21.10.2017

JAXA probe finds 50-km cavern under surface of the moon
Space probe data confirmed that an enormous cavern stretching for about 50 kilometers exists beneath the moon’s surface, offering a possible protected site for future lunar bases, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency said Oct. 18.
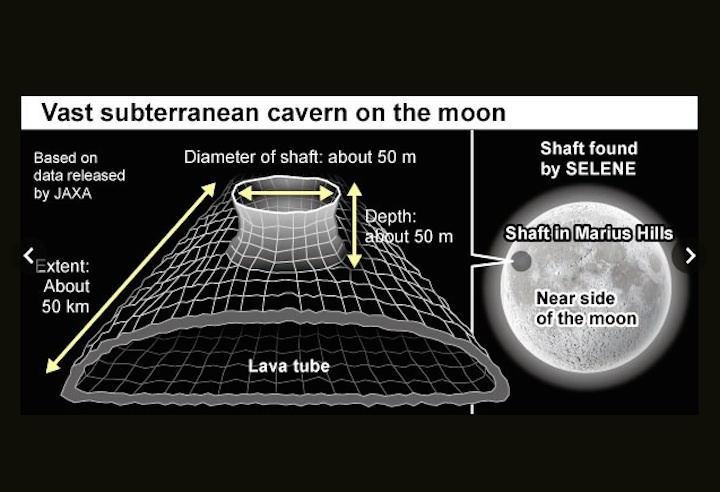
The cavern, found in the Marius Hills area on the near side of the moon, is about 100 meters wide and extends for about 50 km, according to data taken by JAXA’s Selenological and Engineering Explorer (SELENE), also called the Kaguya moon probe.
In 2009, the Kaguya probe found a large shaft with an opening about 50 meters in diameter in the Marius Hills area. The shaft descends about 50 meters beneath the surface.
The JAXA team analyzed data obtained from a lunar radar sounder on the probe that indicated an underground structure extended west from the shaft.
The study confirmed that the cavern, likely created by volcanic activity, has not collapsed, and there is the possibility of ice or water existing in rocks within the cave, the team said.
If future lunar explorers could use the underground space for a base, it could provide shelter from cosmic radiation and menacing temperatures, while water or ice could be used as fuel, the JAXA team said.
It is widely believed the moon was rocked by large-scale volcanic activity until about 1 billion years ago.
The cavern is believed to have been a lava tube formed when the outer lava cooled and hardened while the melted rock within remained hot and continued to flow.
Quelle: The Asahi Shimbun
