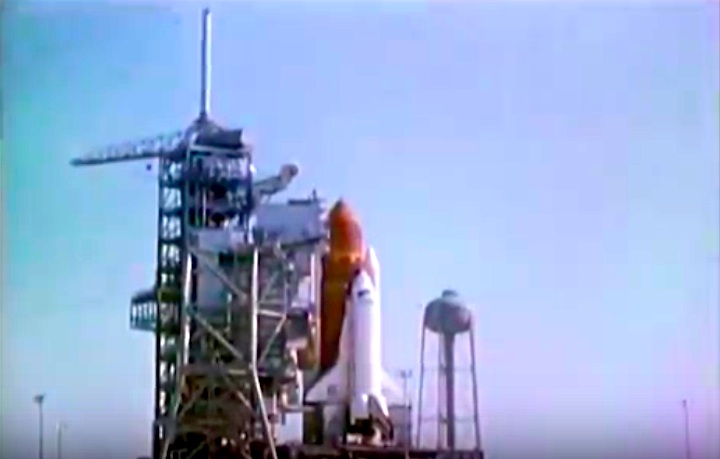
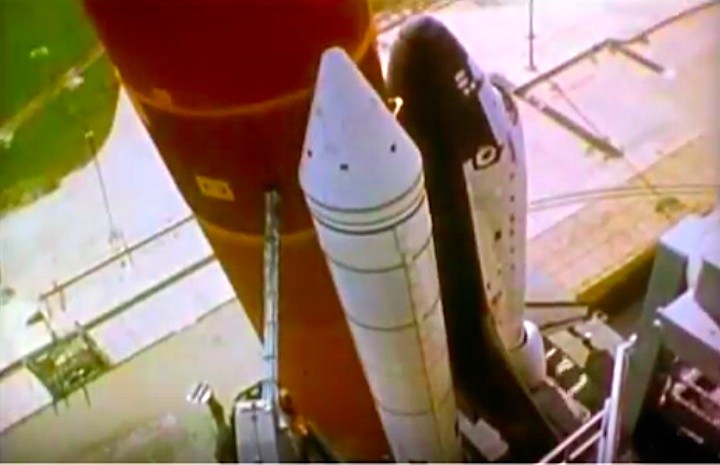
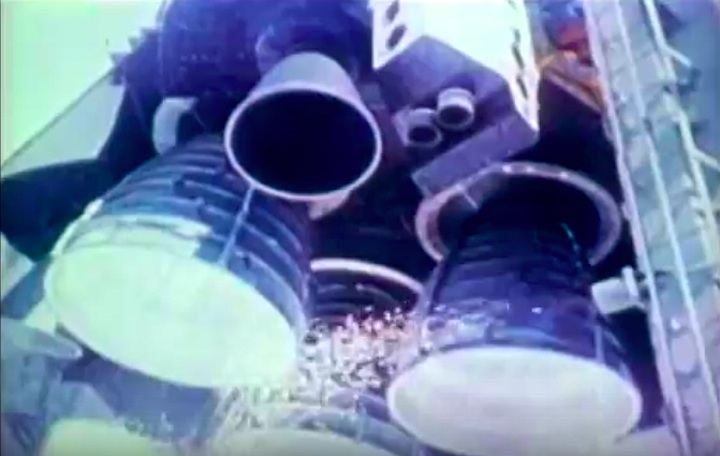
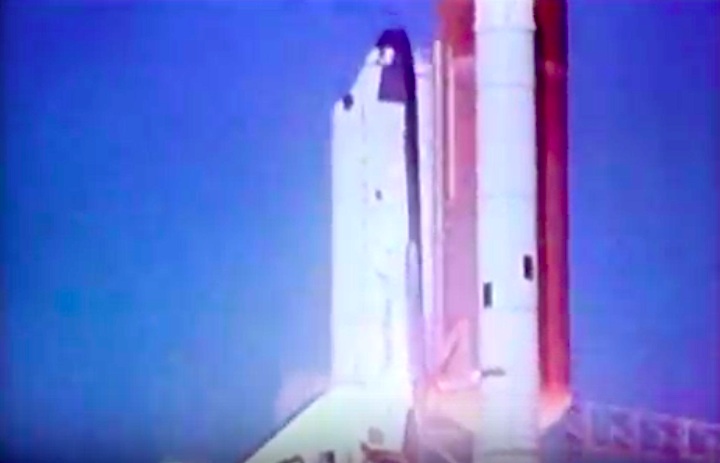
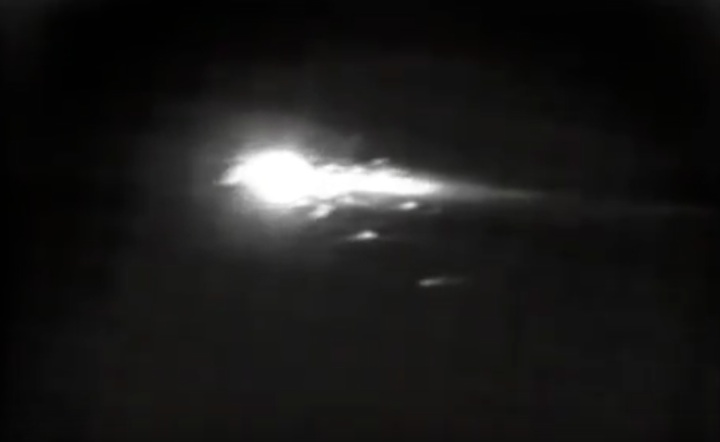
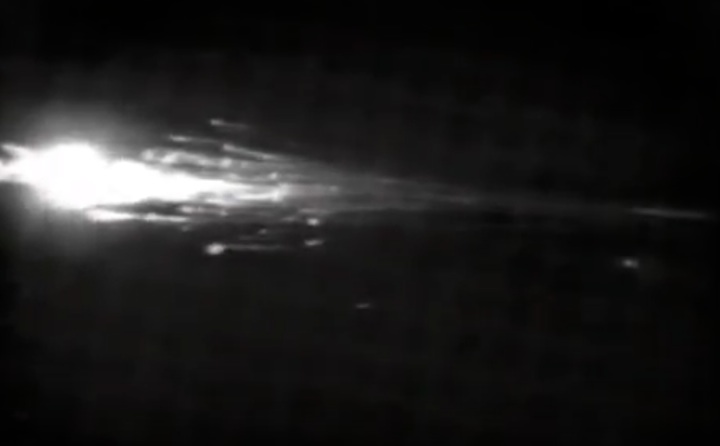
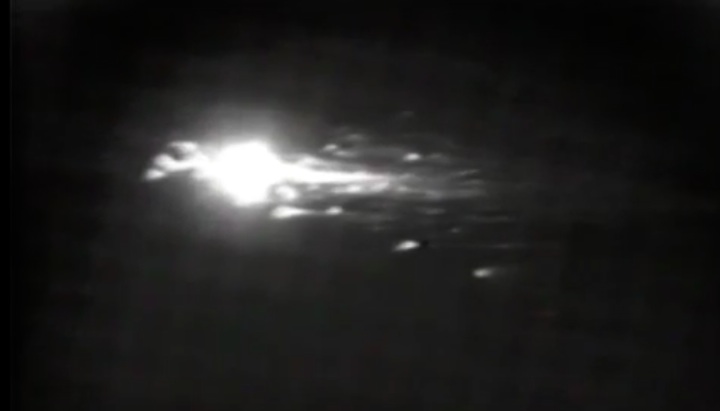
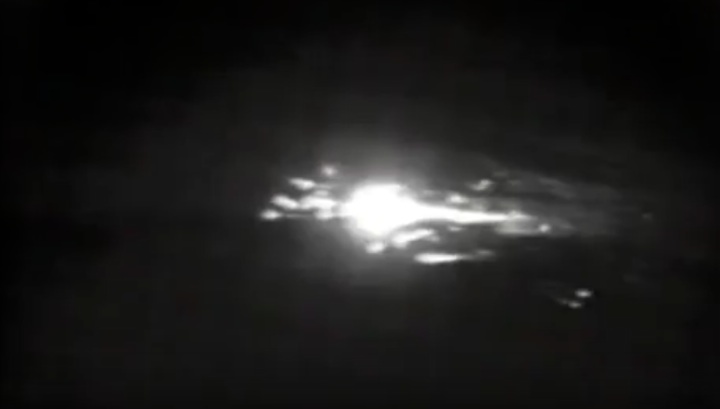
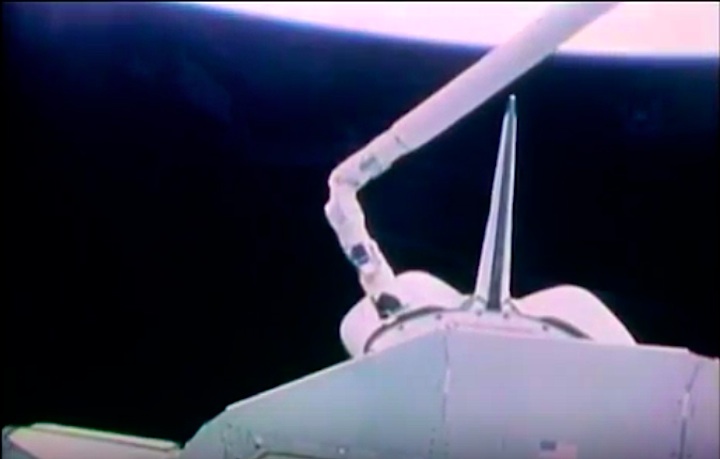
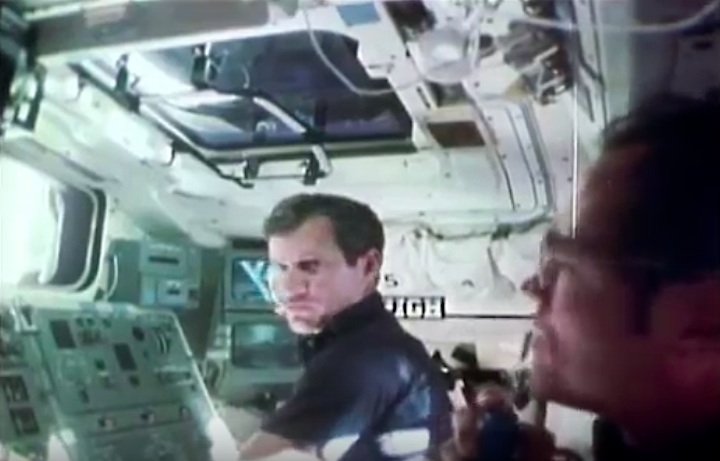































































































Quelle: NASA
