.
Van Allen Probes Discover a New Radiation Belt
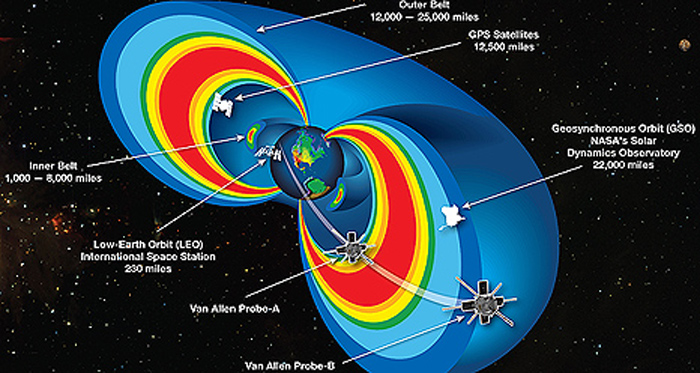
Earth's radiation belts were one of the first discoveries of the Space Age. A new finding published in today's issue of Science shows that we still have much to learn about them. NASA's twin Van Allen Probes, launched just last August, have revealed a previously unknown third radiation belt around Earth.
"Even 55 years after their discovery, Earth's radiation belts still are capable of surprising us," said Nicky Fox, Van Allen Probes deputy project scientist at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md. "We thought we knew the radiation belts, but we don't."

Previous observations of the Van Allen belts dating back to the late 1950s have documented two distinct regions of trapped radiation surrounding our planet, known as the inner and outer radiation belts. Particle sensors aboard the twin Van Allen Probes quickly revealed to scientists the existence of a transient, third radiation belt. Scientists observed the third belt for four weeks before a powerful interplanetary shock wave from the sun annihilated it.
Each of the two Van Allen Probes carries an identical set of five instrument suites that allow scientists to gather data on the belts in unprecedented detail. Key data for this discovery came from the Relativistic Electron Proton Telescope (REPT) instrument, part of the probes' Energetic Particle, Composition, and Thermal Plasma Suite (ECT).
"This is the first time we have had such high-resolution instruments look at time, space and energy together in the outer belt," says Daniel Baker, lead author of the study and REPT instrument lead at the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) at the University of Colorado in Boulder. "Previous observations of the outer radiation belt resolved it as a single blurry element. When we turned REPT on just two days after launch, we clearly saw the new belt and a [gap] between it and the outer belt."
Back in the 1950s when the radiation belts were discovered, they had little effect on ordinary people. Today the radiation belts are crucial to our high-tech society. Hundreds of satellites used for everything from weather prediction to GPS to television routinely skim the belts, subjecting themselves to energetic particles that can damage solar panels and short-circuit sensitive electronics. During geomagnetic storms when the belts are swollen by solar activity, whole fleets of satellites can be engulfed, imperiling the technological underpinnings of daily life on the planet below. The Van Allen Probes directly address these down-to-Earth problems
"The fantastic new capabilities and advances in technology in the Van Allen Probes allow scientists to see in unprecedented detail how the radiation belts are populated with charged particles, what causes them to change, and how they affect the upper reaches of Earth's atmosphere," says John Grunsfeld, NASA's associate administrator for science in Washington DC.
.
After most NASA science spacecraft launches, researchers wait patiently for months as instruments on board are turned on one at a time, slowly ramped up to full power, and tested to make sure they work at full capacity. It's a rite of passage for any new satellite in space, and such a schedule was in place for the Van Allen Probes when they launched on Aug. 30, 2012, to study two giant belts of radiation that surround Earth.
But a group of scientists on the mission made a case for changing the plan. They asked that the Relativistic Electron Proton Telescope (REPT) be turned on early – just three days after launch -- in order that its observations would overlap with another mission called SAMPEX (Solar, Anomalous, and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer), that was soon going to de-orbit and re-enter Earth's atmosphere.
It was a lucky decision. Shortly before REPT turned on, solar activity on the sun had sent energy toward Earth that caused the radiation belts to swell. The REPT instrument worked well from the moment it was turned on Sep. 1. It made observations of these new particles trapped in the belts, recording their high energies, and the belts' increased size.
Then something happened no one had ever seen before: the particles settled into a new configuration, showing an extra, third belt extending out into space. Within mere days of launch, the Van Allen Probes showed scientists something that would require rewriting textbooks.
"By the fifth day REPT was on, we could plot out our observations and watch the formation of a third radiation belt," says Shri Kanekal, the deputy mission scientist for the Van Allen Probes at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. and a coauthor of a paper on these results. "We started wondering if there was something wrong with our instruments. We checked everything, but there was nothing wrong with them. The third belt persisted beautifully, day after day, week after week, for four weeks."
The scientists published their results in a paper in the journal Science on Feb. 28, 2013. Incorporating this new configuration into their models of the radiation belts offers scientists new clues to what causes the changing shapes of the belts – a region that can sometimes swell dramatically in response to incoming energy from the sun, impacting satellites and spacecraft or pose potential threats to manned space flight.
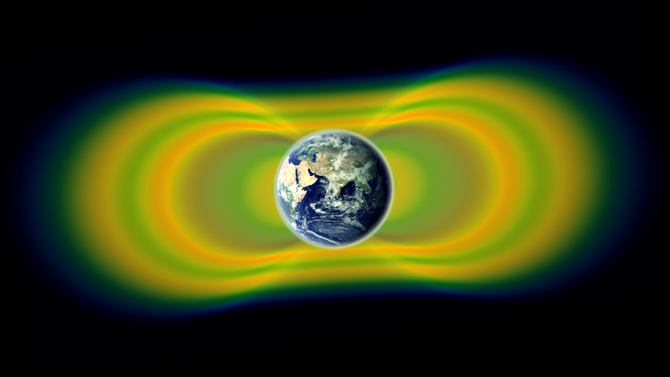
The radiation belts, or Van Allen belts, were discovered with the very first launches of satellites in 1958 by James Van Allen. Subsequent missions have observed parts of the belts – including SAMPEX, which observed the belts from below – but what causes such dynamic variation in the belts has remained something of a mystery. Indeed, seemingly similar storms from the sun have at times caused completely different effects in the belts, or have sometimes led to no change at all.
The Van Allen Probes consist of two identical spacecraft with a mission to map out this region with exquisite detail, cataloguing a wide range of energies and particles, and tracking the zoo of magnetic waves that pulse through the area, sometimes kicking particles up to such frenzied speeds that they escape the belts altogether.
"We've had a long run of data from missions like SAMPEX," says Daniel Baker, who is the principal investigator for REPT at the University of Colorado in Boulder and first author on the Science paper. "But we've never been in the very throat of the accelerator operating a few hundred miles above our head, speeding these particles up to incredible velocities."
.

Two giant swaths of radiation, known as the Van Allen Belts, surrounding Earth were discovered in 1958. In 2012, observations from the Van Allen Probes showed that a third belt can sometimes appear. The radiation is shown here in yellow, with green representing the spaces between the belts. Credit: NASA/Van Allen Probes/Goddard Space Flight Center
.
In its first six months in orbit, the instruments on the Van Allen Probes have worked exceptionally well and scientists are excited about a flood of observations coming in with unprecedented clarity. This is the first time scientists have been able to gather such a complete set of data about the belts, with the added bonus of watching from two separate spacecraft that can better show how events sweep across the area.
Spotting something new in space such as the third radiation belt has more implications than the simple knowledge that a third belt is possible. In a region of space that remains so mysterious, any observations that link certain causes to certain effects adds another piece of information to the puzzle.
Baker likes to compare the radiation belts to the particle storage rings in a particle physics accelerator. In accelerators, magnetic fields are used to hold the particles orbiting in a circle, while energy waves are used to buffet the particles up to ever faster speeds. In such accelerators, everything must be carefully tuned to the size and shape of that ring, and the characteristics of those particles. The Van Allen Belts depend on similar fine-tuning. Given that scientists see the rings only in certain places and at certain times, they can narrow down just which particles and waves must be causing that geometry. Every new set of observations helps narrow the field even further.
"We can offer these new observations to the theorists who model what's going on in the belts," says Kanekal. "Nature presents us with this event – it's there, it's a fact, you can't argue with it -- and now we have to explain why it's the case. Why did the third belt persist for four weeks? Why does it change? All of this information teaches us more about space."
.

On Aug. 31, 2012, a giant prominence on the sun erupted, sending out particles and a shock wave that traveled near Earth. This event may have been one of the causes of a third radiation belt that appeared around Earth a few days later, a phenomenon that was observed for the very first time by the newly-launched Van Allen Probes. This image of the prominence before it erupted was captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Credit: NASA/SDO/AIA/Goddard Space Flight Center
.
Scientists already have theories about just what kind of waves sweep out particles in the "slot" region between the first two belts. Now they must devise models to find which waves have the right characteristics to sweep out particles in the new slot region as well. Another tantalizing observation to explore lies in tracking the causes of the slot region back even further: on Aug. 31, 2012, a long filament of solar material that had been hovering in the sun's atmosphere erupted out into space. Baker says that this might have caused the shock wave that led to the formation of the third ring a few days later. In addition, the new belt was virtually annihilated four weeks after it appeared by another powerful interplanetary shock wave from the sun. Being able to watch such an event in action provides even more material for theories about the Van Allen belts.
Despite the 55 years since the radiation belts were first discovered, there is much left to investigate and explain, and within just a few days of launch the Van Allen Probes showed that the belts are still capable of surprises.
"I consider ourselves very fortunate," says Baker. "By turning on our instruments when we did, taking great pride in our engineers and having confidence that the instruments would work immediately and having the cooperation of the sun to drive the system the way it did – it was an extraordinary opportunity. It validates the importance of this mission and how important it is to revisit the Van Allen Belts with new eyes."
The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) built and operates the twin Van Allen Probes. The Van Allen Probes comprise the second mission in NASA's Living With a Star (LWS) program to explore aspects of the connected sun-Earth system that directly affect life and society. The program is managed by NASA Goddard.
Despite the 55 years since the radiation belts were first discovered, there is much left to investigate and explain, and within just a few days of launch the Van Allen Probes showed that the belts are still capable of surprises.
"I consider ourselves very fortunate," says Baker. "By turning on our instruments when we did, taking great pride in our engineers and having confidence that the instruments would work immediately and having the cooperation of the sun to drive the system the way it did – it was an extraordinary opportunity. It validates the importance of this mission and how important it is to revisit the Van Allen Belts with new eyes."
The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) built and operates the twin Van Allen Probes. The Van Allen Probes comprise the second mission in NASA's Living With a Star (LWS) program to explore aspects of the connected sun-Earth system that directly affect life and society. The program is managed by NASA Goddard.
Quelle: NASA
5911 Views
