.
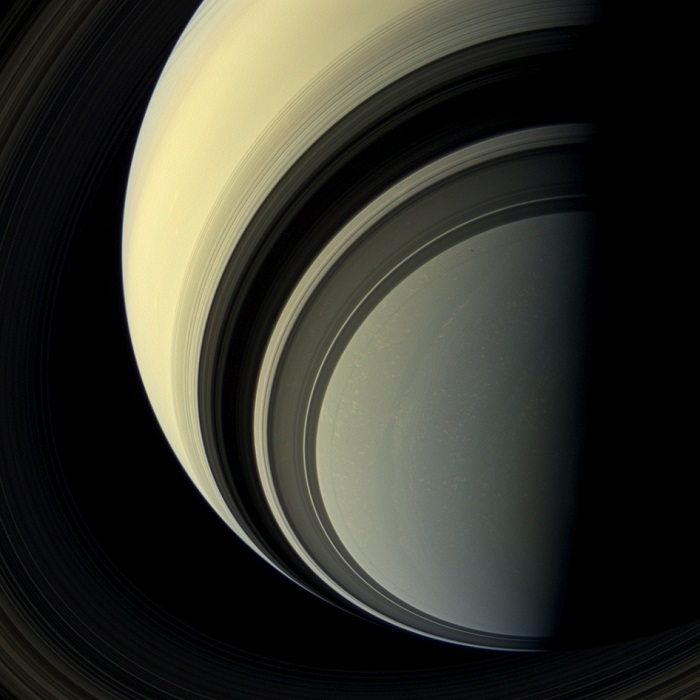
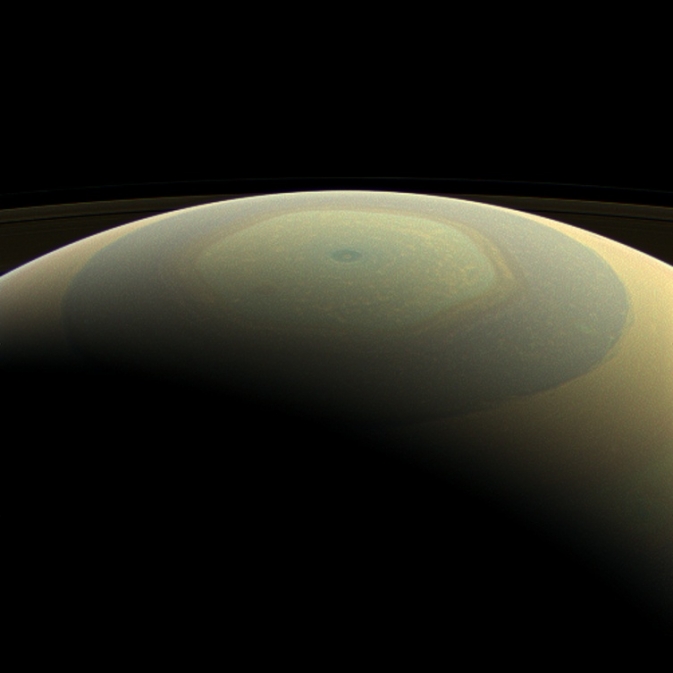

Winter is approaching in the southern hemisphere of Saturn and with this cold season has come the familiar blue hue that was present in the northern winter hemisphere at the start of NASA's Cassini mission. The changing blue hue that we have learned marks winter at Saturn is likely due to reduction of ultraviolet sunlight and the haze it produces, making the atmosphere clearer and increasing the opportunity for Rayleigh scattering (scattering by molecules and smaller particles) and methane absorption: both processes make the atmosphere blue. The small black dot seen to the right and up from image center, within the ring shadows of the A and F rings, is the shadow of the moon, Prometheus.
This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 44 degrees below the ring plane. Images taken using red, green and blue spectral filters were combined to create this natural color view. The images were taken with the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera on July 29, 2013.
This view was acquired at a distance of approximately 1.003 million miles (1.615 million kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale is 58 miles (93 kilometers) per pixel.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.
.
"During this, our tenth holiday season at Saturn, we hope that these images from Cassini remind everyone the world over of the significance of our discoveries in exploring such a remote and beautiful planetary system," said Carolyn Porco, Cassini imaging team leader, based at the Space Science Institute, Boulder, Colo. "Happy holidays from all of us on Cassini."
Two views of Enceladus are included in the package and highlight the many fissures, fractures and ridges that decorate the icy moon's surface. Enceladus is a white, glittering snowball of a moon, now famous for the nearly 100 geysers that are spread across its south polar region and spout tiny icy particles into space. Most of these particles fall back to the surface as snow. Some small fraction escapes the gravity of Enceladus and makes its way into orbit around Saturn, forming the planet's extensive and diffuse E ring. Because scientists believe these geysers are directly connected to a subsurface, salty, organic-rich, liquid-water reservoir, Enceladus is home to one of the most accessible extraterrestrial habitable zones in the solar system.
Packaged along with Saturn and Enceladus is a group of natural-color images of Saturn's largest moon, Titan, highlighting two of Titan's most outstanding features. Peering through the moon's hazy, orange atmosphere, the Cassini narrow-angle camera spots dark, splotchy features in the polar regions of the moon. These features are the lakes and seas of liquid methane and ethane for which the moon is renowned. Titan is the only other place in the solar system that we know has stable liquids on its surface, though in Titan's case, the liquids are ethane and methane rather than water. At Titan's south pole, a swirling high-altitude vortex stands out distinctly against the darkness of the moon's un-illuminated atmosphere. Titan's hazy atmosphere and surface environment are believed to be similar in certain respects to the early atmosphere of Earth.
But the planet that towers over these moons is a celestial wonder itself. The north and south poles of Saturn are highlighted and appear drastically different from each other, as seen in new natural-color views. The globe of Saturn resembles a holiday ornament in a wide-angle image overlooking its north pole, bringing into view the hexagonal jet stream and rapidly spinning polar vortex that reside there. And the planet's south pole, now in winter, looking very different than the springtime north, displays brilliant blue hues, reminiscent of a frosty winter wonderland.
"Until Cassini arrived at Saturn, we didn't know about the hydrocarbon lakes of Titan, the active drama of Enceladus' jets, and the intricate patterns at Saturn's poles," said Linda Spilker, the Cassini project scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. "Spectacular images like these highlight that Cassini has given us the gift of knowledge, which we have been so excited to share with everyone."
Launched in 1997, Cassini has explored the Saturn system for more than nine years. NASA plans to continue the mission through 2017, with the anticipation of much more groundbreaking science and imagery to come.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Cassini-Huygens mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging team consists of scientists from the U.S., England, France, and Germany. The imaging team is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.
.
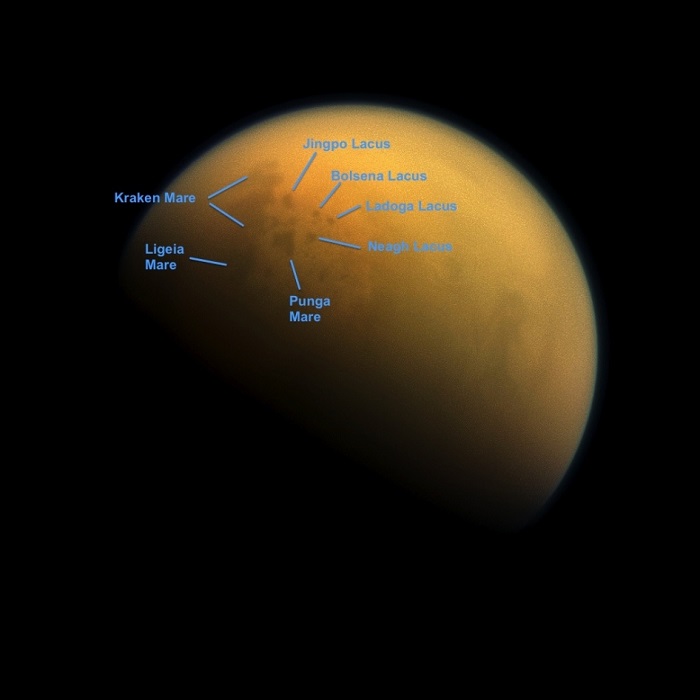
Using a special spectral filter, the high-resolution camera aboard NASA's Cassini spacecraft was able to peer through the hazy atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan. It captured this image, which features the largest seas and some of the many hydrocarbon lakes that are present on Titan's surface. Titan is the only place in the solar system, other than Earth, that has stable liquids on its surface. In this case, the liquid consists of ethane and methane rather than water. This annotated version of the image indicates the names assigned to the visible features. Titan's largest sea is Kraken Mare.
This view looks towards the side of Titan (3,200 miles or 5,150 kilometers across) that leads in its orbit around Saturn. North on Titan is up and rotated 36 degrees to the left. Images taken using red, green and blue spectral filters were combined to create this natural-color view. The images were taken with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on Oct. 7, 2013.
The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 809,000 miles (1.303 million kilometers) from Titan. Image scale is 5 miles (8 kilometers) per pixel.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.
.
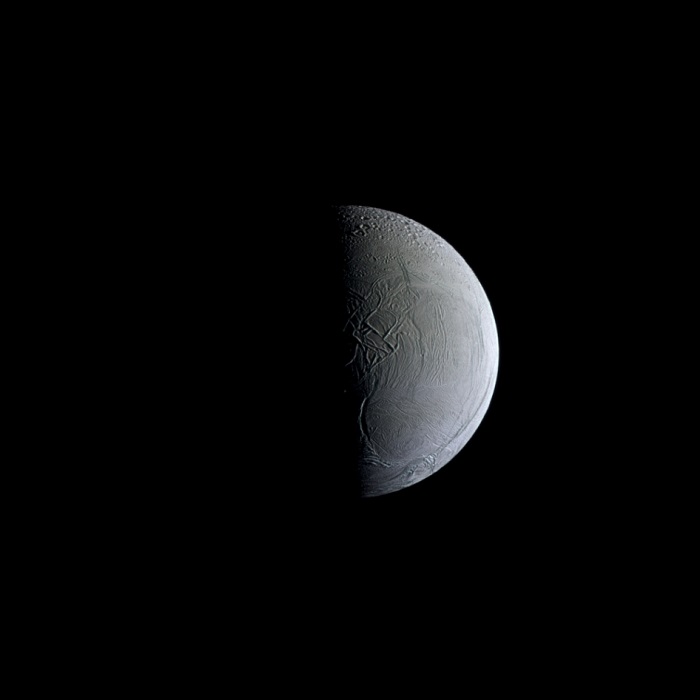

NASA's Cassini captures a still and partially sunlit Enceladus. The Saturnian moon is covered in ice that reflects sunlight similar to freshly fallen snow, making Enceladus one of the most reflective objects in the solar system. The blue color in this false-color image indicates larger-than-average ice particles. The moon's surface is decorated with fractures, folds and ridges caused by tectonic stresses.
This view looks toward the side of Enceladus (313 miles or 504 kilometers across) that faces backward in the moon's orbit around Saturn. North on Enceladus is up. The images were taken with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on April 7, 2010, using filters sensitive to ultraviolet, visible and infrared light (spanning wavelengths from 338 to 750 nanometers).
The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 123,000 miles (198,000 kilometers) from Enceladus. Image scale is 3,889 feet (1 kilometer) per pixel.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.
Quelle: NASA
