9.10.2024
Nasa spacecraft Psyche receives laser signal from 290 million miles away
Breakthrough could transform our exploration of the solar system, space agency says

Nasa spacecraft receives laser signal from 290 million miles away
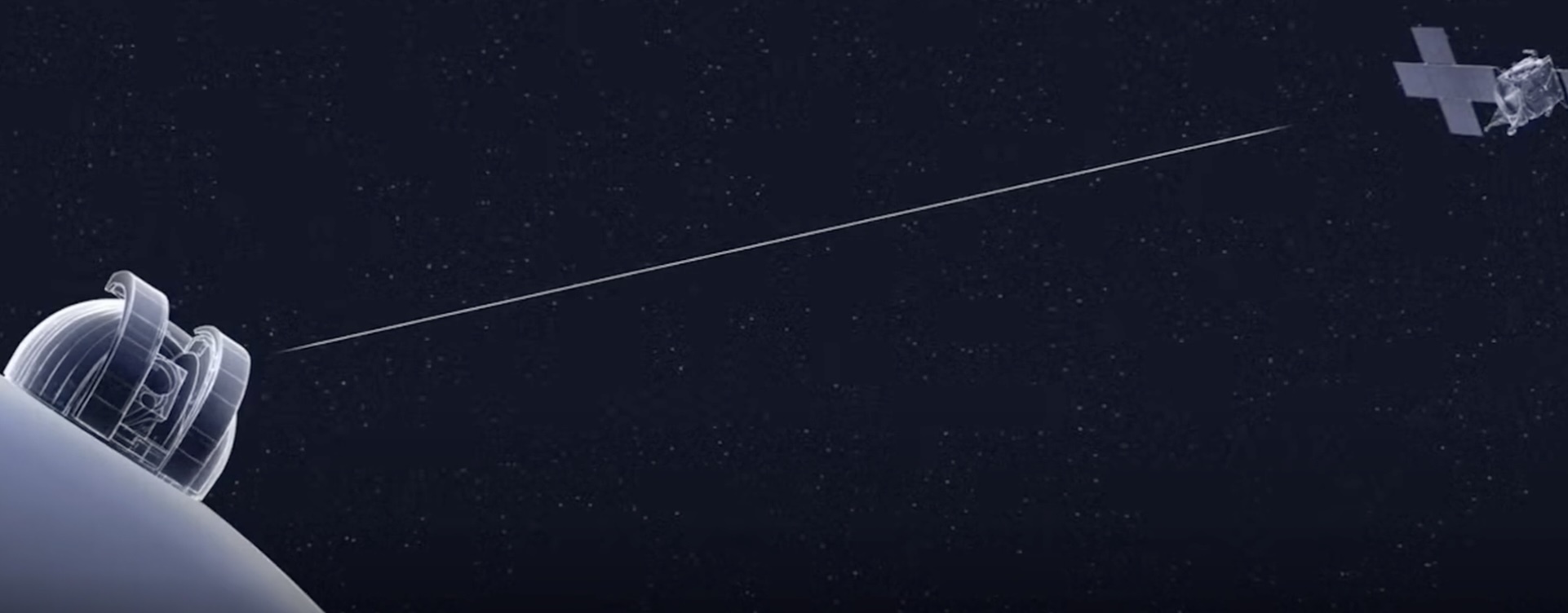
Nasa has successfully sent a laser signal about 290 million miles, smashing previous records and potentially transforming our exploration of the solar system.
The milestone was reached by Nasa’s Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which is exploring whether it is possible to use lasers to send messages deep into space. Lasers can send data at rates up to 100 times that of the radio frequencies used today, allowing for more complex and high-definition data, but they also require much greater precision to work.
It was sent to the Psyche spacecraft, which launched in October 2023. Its main mission is to study an asteroid with the same name, but it is also carrying the Nasa experiment to test laser communication through space.
The distance – which equates to about 460 million kilometres – is roughly the same as that between the Earth and Mars when they are their most distant.
Nasa hopes that the laser technology can help empower future crewed missions to Mars, among other exploration of our solar system, and so the successful test marks a major breakthrough.
“The milestone is significant. Laser communication requires a very high level of precision, and before we launched with Psyche, we didn’t know how much performance degradation we would see at our farthest distances,” said Meera Srinivasan, the project’s operations lead at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in a statement.
“Now the techniques we use to track and point have been verified, confirming that optical communications can be a robust and transformative way to explore the solar system.”
Nasa administrator Bill Nelson sent his congratulations to the team involved, on Twitter/X. “This extraordinary achievement will transform the way we explore the solar system,” he wrote.
Late last year, Nasa announced that it had successfully completed one such transmission from 10 million miles away. In the time since, it has broken through a whole set of records as Psyche continues to travel further from Earth.
That also included the first ultra high-definition video beamed from space. That happened late last year – when Psyche sent pictures of a cat named Taters.
As the distance from Earth increases, the speed of the connection is reduced. When it was 33 miles away, the spacecraft could receive data at its maximum rate of 267 megabits per second – but when the latest record was broken, in summer, it was hitting maximums of only 8.3 megabits per second.
Quelle: INDEPENDENT
----
Update: 2.05.2025
.
NASA’s Psyche spacecraft hits a speed bump on the way to a metal asteroid
“This kind of thing happens, and that’s why we build redundancy into our missions."
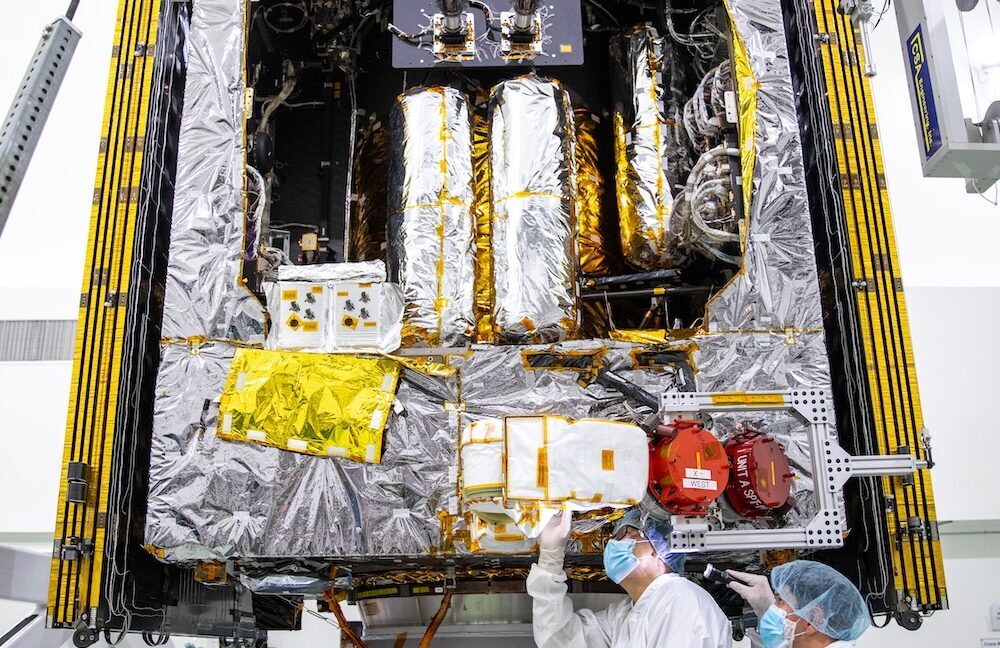

Engineers and technicians work on deploying and stowing stationary plasma thrusters on NASA's Psyche spacecraft before its launch in 2023. Two plasma engines are visible here mounted to a dual-axis positioning mechanism, which vectors their thrust in space. Some of Psyche's xenon fuel tanks are visible inside the main body of the spacecraft. Credit: NASA
NASA's Psyche spacecraft, located nearly 150 million miles from Earth on the way to an unexplored metal asteroid, has stopped firing its engines after detecting a problem in its propulsion system.
NASA published an update Tuesday revealing that the robotic spacecraft shut off its plasma thrusters earlier this month. The news wasn't widely shared until Wednesday, when NASA science chief Nicky Fox posted it on X.
"Engineers with NASA’s Psyche mission are working to determine what caused a recent decrease in fuel pressure in the spacecraft’s propulsion system," the agency said. The spacecraft detected the drop in pressure April 1 inside the line that feeds xenon fuel to the spacecraft's four plasma thrusters.
Sensors aboard the Psyche probe detected a pressure reduction in the xenon fuel line from about 36 pounds per square inch to about 26 psi. "As designed, the orbiter powered off the thrusters in response to the decrease," NASA said.
The Psyche spacecraft uses solar electric propulsion, a highly efficient means of maneuvering through space that relies on solar-generated electricity and more than a ton of xenon gas stored in seven 22-gallon (82-liter) tanks. Inside each of the mission's four thrusters, an electromagnetic field ionizes the xenon gas before expelling the ions to produce thrust.
These things happen
Louise Prockter, director of NASA's planetary science division, said engineers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California are looking into the problem.
So far, there's no effect on the Psyche spacecraft's trajectory. Psyche's plasma thrusters can remain unpowered until at least mid-June before the spacecraft would begin to drift off course, according to NASA. Mission managers decided to keep Psyche's engines turned off until they better understand the pressure decrease. If engineers trace the problem to the fuel line itself, NASA has the option of switching to a backup fuel line to resume thrusting.
"This kind of thing happens, and that’s why we build redundancy into our missions," Prockter said at a meeting of Mars scientists Wednesday. "We don't have any concerns at the moment about it, but we’re obviously keeping tabs on it.”
Each electric thruster on Psyche generates just 250 milli-newtons of thrust, roughly equivalent to the weight of three quarters. But they can operate for months at a time, and over the course of a multi-year cruise, these thrusters provide a more efficient means of propulsion than conventional rockets.
The plasma thrusters are reshaping the Psyche spacecraft's path toward its destination, a metal-rich asteroid also named Psyche. The spacecraft's four electric engines, known as Hall effect thrusters, were supplied by a Russian company named Fakel. Most of the other components in Psyche's propulsion system—controllers, xenon fuel tanks, propellant lines, and valves—come from other companies or the spacecraft's primary manufacturer, Maxar Space Systems, in California.
The Psyche mission is heading first for Mars, where the spacecraft will use the planet's gravity next year to slingshot itself into the asteroid belt, setting up for arrival and orbit insertion around the asteroid Psyche in August 2029.
Psyche launched in October 2023 aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on the opening leg of a six-year sojourn through the Solar System. The mission's total cost adds up to more than $1.4 billion, including development of the spacecraft and its instruments, the launch, operations, and an experimental laser communications package hitching a ride to deep space with Psyche.
Psyche, the asteroid, is the size of Massachusetts and circles the Sun in between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. No spacecraft has visited Psyche before. Of the approximately 1 million asteroids discovered so far, scientists say only nine have a metal-rich signature like Psyche. The team of scientists who put together the Psyche mission have little idea of what to expect when the spacecraft gets there in 2029.
Metallic asteroids like Psyche are a mystery. Most of Psyche's properties are unknown other than estimates of its density and composition. Predictions about the look of Psyche's craters, cliffs, and color have inspired artists to create a cacophony of illustrations, often showing sharp spikes and grooves alien to rocky worlds.
In a little more than five years, assuming NASA gets past Psyche's propulsion problem, scientists will supplant speculation with solid data.
Quelle: arsTechnica
----
Update: 30.05.2025
.
NASA’s Psyche Mission Looking Into Propulsion System
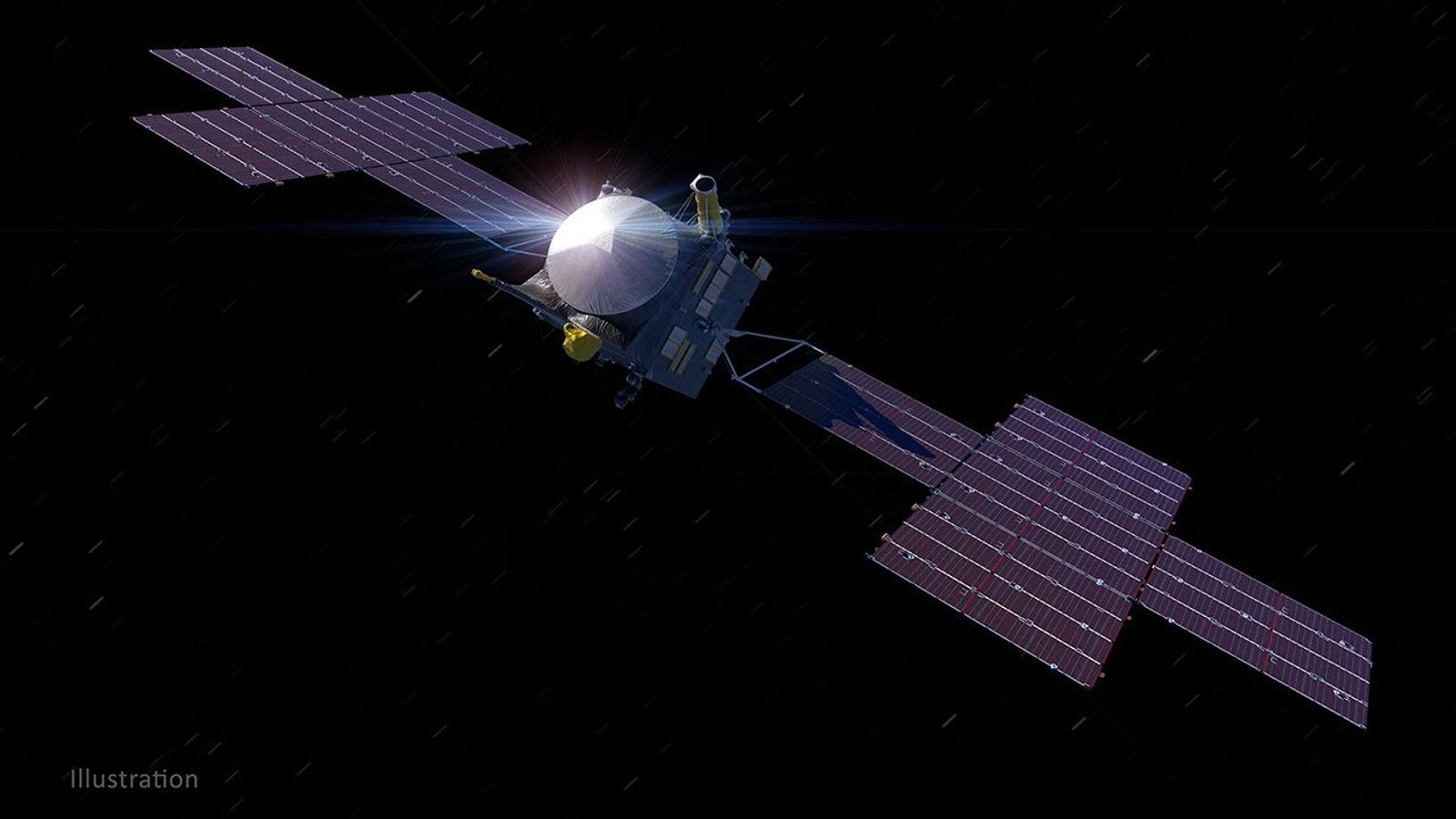

Engineers with NASA’s Psyche mission are working to determine what caused a recent decrease in fuel pressure in the spacecraft’s propulsion system. The spacecraft relies on solar electric propulsion, a system that uses energy to generate power for four electric thrusters. The thrusters then propel the spacecraft by expelling charged atoms, or ions, of the neutral gas xenon.
Psyche began firing its thrusters in May 2024. On April 1, the spacecraft detected a pressure drop in the line that feeds the xenon gas to the thrusters, going from 36 pounds per square inch (psi) to about 26 psi. As designed, the orbiter powered off the thrusters in response to the decrease.
The mission team has chosen to defer thrusting while engineers work to understand the pressure decrease. The mission design supports a pause in thrusting until at least mid-June before the spacecraft would see an effect on its trajectory. The electric propulsion system has two identical fuel lines, and the team may decide to switch to the backup fuel line to resume thrusting.
Psyche launched from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 13, 2023, and is now about 148 million miles (238 million kilometers) from Earth. In spring 2026, the spacecraft’s trajectory will bring it back toward Mars so that it can use the planet’s gravity to slingshot toward the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The probe will begin orbiting the asteroid Psyche in 2029.
Quelle: NASA
----
Update: 22.06.2025
.
NASA’s Psyche Spacecraft Resumes Full-Time Propulsion

NASA’s Psyche spacecraft resumed full thruster operations on June 16, and the propulsion system is performing as expected after mission engineers switched to a backup propellant line. They will operate the thrusters for the equivalent of three months between now and November to keep the orbiter’s trajectory to the metal-rich asteroid Psyche on track.
Operation of all four electric thrusters had been paused since early April while the mission team investigated an unexpected drop in pressure in the primary xenon propellant line. Through comprehensive testing and analysis, the team narrowed down the potential causes to a valve that may have malfunctioned in the primary line. The switch to the identical backup propellant line in late May restored full functionality to the propulsion system.
“The mission team’s dedication and systematic approach to this investigation exemplifies the best of NASA engineering,” said Bob Mase, Psyche project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “Their thorough diagnosis and recovery, using the backup system, demonstrates the value of robust spacecraft design and exceptional teamwork.”
Psyche is propelled by xenon gas, which is ionized by the thrusters to create a gentle push on the spacecraft that builds throughout its journey. The three months’ worth of thrusting will keep the spacecraft on track for its long-planned flyby of Mars in May 2026. The spacecraft will use the planet’s gravity as a slingshot to help it on its way to the asteroid Psyche.
Psyche remains set for an on-time arrival in August 2029 at its target asteroid, located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The spacecraft launched from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in October 2023.
Quelle: NASA
----
Update: 20.08.2025
.
NASA’s Psyche Captures Images of Earth, Moon

NASA’s Psyche captured images of Earth and our Moon from about 180 million miles (290 kilometers) away in July 2025, as it calibrated its imager instrument. When choosing targets for the imager testing, scientists look for bodies that shine with reflected sunlight, just as the asteroid Psyche does. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU
Headed for a metal-rich asteroid of the same name, the Psyche spacecraft successfully calibrated its cameras by looking homeward.
On schedule for its 2029 arrival at the asteroid Psyche, NASA’s Psyche spacecraft recently looked back toward home and captured images of Earth and our Moon from about 180 million miles (290 million kilometers) away. The images were obtained during one of the mission team’s periodic checkouts of the spacecraft’s science instruments.
On July 20 and July 23, the spacecraft’s twin cameras captured multiple long-exposure (up to 10-second) pictures of the two bodies, which appear as dots sparkling with reflected sunlight amid a starfield in the constellation Aries.
The Psyche multispectral imager instrument comprises a pair of identical cameras equipped with filters and telescopic lenses to photograph the asteroid Psyche’s surface in different wavelengths of light. The color and shape of a planetary body’s spectrum can reveal details about what it’s made of. The Moon and the giant asteroid Vesta, for example, have similar kinds of “bumps and wiggles” in their spectra that scientists could potentially also detect at Psyche. Members of the mission’s science team are interested in Psyche because it will help them better understand the formation of rocky planets with metallic cores, including Earth.
When choosing targets for the imager testing and calibration, scientists look for bodies that shine with reflected sunlight, just as the asteroid Psyche does. They also look at objects that have a spectrum they’re familiar with, so they can compare previous telescopic or spacecraft data from those objects with what Psyche’s instruments observe. Earlier this year, Psyche turned its lenses toward Jupiter and Mars for calibration — each has a spectrum more reddish than the bluer tones of Earth. That checkout also proved a success.
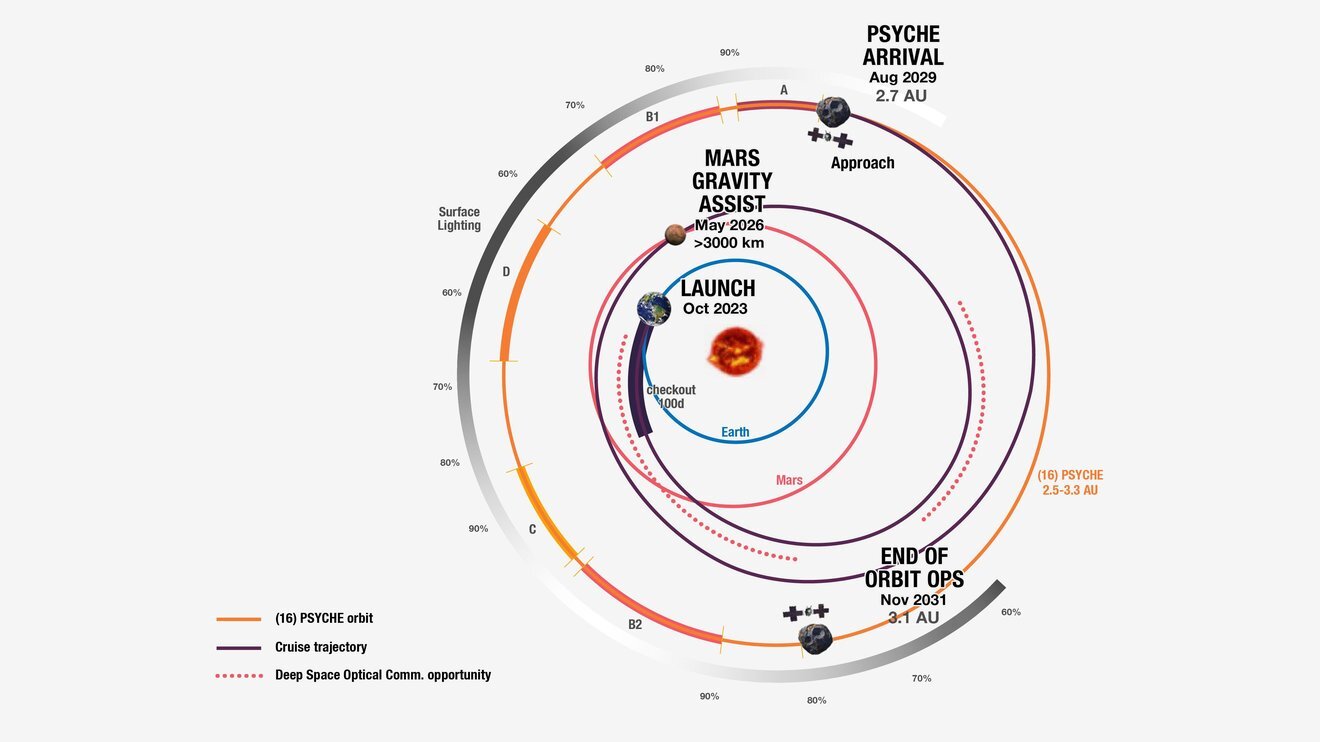
The Psyche spacecraft is taking a spiral path around the solar system in order to get a boost from a Mars gravity assist in 2026. It will arrive at the asteroid Psyche in 2029.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
To determine whether the imager’s performance is changing, scientists also compare data from the different tests. That way, when the spacecraft slips into orbit around Psyche, scientists can be sure that the instrument behaves as expected.
“After this, we may look at Saturn or Vesta to help us continue to test the imagers,” said Jim Bell, the Psyche imager instrument lead at Arizona State University in Tempe. “We’re sort of collecting solar system ‘trading cards’ from these different bodies and running them through our calibration pipeline to make sure we’re getting the right answers.”
trong and Sturdy
The imager wasn’t the only instrument that got a successful checkout in late July: The mission team also put the spacecraft’s magnetometer and the gamma-ray and neutron spectrometer through a gamut of tests — something they do every six months.
“We are up and running, and everything is working well,” said Bob Mase, the mission’s project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “We’re on target to fly by Mars in May 2026, and we are accomplishing all of our planned activities for cruise.”
That flyby is the spacecraft’s next big milestone, when it will use the Red Planet’s gravity as a slingshot to help the spacecraft get to the asteroid Psyche. That will mark Psyche’s first of two planned loops around the solar system and 1 billion miles (1.6 billion kilometers) since launching from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in October 2023.
More About Psyche
The Psyche mission is led by ASU. Lindy Elkins-Tanton of the University of California, Berkeley is the principal investigator. A division of Caltech in Pasadena, JPL is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and test, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. ASU leads the operations of the imager instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego on the design, fabrication, and testing of the cameras.
Psyche is the 14th mission selected as part of NASA’s Discovery Program, managed by the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy, managed the launch service.
Quelle: NASA
----
Update: 25.09.2025
.
Psyche asteroid probe uses lasers to phone home from 218 million miles away

