.
13.10.2014
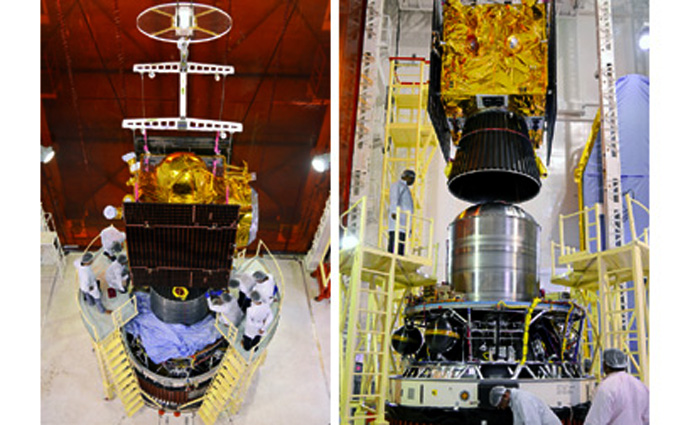

IRNSS-1C being assembled with PSLV-C26. (Image Courtesy: ISRO Website)
.
The countdown for the launch of India's navigation satellite IRNSS 1C, the third of seven satellites in the series to put in place India's navigation system on par with US' Global Positioning System, on board PSLV C 26 will commence at the spaceport of Sriharikota tomorrow.
The earlier planned launch on October six was postponed following a technical problem.
"The 67-hour countdown for the mission will commence at 0632 hrs IST on October 13," ISRO said.
IRNSS 1C with a lift-off mass of 1,425.4 kg would be launched on the 28th flight of India's PSLV-C26 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota, some 100 km from here. Like the launch of similar missions of IRNSS 1A and IRNSS 1B earlier, this mission would be launched on the XL version of the PSLV.
As part of its aspirations to build a regional navigational system equivalent to Global Positioning System of the US, ISRO plans to send seven satellites to put in place the Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS).
The first two satellites in the series, IRNSS 1A and IRNSS 1B were launched from Sriharikota on July 1, 2013 and April 4 this year respectively.
ISRO needs to launch at least four of the seven satellites to start operations of IRNSS, ISRO officials said.
IRNSS is similar to US' Global Positioning System, Russia's Glonass and Europe's Galileo. China and Japan also have similar systems, 'Beidou' and 'Quasi Zenith.
Quelle: TFE
.
Countdown begins for launch of PSLV-C26 carrying IRNSS-1C
The lift off will happen on Oct 16 at 1.32 am
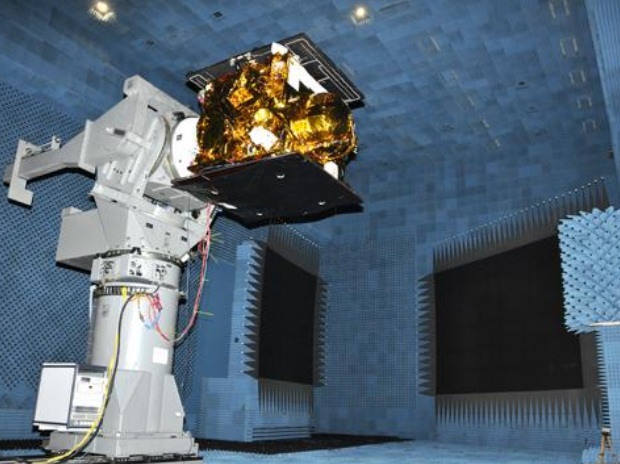

RNSS 1C spacecraft photographed during ElectroMagnetic Interference & ElectroMagnetic Compatibility (EMI-EMC) tests (pic: ISRO
-
The countdown for the launch of IRNSS-1C, the third in the series of seven navigation satellites, has commenced today at Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC)-SHAR, Sriharikota, about 100 km from Chennai.
IRNSS-1C is the third in the series of planned seven satellites, part of India’s navigation system, on par with the US Global Positioning System or the Russian Glonass.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (Isro) is scheduled to launch its workhorse Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)-C26, which will carry the navigation satellite IRNSS 1C on October 16 at 1.32 am.
Originally, the countdown was planned on October 10, but was postponed for two days.
The Launch Authorisation Board of Isro has authorised the countdown for PSLV-C26 / IRNSS-1C Mission, to commence at 6.32 am (IST) today, said ISRO.
Following this, the mono-methyl hydrazine (MMH) propellant filling operation of the fourth stage (PS4) of PSLV-C26 and the propellant (MMH) filling of the reaction control thrusters (RCT) of first stage (PS1) have been completed.
The satellite had already been integrated with the vehicle and the final phase of the check was in progress.
PSLV-C26 will use the ‘XL’ version of PSLV, and this is the seventh time the XL configuration is being flown, while the last one being the PSLV-C25, used for Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM).
IRNSS was designed to provide accurate position information service to users in India as well as the region extending up to 1,500 km from the country’s maritime boundary, said ISRO.
Its predecessors, IRNSS-1A and IRNSS-1B, were launched by PSLV-C22 and PSLV-C24, in Jul 2013 and Apr 2014, respectively.
IRNSS-1C has a lift-off mass of 1,425.40 kg. Its configuration is similar to that of its predecessor satellites. It will carry two types of payloads-- the navigation payload and ranging payload. The navigation payload of IRNSS-1C will transmit navigation service signals to the users.
The payload will operate in L5-band (1176.45 MHz) and S-band (2492.028 MHz). A highly accurate rubidium atomic clock is part of the navigation payload of the satellite.
The ranging payload of IRNSS-1C consists of a C-band transponder, which facilitates accurate determination of the range of the satellite.
IRNSS-1C also carries the corner cube retro reflectors for laser ranging, said ISRO.
Quelle: BS
.
Update: 14.10.2014
.
.

,
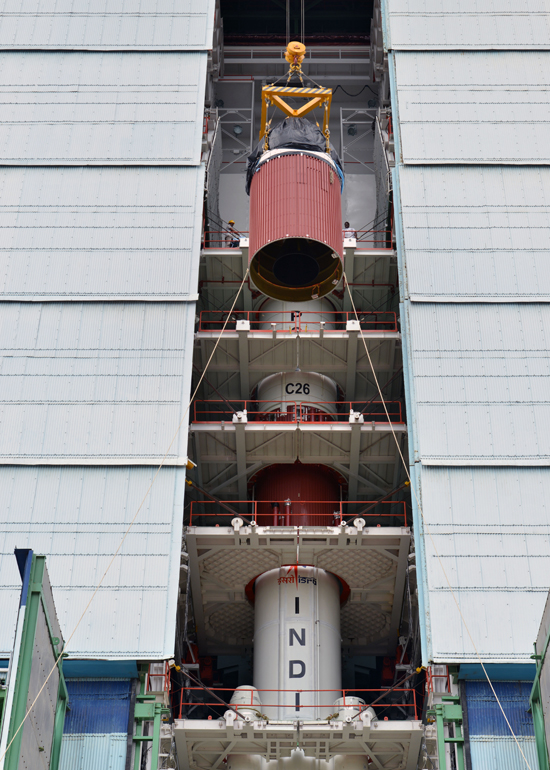

Assembly of PSLV-C26, Third and Fourth Stages
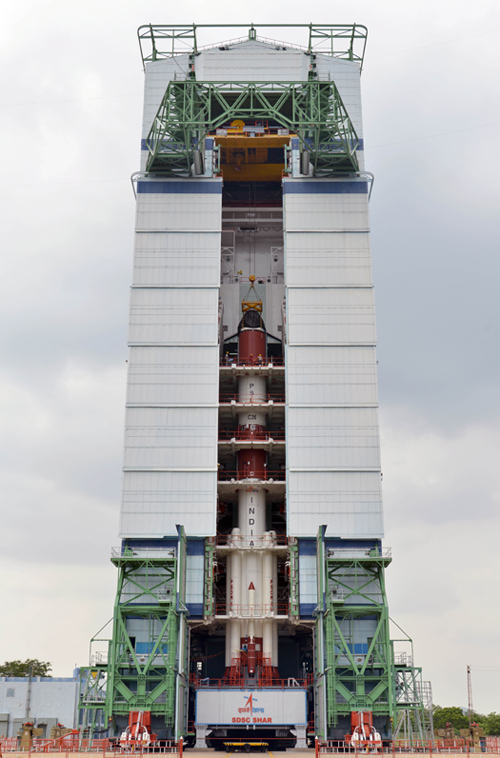

PSLV-C26 inside Mobile Service Tower prior to Satellite Integration
Quelle: ISRO
.
Update: 16.10.2014
.
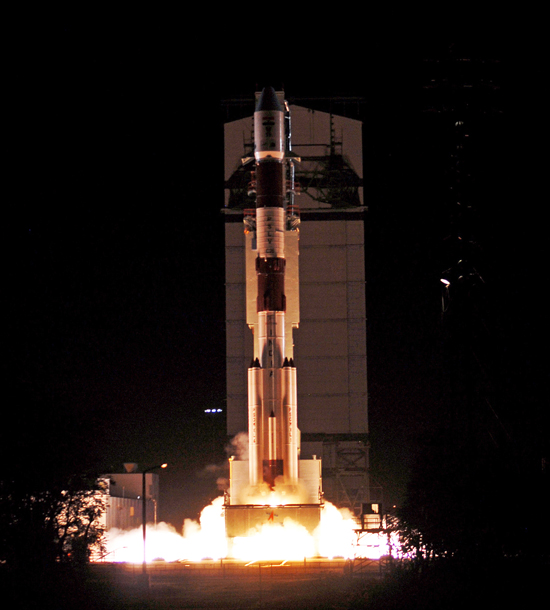
PSLV-C26 Successfully Launches India's Third Navigation Satellite IRNSS-1C
ISRO's Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, PSLV-C26, successfully launched IRNSS-1C, the third satellite in the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), in the early morning hours of today (October 16, 2014) at 0132 hours IST from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota. This is the twenty seventh consecutively successful mission of PSLV. The 'XL' configuration of PSLV was used for this mission. Previously, the same configuration of the vehicle was successfully used six times.
Hon'ble Minister of State (Space), Dr Jitendra Singh, witnessed the launch from the Mission Control Centre at SDSC, Sriharikota.
After the lift-off of PSLV-C26 with the ignition of the first stage, the important flight events, namely, stage and strap-on ignitions, heat-shield separation, stage and strap-on separations and satellite injection, took place as planned. After a flight of about 20 minutes 18 seconds, IRNSS-1C Satellite, weighing 1425 kg, was injected to an elliptical orbit of 282.56 km X 20,670 km, which is very close to the intended orbit.
After injection, the solar panels of IRNSS-1C were deployed automatically. ISRO's Master Control Facility (at Hassan, Karnataka) assumed the control of the satellite. In the coming days, four orbit manoeuvres will be conducted from Master Control Facility to position the satellite in the Geostationary Orbit at 83 deg East longitude.
IRNSS-1C is the third of the seven satellites constituting the space segment of the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System. IRNSS-1A and IRNSS-1B, the first two satellites of the constellation, were successfully launched by PSLV on July 02, 2013 and April 04, 2014 respectively. Both IRNSS-1A and 1B are functioning satisfactorily from their designated geosynchronous orbital positions.
IRNSS is an independent regional navigation satellite system designed to provide position information in the Indian region and 1500 km around the Indian mainland. IRNSS would provide two types of services, namely, Standard Positioning Services (SPS) - provided to all users - and Restricted Services (RS), provided to authorised users.
A number of ground stations responsible for the generation and transmission of navigation parameters, satellite control, satellite ranging and monitoring, etc., have been established in as many as 15 locations across the country.
In the coming months, the next satellite of this constellation, namely, IRNSS-1D, is scheduled to be launched by PSLV. The entire IRNSS constellation of seven satellites is planned to be completed by 2015.
.

.
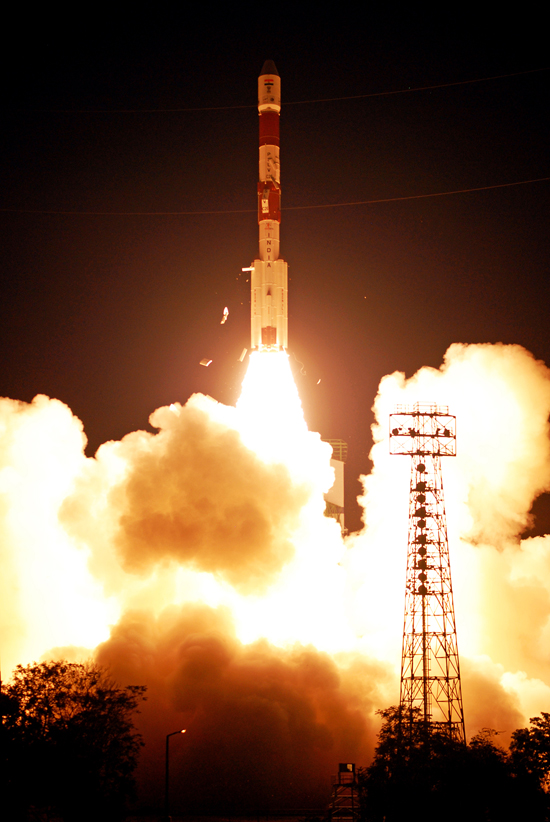

Quelle: ISRO
5697 Views
