30.05.2019
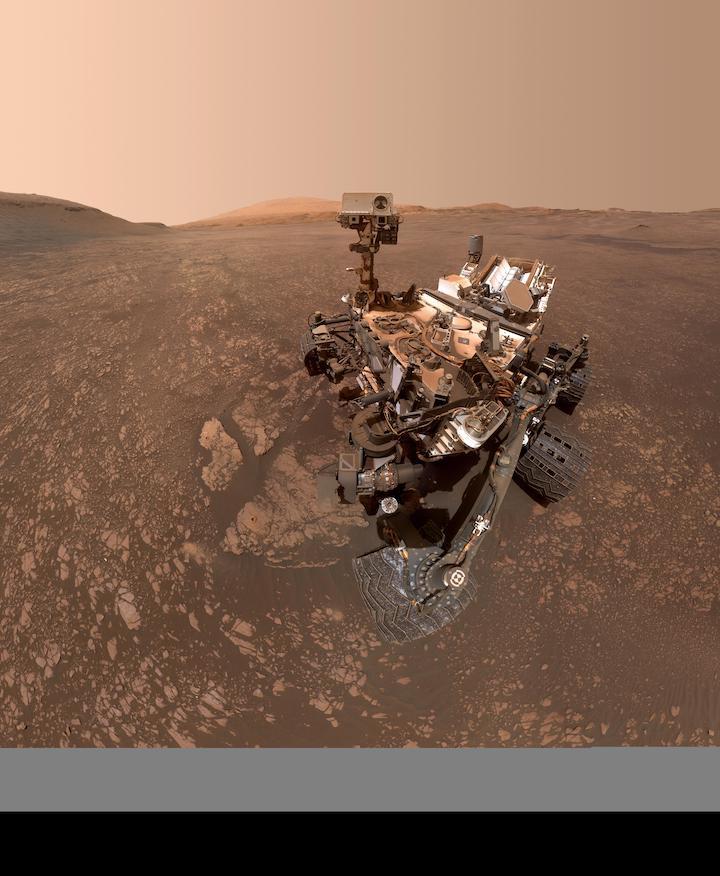

NASA's Curiosity rover has confirmed that the region on Mars it's exploring, called the "clay-bearing unit," is well deserving of its name. Two samples the rover recently drilled at rock targets called "Aberlady" and "Kilmarie" have revealed the highest amounts of clay minerals ever found during the mission. Both drill targets appear in a new selfie taken by the rover on May 12, 2019, the 2,405th Martian day, or sol, of the mission.
This clay-enriched region, located on the side of lower Mount Sharp, stood out to NASA orbiters before Curiosity landed in 2012. Clay often forms in water, which is essential for life; Curiosity is exploring Mount Sharp to see if it had the conditions to support life billions of years ago. The rover's mineralogy instrument, called CheMin (Chemistry and Mineralogy), provided the first analyses of rock samples drilled in the clay-bearing unit. CheMin also found very little hematite, an iron oxide mineral that was abundant just to the north, on Vera Rubin Ridge.
Other than proof that there was a significant amount of water once in Gale Crater, what these new findings mean for the region is still up for debate. It's likely that the rocks in the area formed as layers of mud in ancient lakes - something Curiosity also found lower on Mount Sharp. Water interacted with sediment over time, leaving an abundance of clay in the rocks there.
Amid this new drilling and analyzing, Curiosity took a break to watch some clouds - all in the name of science. The rover used its black-and-white Navigation Cameras (Navcams) to snap images of drifting clouds on May 7 and May 12, 2019, sols 2400 and 2405. They're likely water-ice clouds about 19 miles (31 kilometers) above the surface.
The mission's team has been trying to coordinate cloud observations with NASA's InSight lander, located about 373 miles (600 kilometers) away, which recently took its own cloud images. Capturing the same clouds from two vantage points can help scientists calculate their altitude.
+++
Curiosity's Three-Frame Mosaic of Clouds
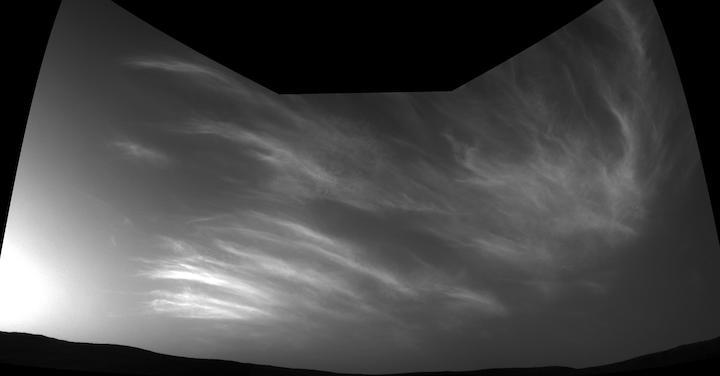
NASA's Curiosity Mars rover imaged these drifting clouds on May 17, 2019, the 2,410th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, using its black-and-white Navigation Cameras (Navcams).
These are likely water-ice clouds about 19 miles (31 kilometers) above the surface. They are also "noctilucent" clouds, meaning they are so high that they are still illuminated by the Sun, even when it's night at Mars' surface. Scientists can watch when light leaves the clouds and use this information to infer their altitude.
Quelle: NASA
