.

Space Shuttle: Discovery
Launch Pad: 39B
Launch Weight: 249,109 pounds
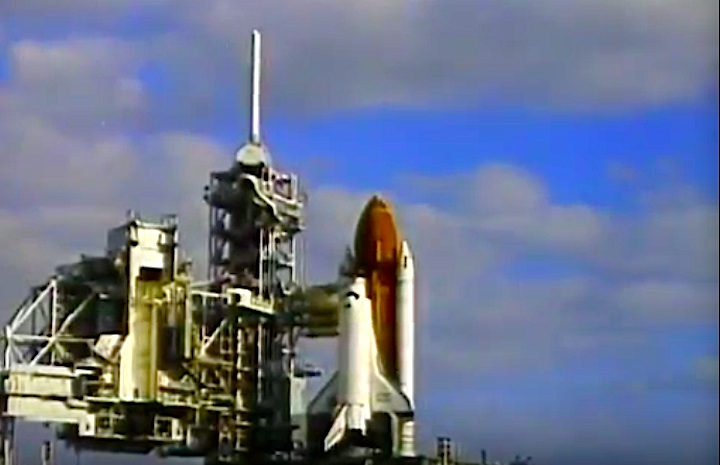
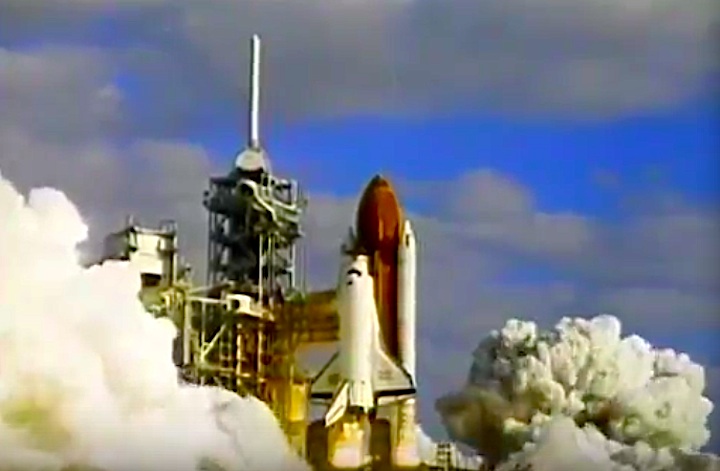
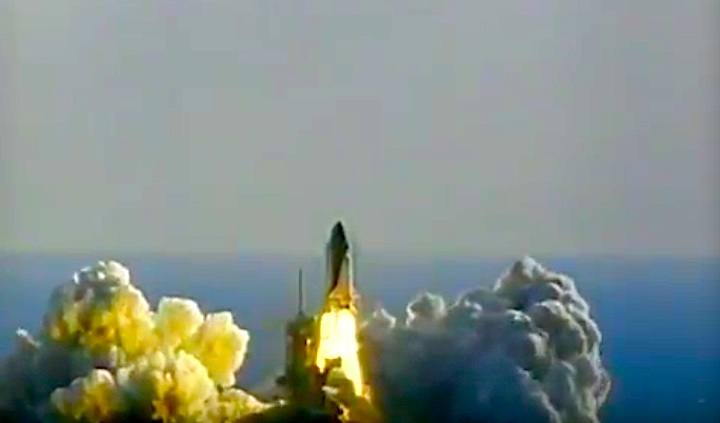
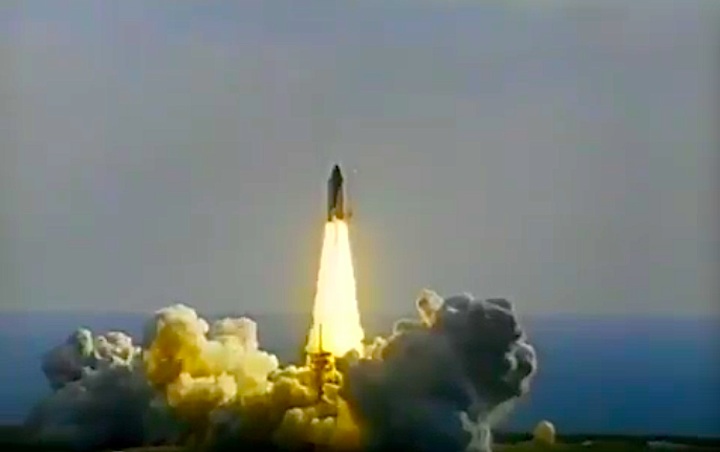
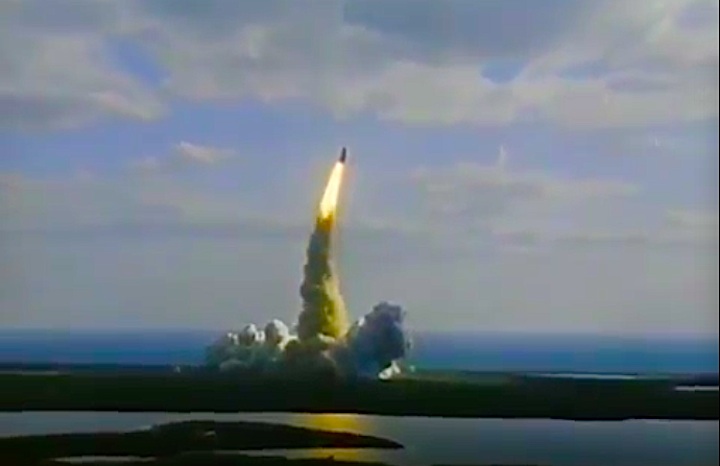
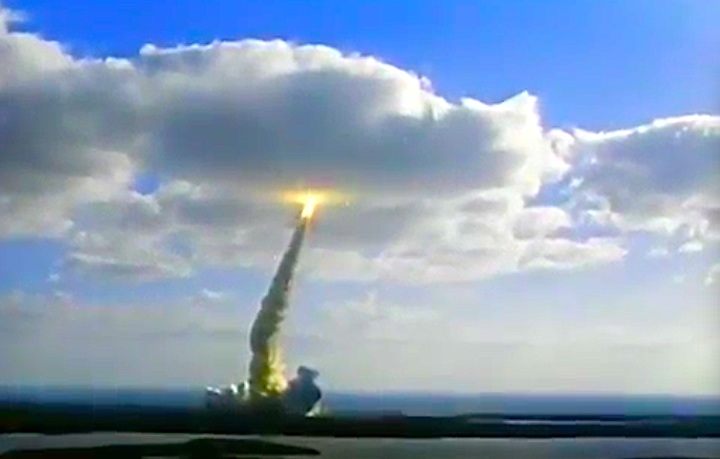
Launched: April 24, 1990, 8:33:51 a.m. EDT
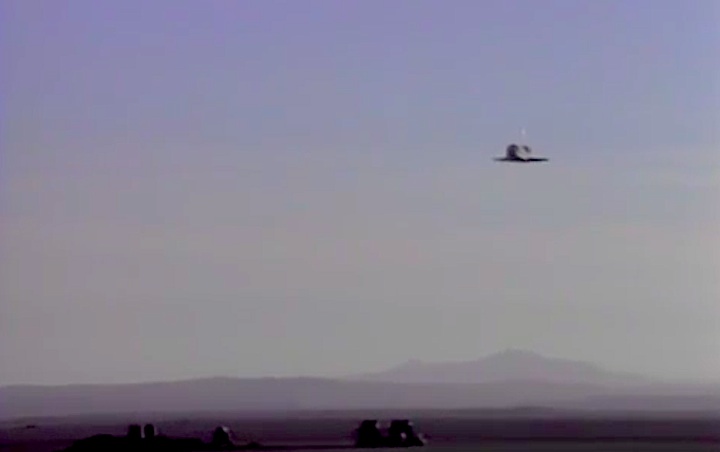
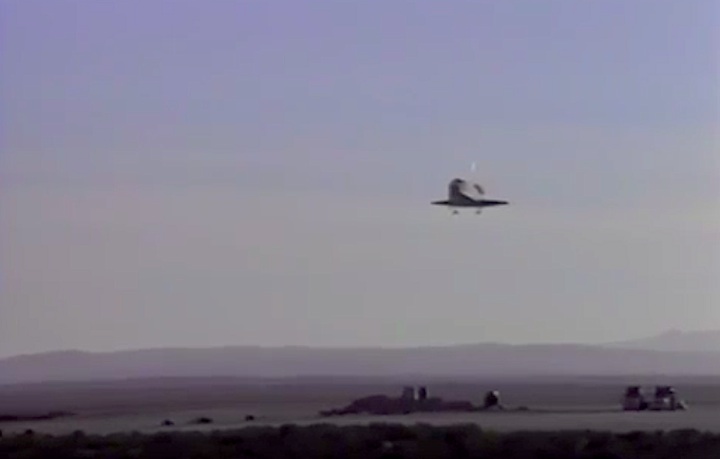
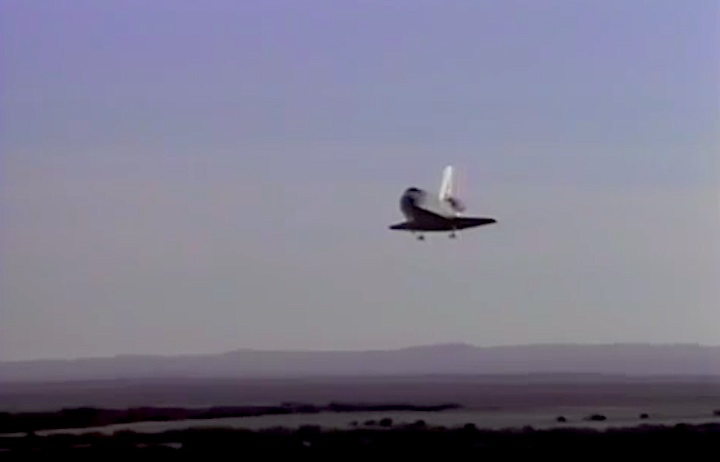
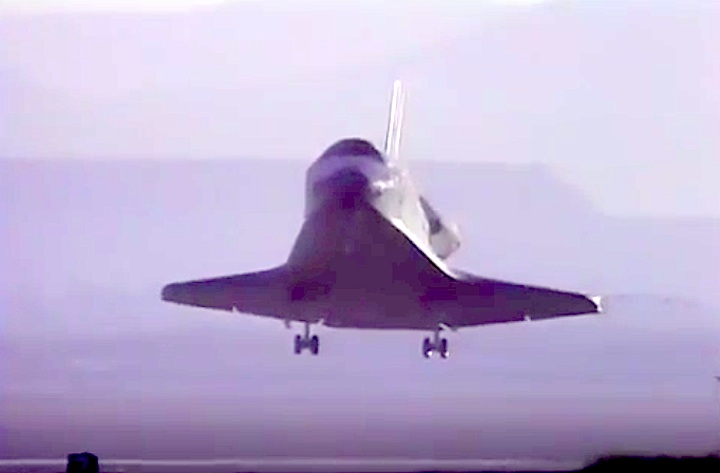
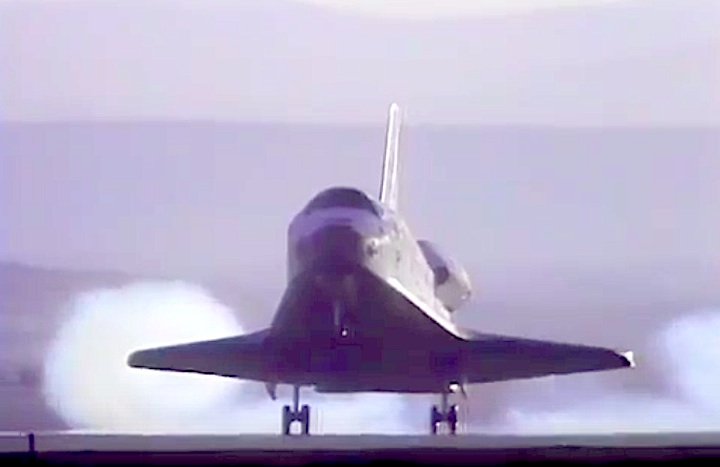
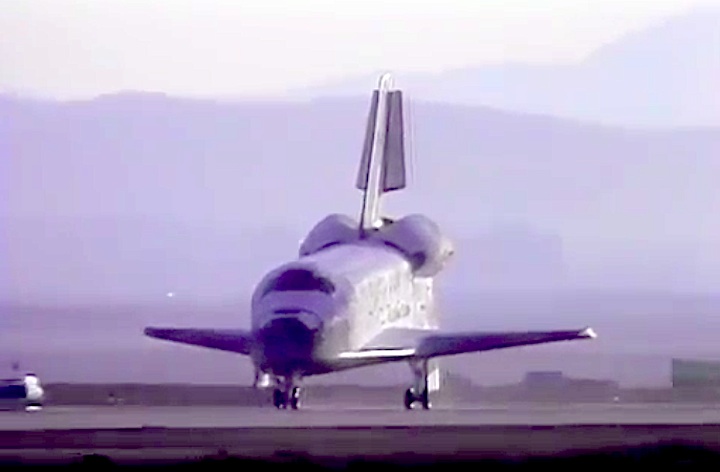
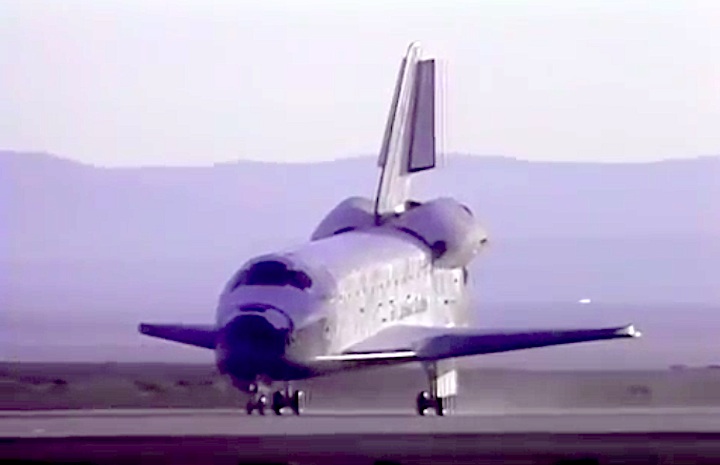
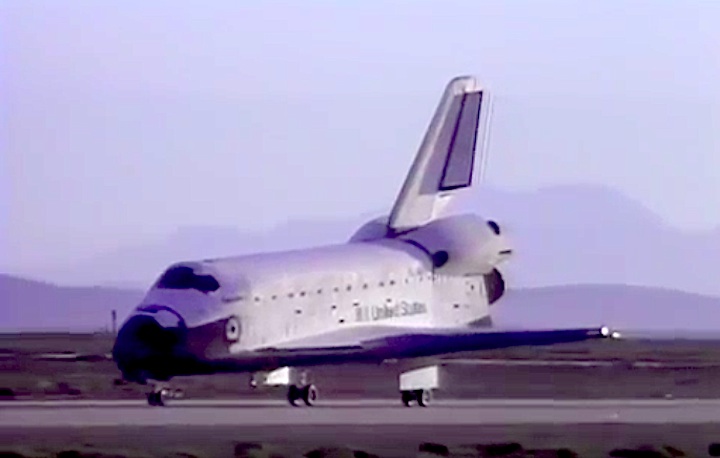
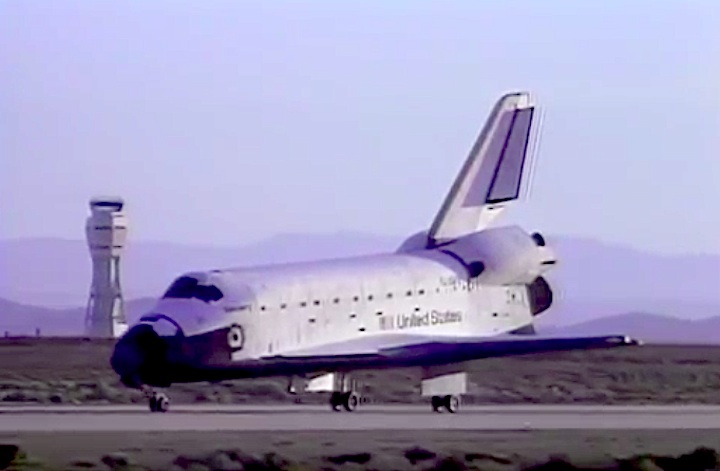
Landing Site: Edwards Air Force Base, Calif.
Landing: April 29, 1990, 6:49:57 a.m. PDT
Landing Weight: 189,118 pounds
Runway: 22
Rollout Distance: 8,874 feet
Rollout Time: 61 seconds
Revolution: 80
Mission Duration: 5 days, 1 hour, 16 minutes, 6 seconds
Returned to KSC: May 7, 1990
Orbit Altitude: 330 nautical miles
Orbit Inclination: 28.45 degrees
Miles Traveled: 2.1 million
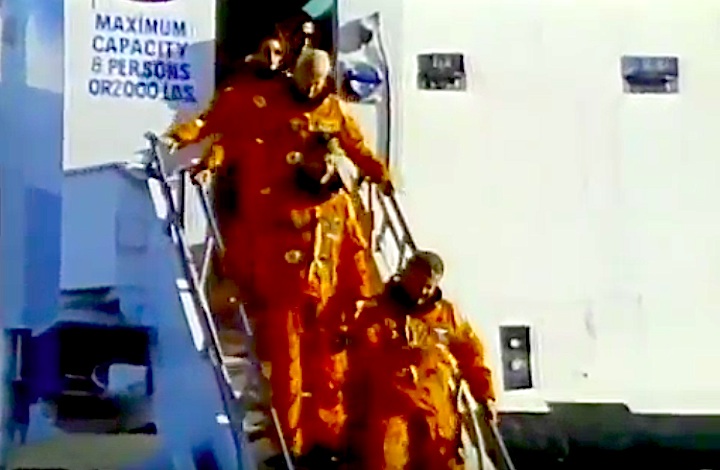
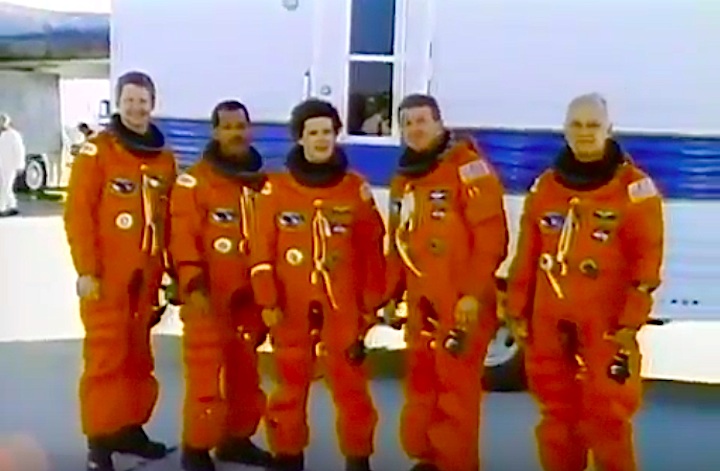
Crew Members

Image above: STS-31 Crew photo with Commander Loren J. Shriver, Pilot Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Mission Specialists Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn D. Sullivan. Image Credit: NASA
Launch Highlights
 The launch was scheduled for April 18, then April 12, then April 10, following the Flight Readiness Review (FRR). The first date set at FRR was earlier than that shown on previous planning schedules. The launch scheduled for April 10 was scrubbed at T-4 minutes due to a faulty valve in auxiliary power unit (APU) number one. The APU was replaced and payload batteries recharged. Countdown briefly halted at T-31 seconds when computer software failed to shut down a fuel valve line on ground support equipment. Engineers ordered valve to shut and countdown continued.
The launch was scheduled for April 18, then April 12, then April 10, following the Flight Readiness Review (FRR). The first date set at FRR was earlier than that shown on previous planning schedules. The launch scheduled for April 10 was scrubbed at T-4 minutes due to a faulty valve in auxiliary power unit (APU) number one. The APU was replaced and payload batteries recharged. Countdown briefly halted at T-31 seconds when computer software failed to shut down a fuel valve line on ground support equipment. Engineers ordered valve to shut and countdown continued.Mission Highlights
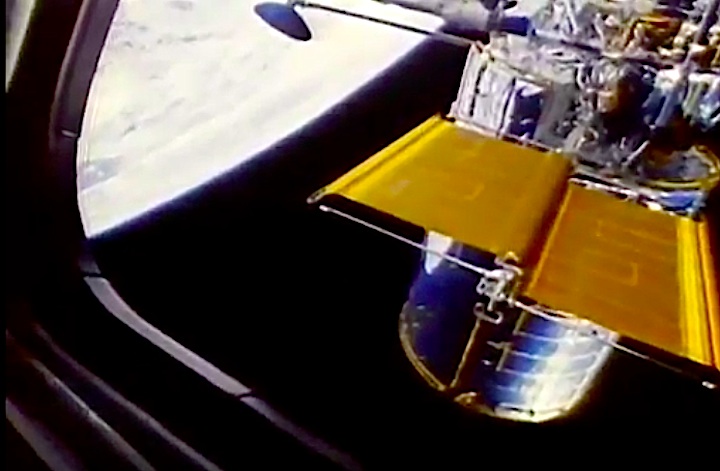
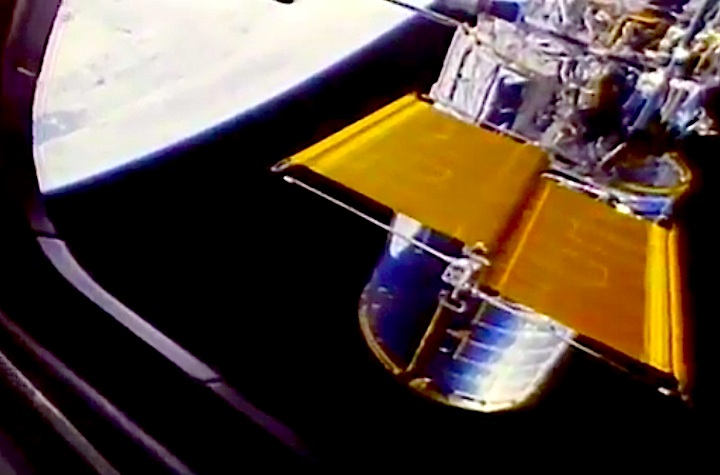
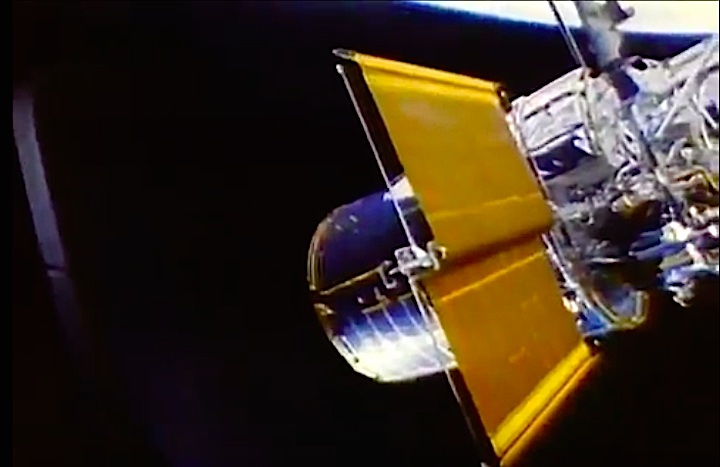
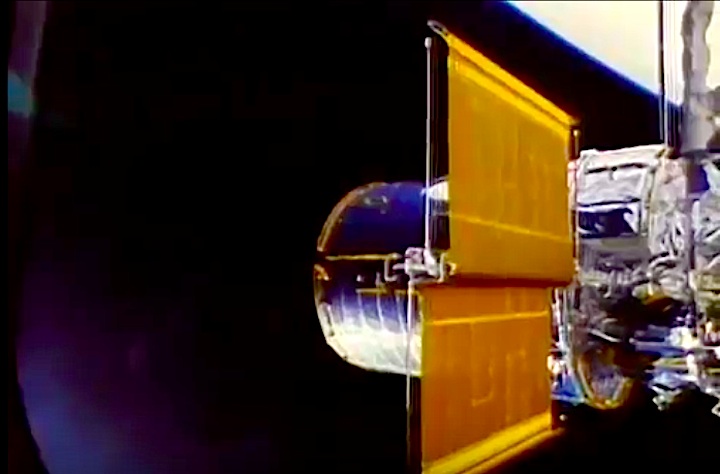
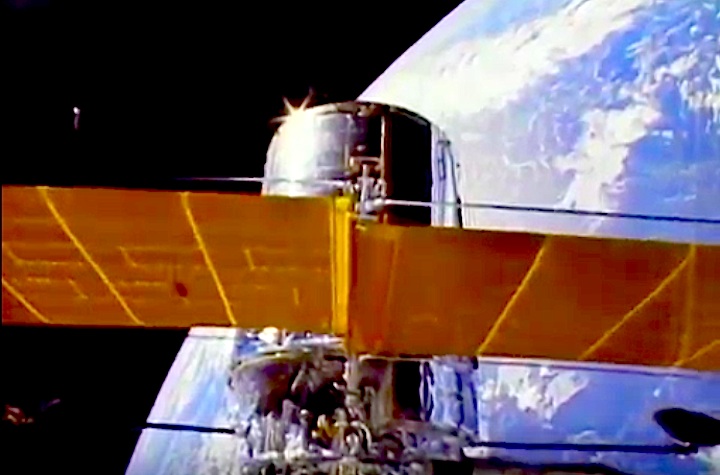
The primary payload, Hubble Space Telescope, deployed in a 380-statute-mile orbit. Secondary payloads: IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC) to document operations outside crew cabin and hand-held IMAX camera for use inside crew cabin; Ascent Particle Monitor (APM) to detect particulate matter in payload bay; Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) to provide data on growing protein crystals in microgravity; Radiation Monitoring Equipment III (RME III) to measure gamma ray levels in crew cabin; Investigations into Polymer Membrane Processing (IPMP) to determine porosity control in microgravity environment; Shuttle Student Involvement Program (SSIP) experiment to study effects of near-weightlessness on electrical arcs, and Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) experiment.
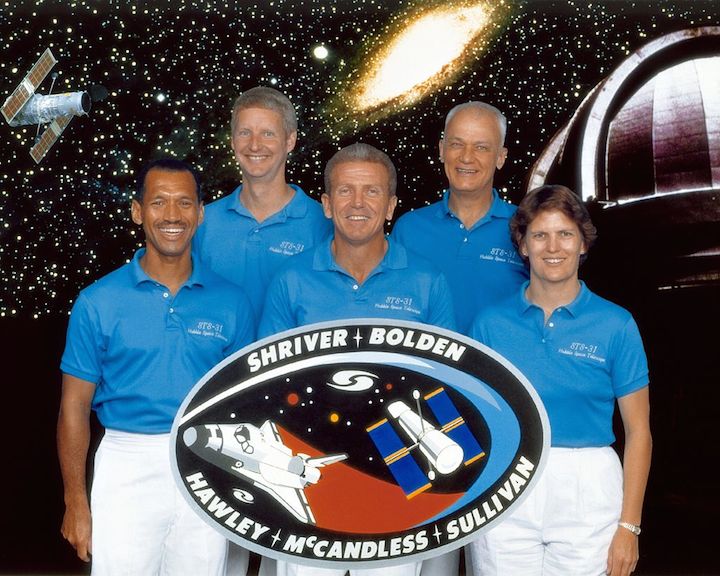
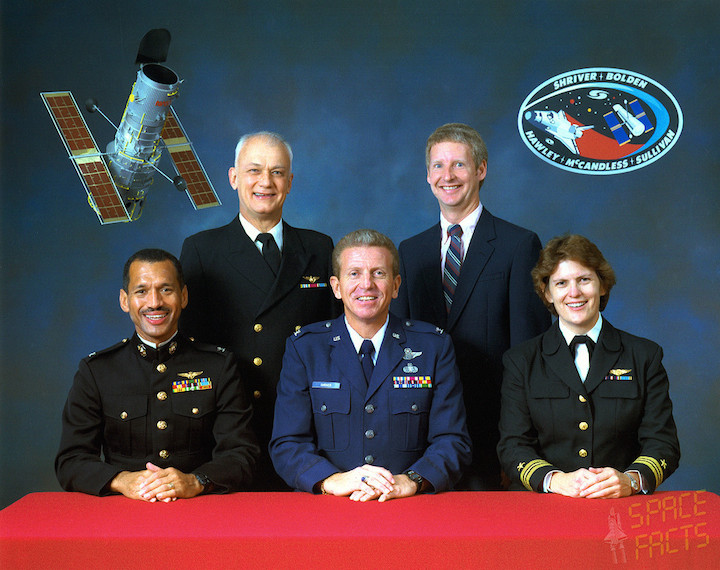
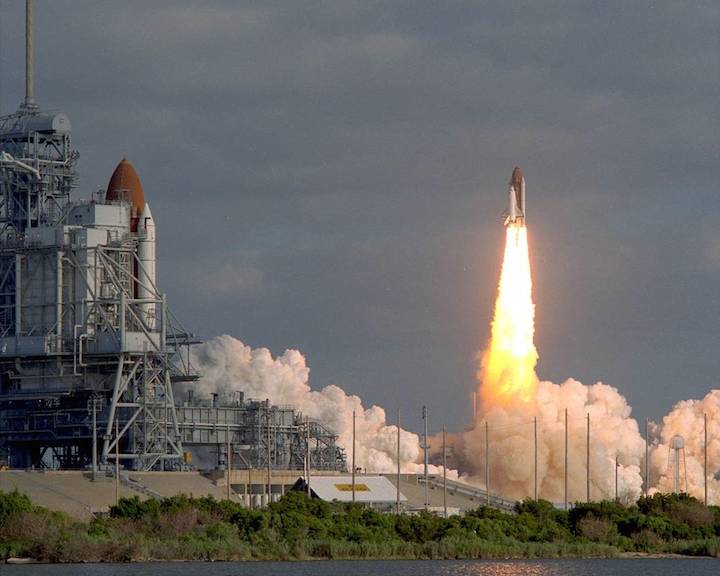




Image credit: NASA
April 24, 1990
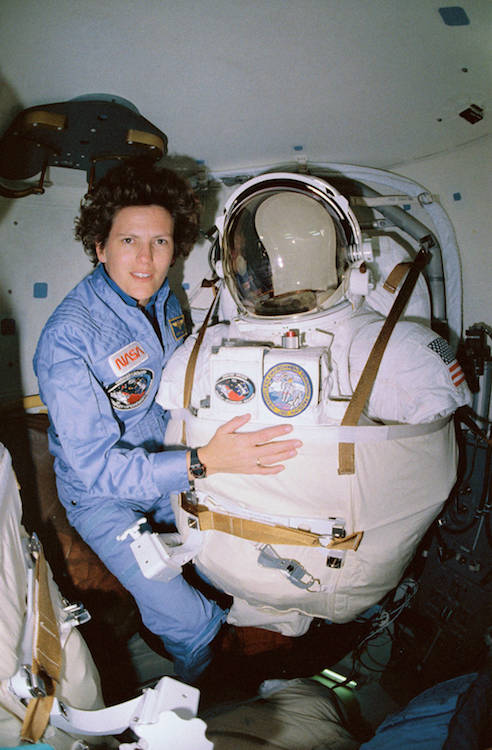

Sullivan's first venture into space began in October 1984, when she became the first American woman to walk in space.
In 1992, Sullivan served as payload commander on STS-45, the first Spacelab mission dedicated to NASA's Mission to Planet Earth. During the 9-day mission, the crew conducted experiments that produced detailed measurements of atmospheric chemical and physical properties, which contributed significantly to scientific understanding of Earth's climate and atmosphere.
With the completion of her third mission, Sullivan logged over 532 hours in space.
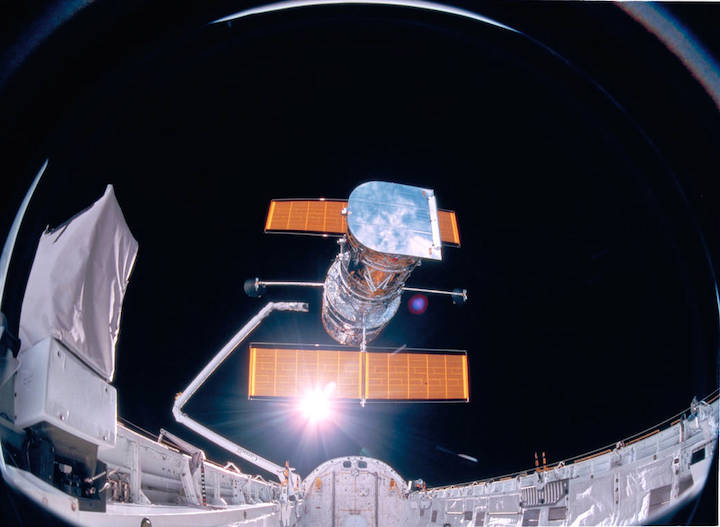
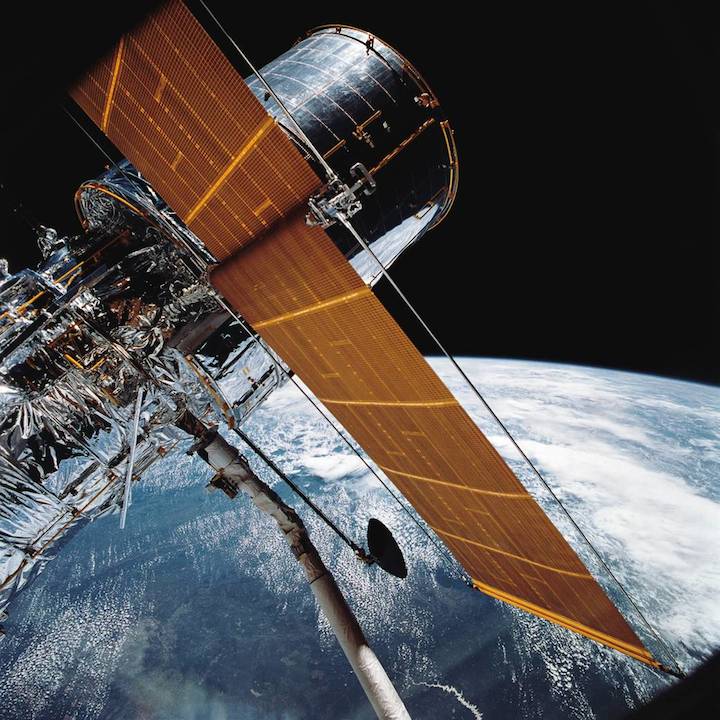



On April 24, 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope was launched aboard Space Shuttle Discovery on the STS-31 mission. The mission featured the deployment of Hubble, the first of NASA's Great Observatories to reach orbit. STS-31 was the tenth launch of the shuttle Discovery. On board were astronauts Charles F. Bolden (pilot, now NASA Administrator), Steven A. Hawley (mission specialist), Loren J. Shriver (commander), Bruce McCandless (mission specialist) and Kathryn D. Sullivan (mission specialist, now NOAA Administrator).
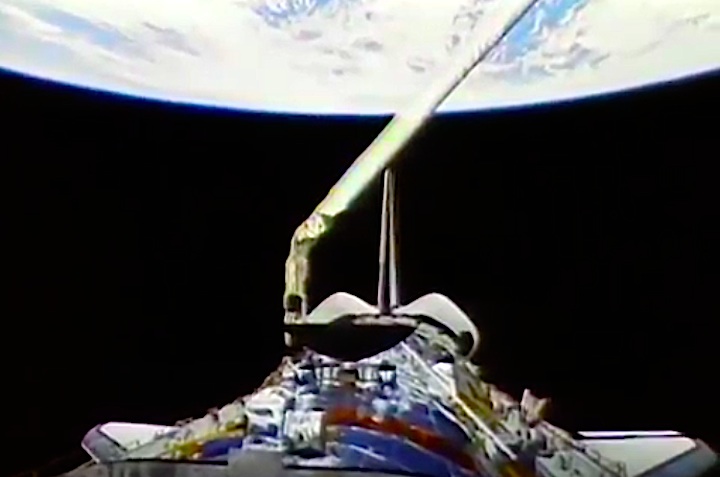
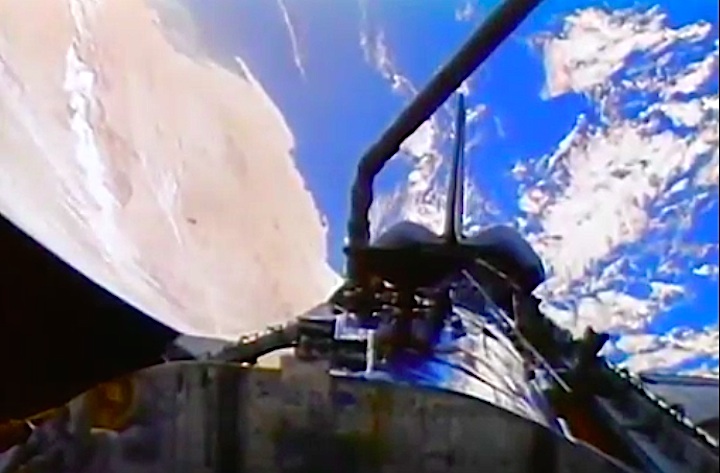
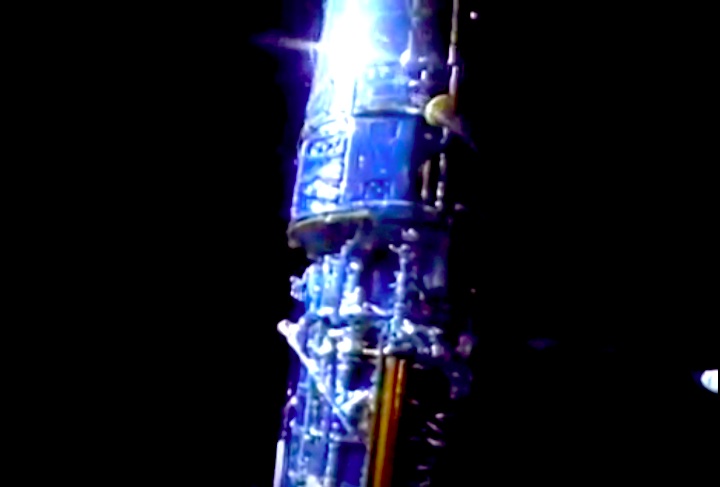
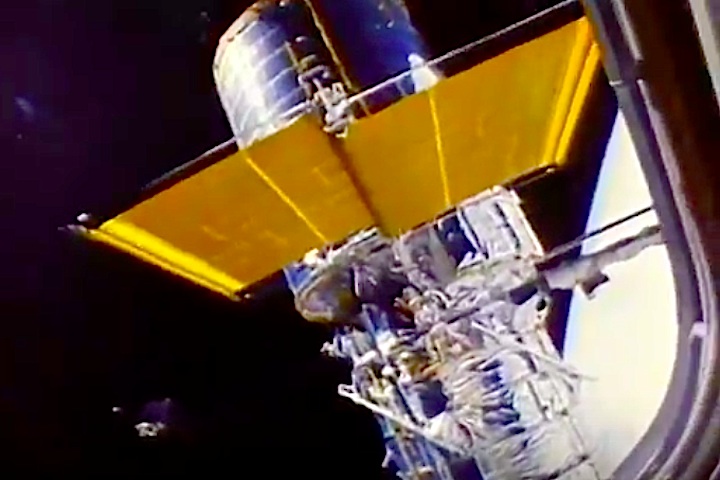
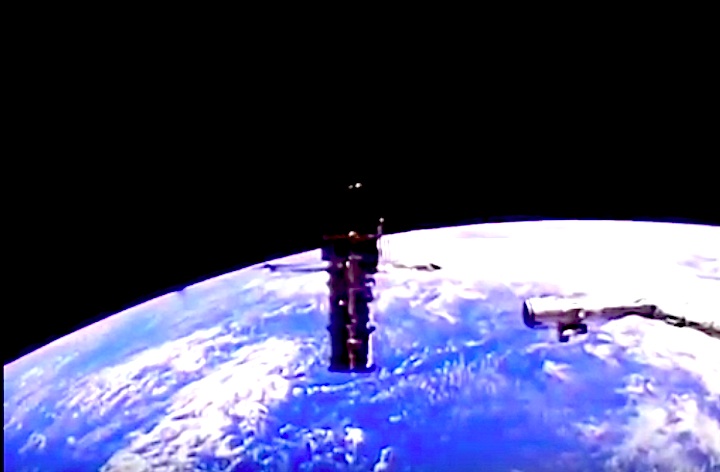
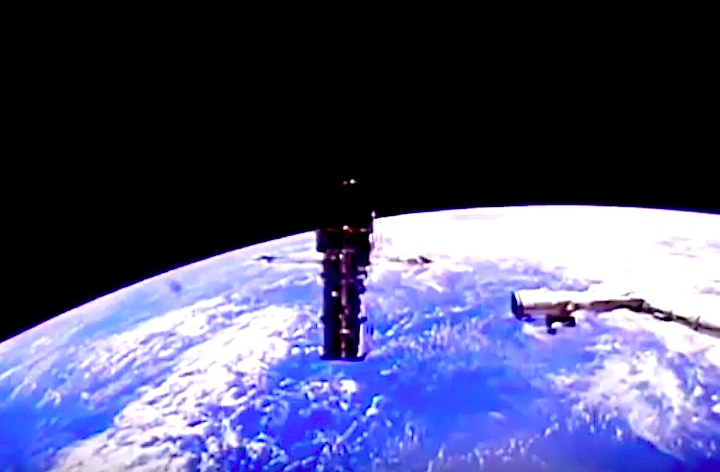
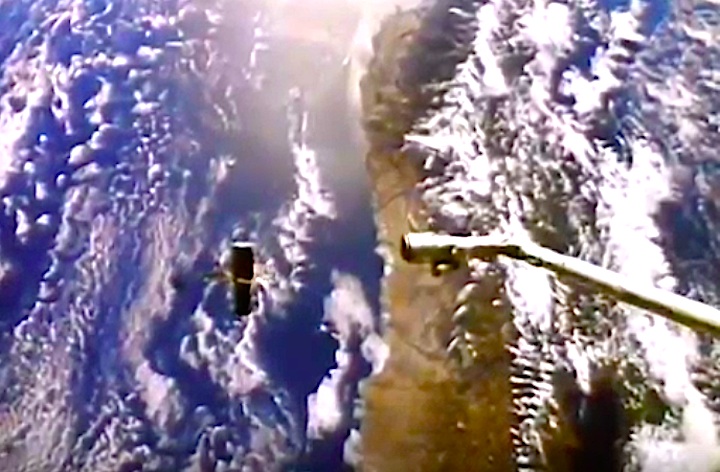
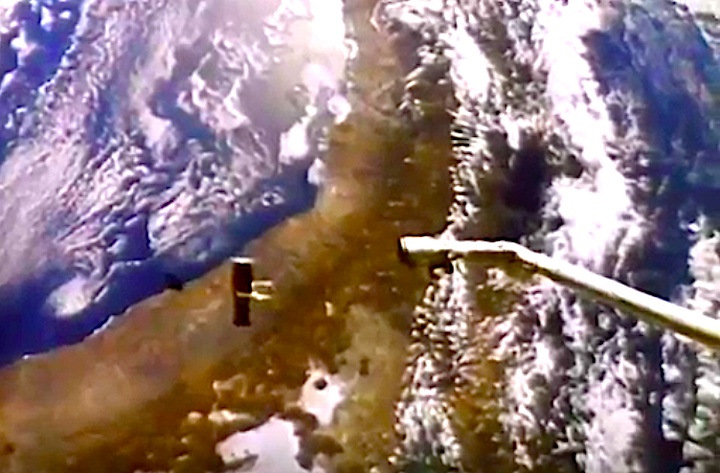
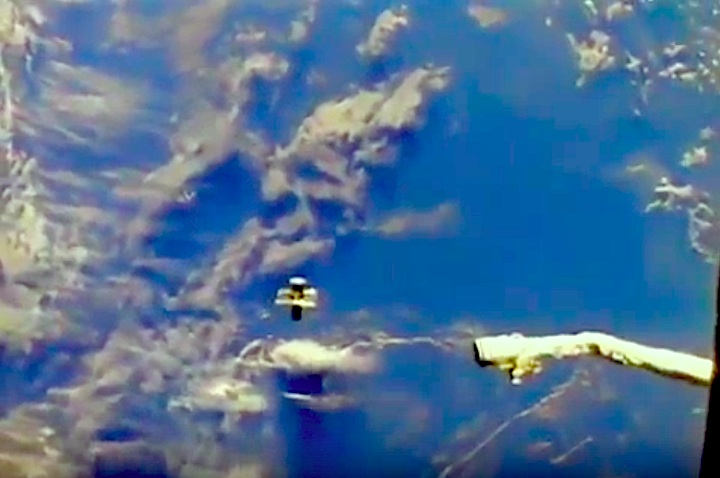
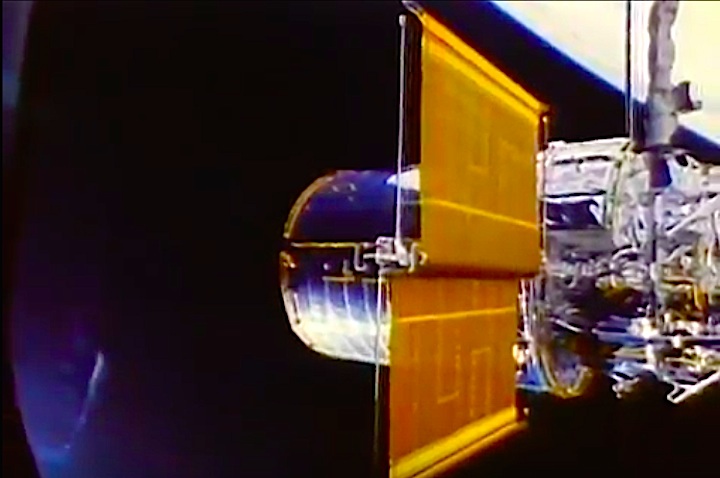
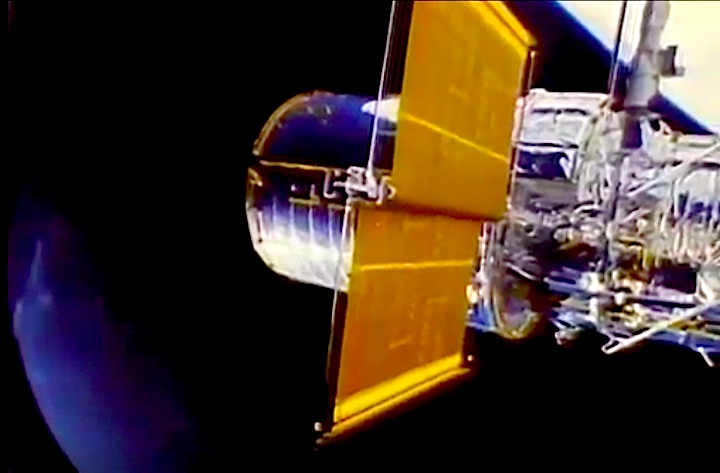
In this April 25, 1990 photograph taken with a handheld Hasselblad camera, most of the giant Hubble Space Telescope can be seen as it is suspended in space by Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) following the deployment of part of its solar panels and antennae. This was among the first photos NASA released on April 30 from the five-day STS-31 mission.
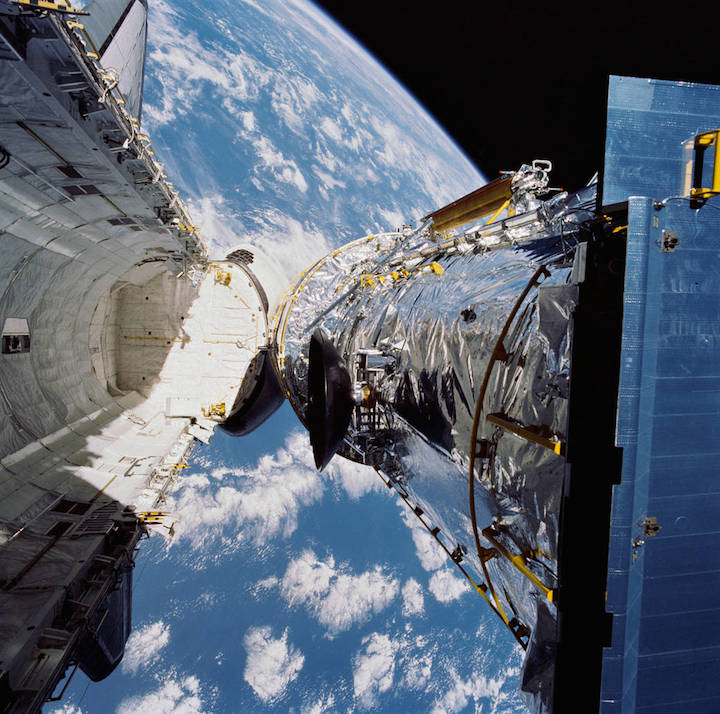

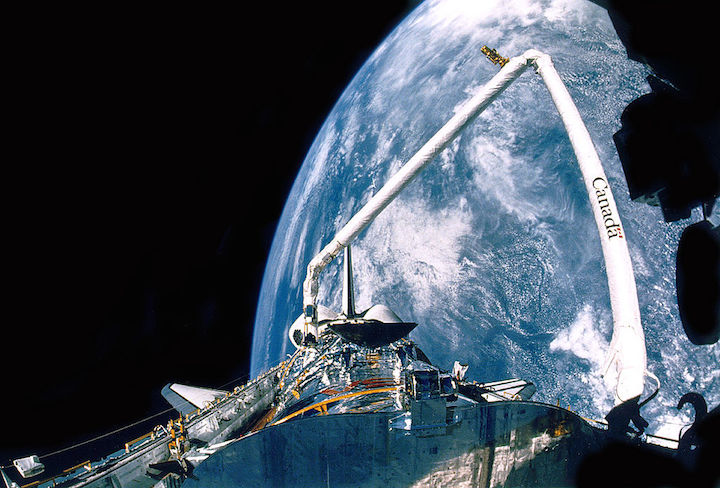
In this April 25, 1990, photograph taken by the crew of the STS-31 space shuttle mission, the Hubble Space Telescope is suspended above shuttle Discovery's cargo bay some 332 nautical miles above Earth. The Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, controlled from in-cabin by the astronaut crew members, held the huge telescope in this position during pre-deployment procedures, which included extension of solar array panels and antennae.
STS-31 was the tenth launch of the shuttle Discovery. On board were Commander Loren J. Shriver, Pilot Charles F. Bolden, Jr. (now NASA Administrator), Mission Specialists Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn D. Sullivan (now NOAA Administrator). To launch Hubble into an orbit that guaranteed longevity, Discovery soared to a record altitude of 600 km.
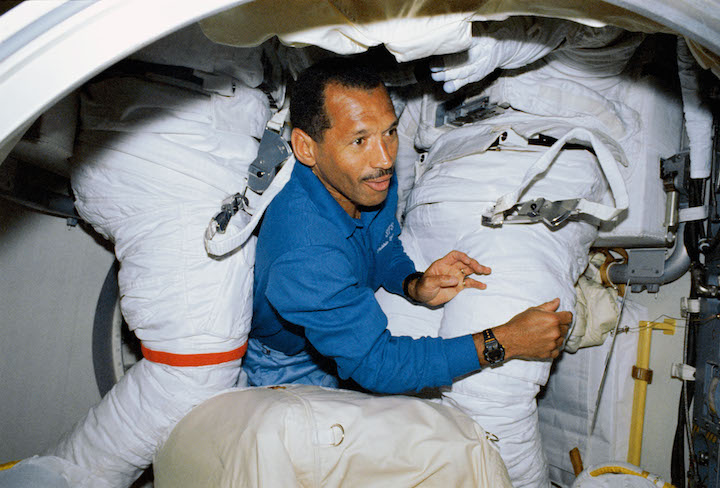


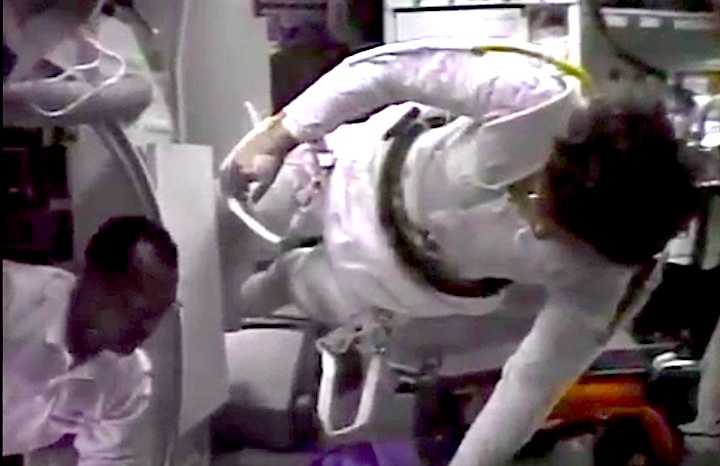
STS031-02-021 (24-29 April 1990) --- STS-31 Pilot Charles F. Bolden, is surrounded by extravehicular mobility unit spacesuits in the airlock of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Discovery. The suits did not get used outside the spacecraft as the mission's spacewalk was cancelled. Bolden's role in the spacewalk, had it happened, would have kept him inside the orbiter, supporting the efforts of two crewmates. Photo credit: NASA