.
STS-44
Space Shuttle: Atlantis
Launch Pad: 39A
Launch Weight: 259,629 pounds
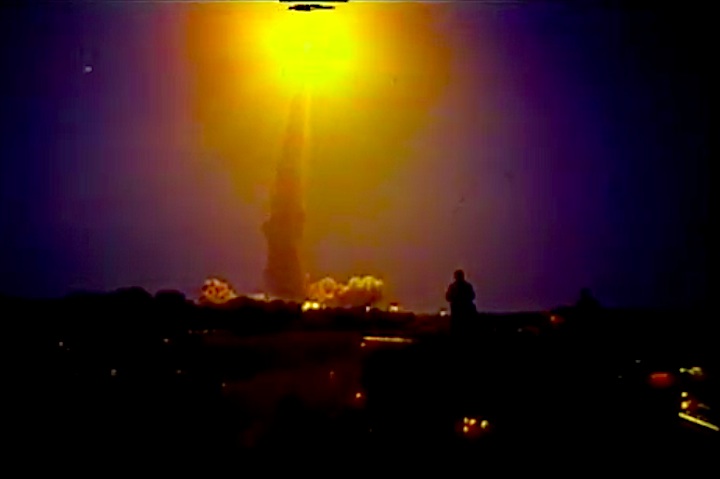
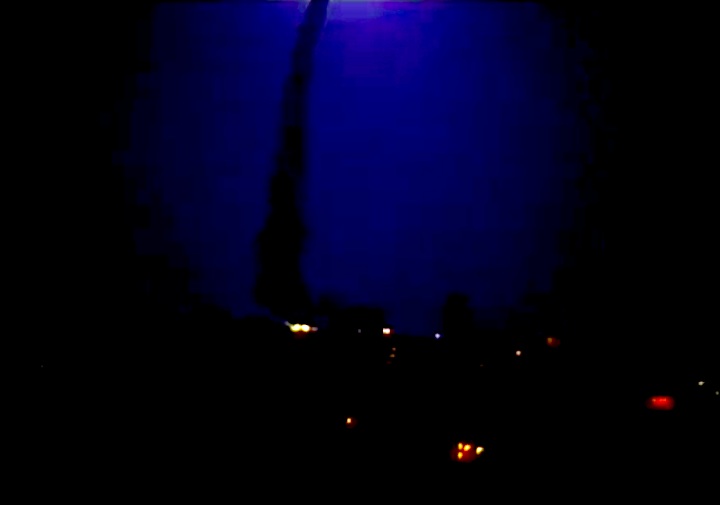
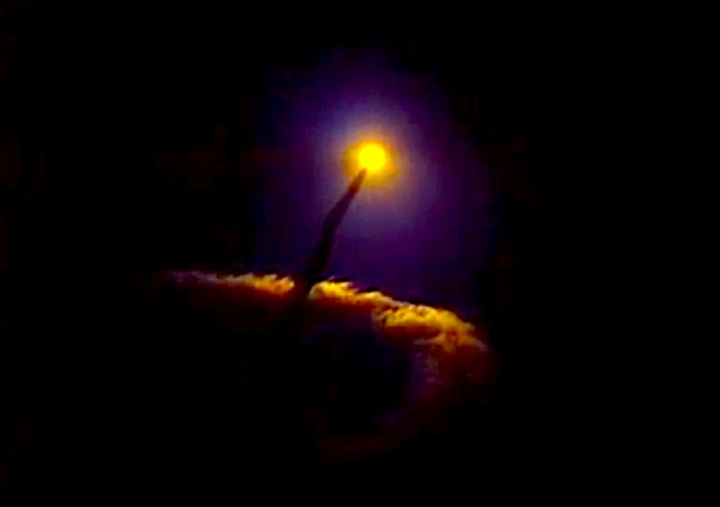
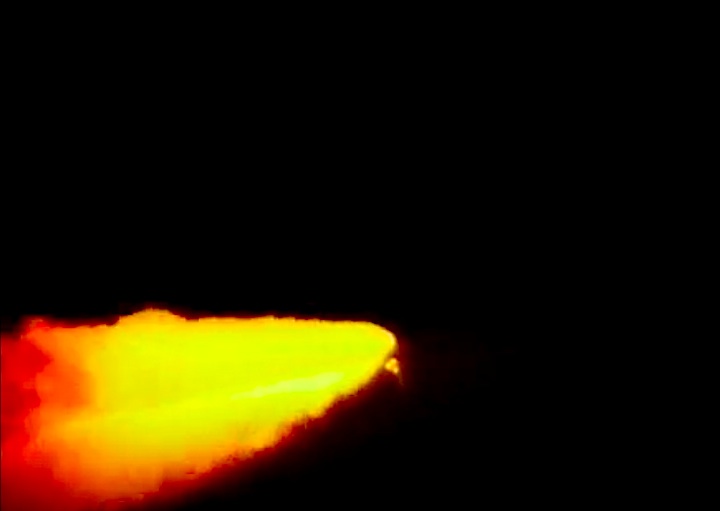
Launched: November 24, 1991, 6:44:00 p.m. EST
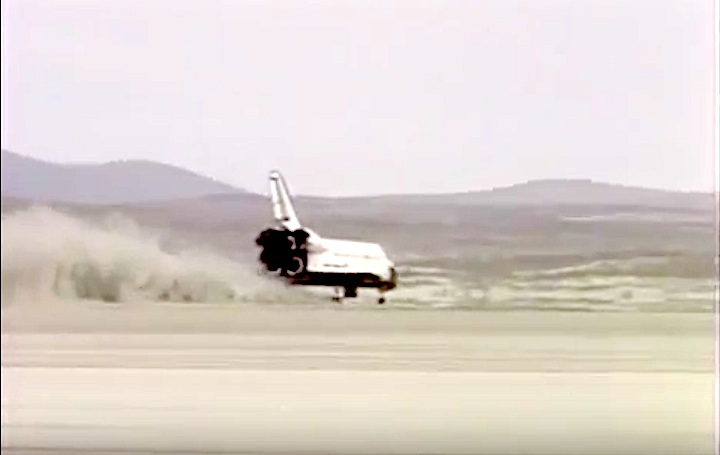
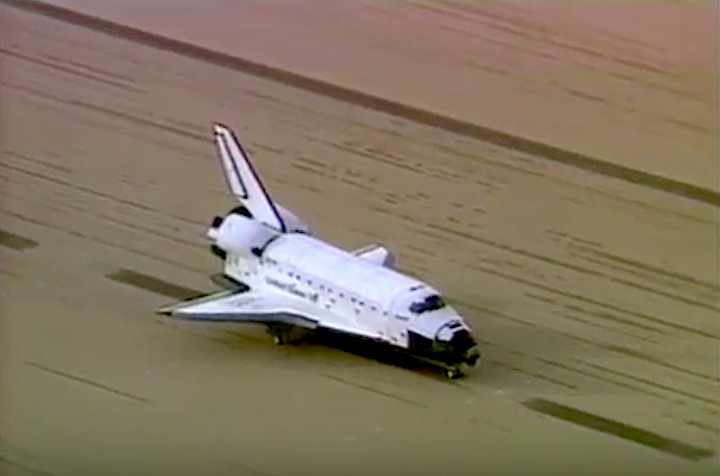
Landing Site: Edwards Air Force Base, Calif.
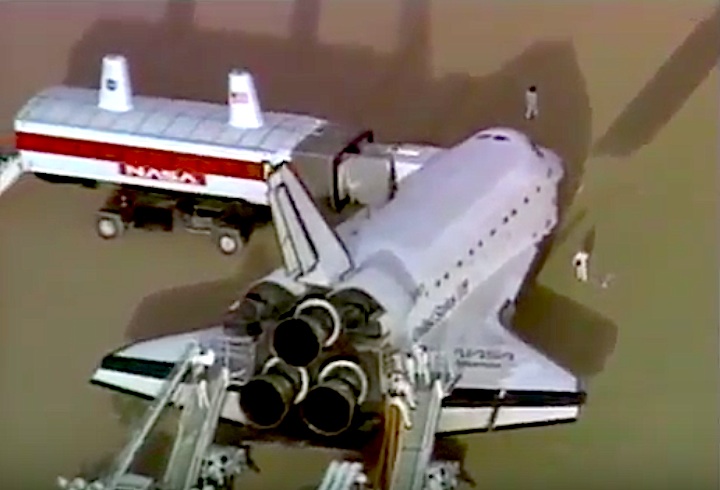
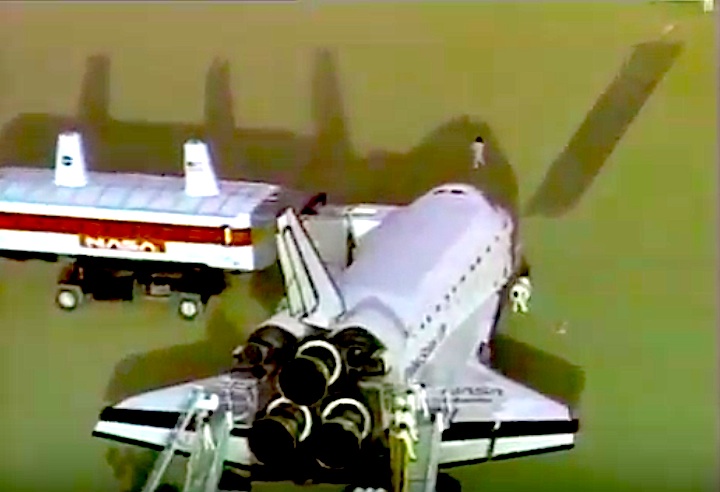
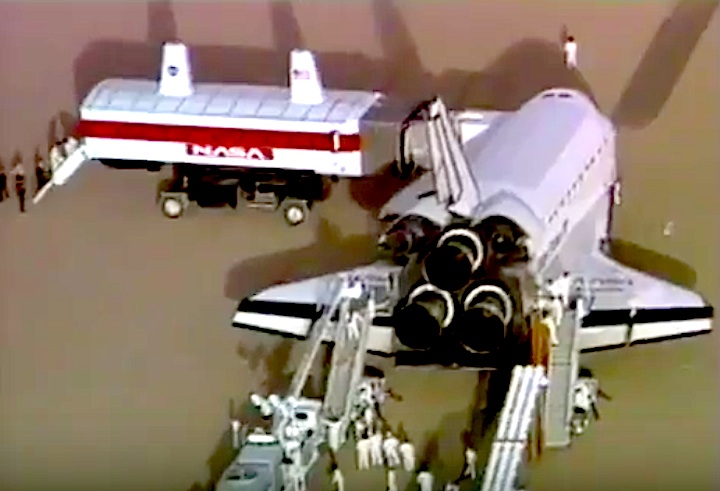
Landing: December 1, 1991, 2:34:44 p.m. PST
Landing Weight: 193,825 pounds
Runway: 5
Rollout Distance: 11,191 feet
Rollout Time: 107 seconds
Revolution: 110
Mission Duration: 6 days, 22 hours, 50 minutes, 44 seconds
Returned to KSC: December 8, 1991
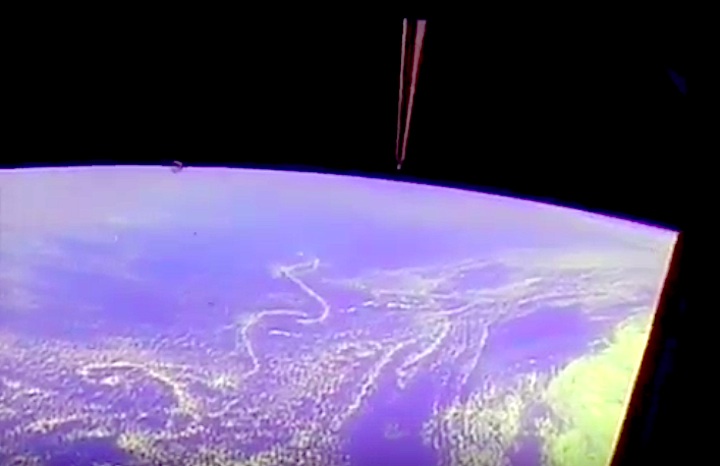
Orbit Altitude: 197 nautical miles
Orbit Inclination: 28.5 degrees
Miles Traveled: 2.9 million
Crew Members

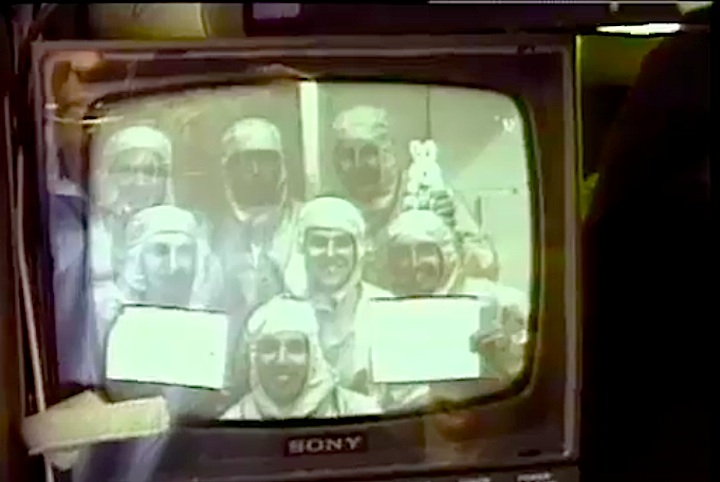
Image above: STS-44 Crew photo with Commander Frederick D. Gregory, Pilot Terence T. Henricks, Mission Specialists Mario Runco, Jr., James S. Voss, F. Story Musgrave and Thomas J. Hennen. Image Credit: NASA
Launch Highlights
 The launch set for November 19 was delayed due to a malfunctioning redundant inertial measurement unit on the Inertial Upper Stage booster attached to the Defense Support Program satellite. The unit was replaced and tested. The launch was reset for November 24, delayed 13 minutes to allow an orbiting spacecraft to pass and allow external tank liquid oxygen replenishment after minor repairs to the valve in the liquid oxygen replenishment system in the mobile launcher platform.
The launch set for November 19 was delayed due to a malfunctioning redundant inertial measurement unit on the Inertial Upper Stage booster attached to the Defense Support Program satellite. The unit was replaced and tested. The launch was reset for November 24, delayed 13 minutes to allow an orbiting spacecraft to pass and allow external tank liquid oxygen replenishment after minor repairs to the valve in the liquid oxygen replenishment system in the mobile launcher platform.Mission Highlights
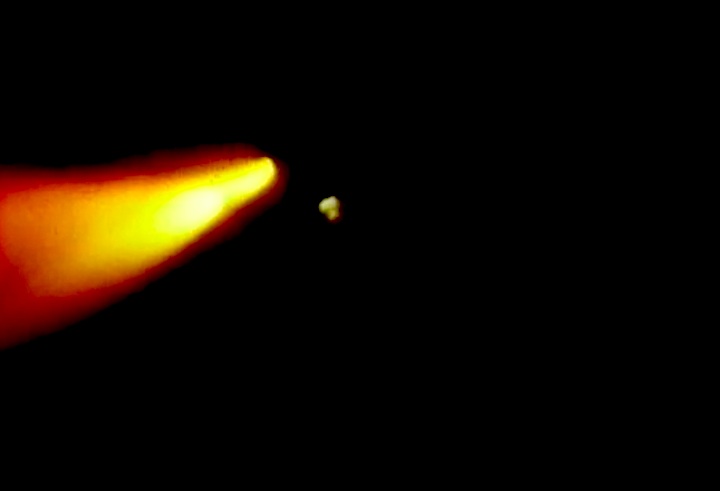
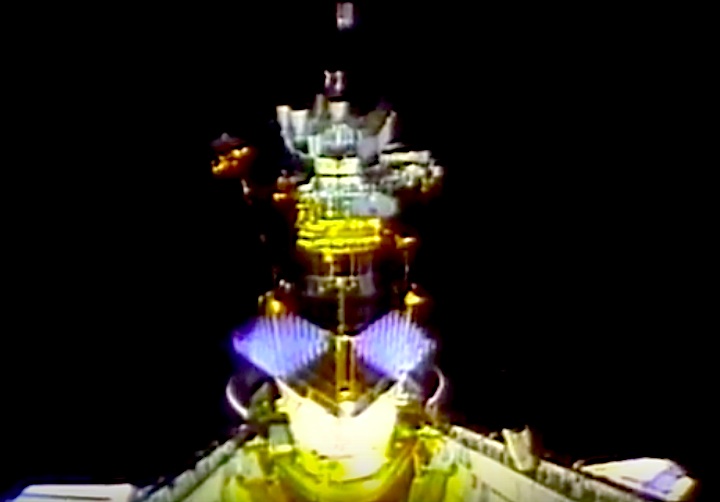
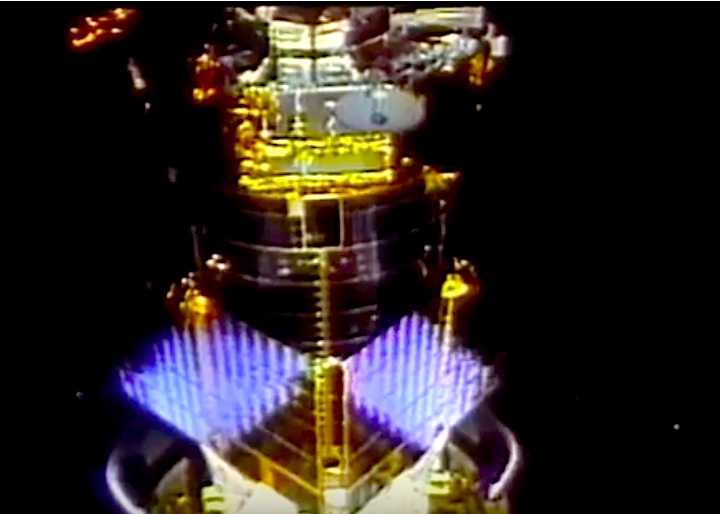
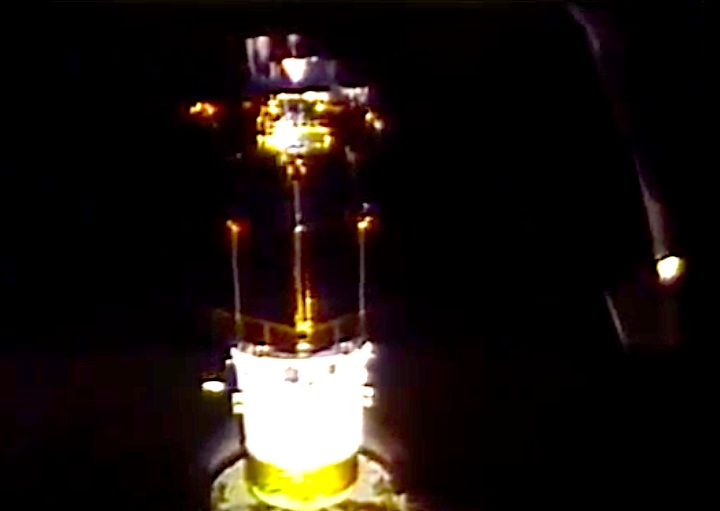
A dedicated Department of Defense mission. The unclassified payload included a Defense Support Program (DSP) satellite and attached Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), which were deployed on flight day one. Cargo bay and middeck payloads: Interim Operational Contamination Monitor (IOCM); Terra Scout; Military Man in Space (M88-1); Air Force Maui Optical System (AMOS); Cosmic Radiation Effects and Activation Monitor (CREAM); Shuttle Activation Monitor (SAM); Radiation Monitoring Equipment III (RME III); Visual Function Tester-1 (VFT-1); Ultraviolet Plume Instrument (UVPI). Bioreactor Flow and Particle Trajectory experiment; and Extended Duration Orbiter Medical Project, a series of investigations in support of Extended Duration Orbiter.
---
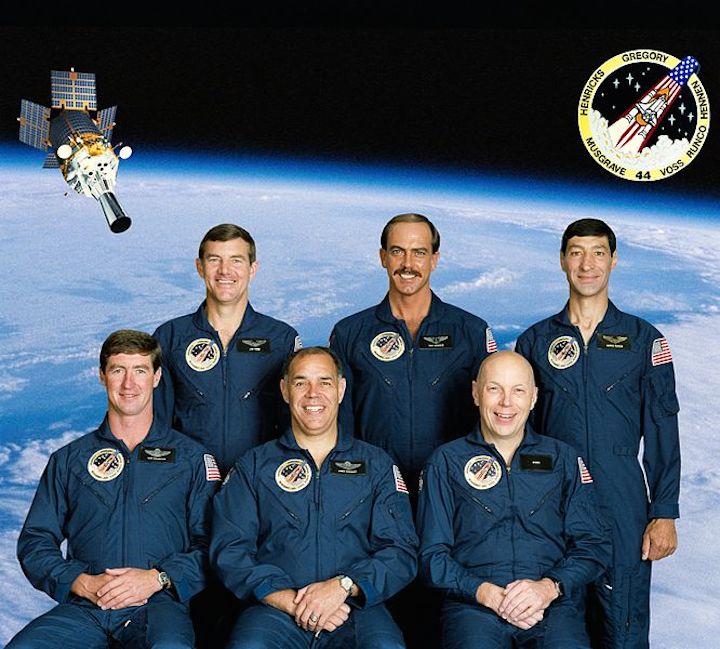

The STS-44 crew portrait includes 6 astronauts. Pictured seated, from left to right, are Terence T. Hendricks, pilot; Frederick D. Gregory, commander; and F. Story Musgrave, mission specialist. Standing on the back row (left to right) are James S. Voss, mission specialist; Thomas J. Hennen, payload specialist; and Mario Runco, Jr., mission specialist. The 6 crew members launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis on November 24, 1991 at 6:44:00 pm (EST). Dedicated to the Department of Defense (DOD), the mission's primary unclassified payload was the Defense Support Program (DSP) satellite and attached Inertial Upper Stage (IUS).
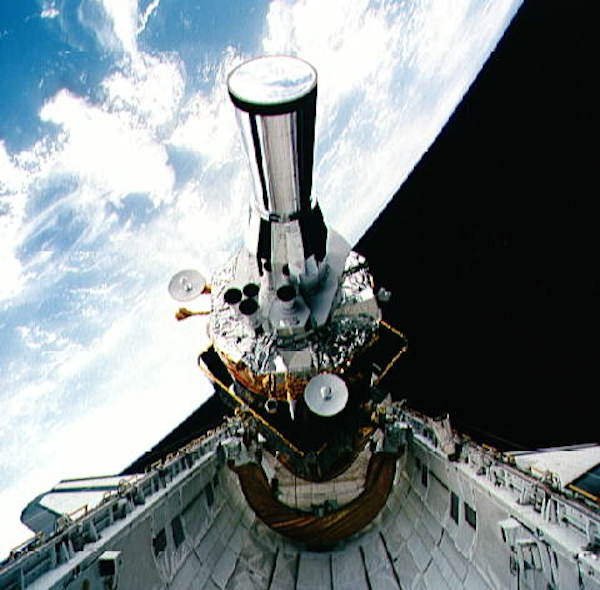
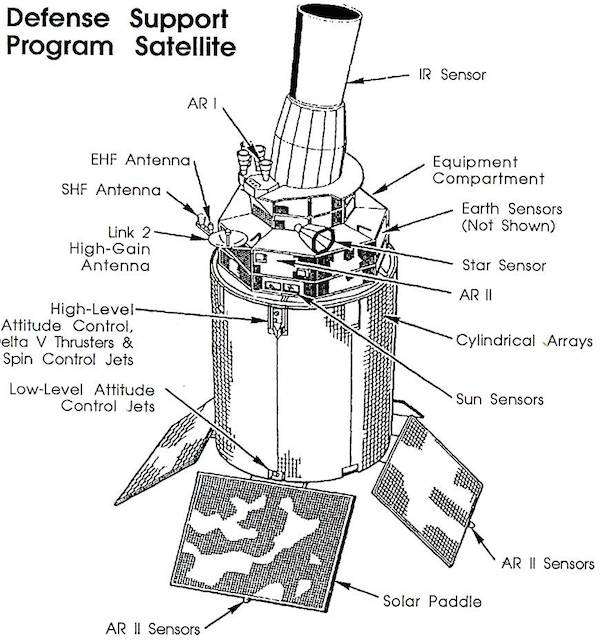
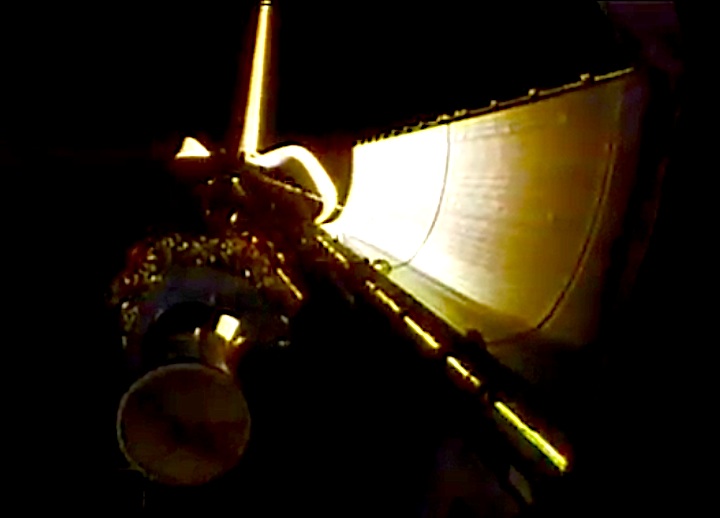
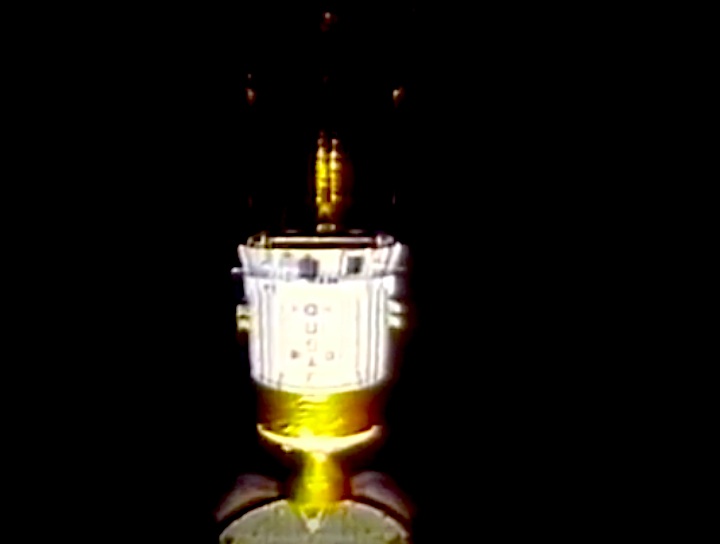
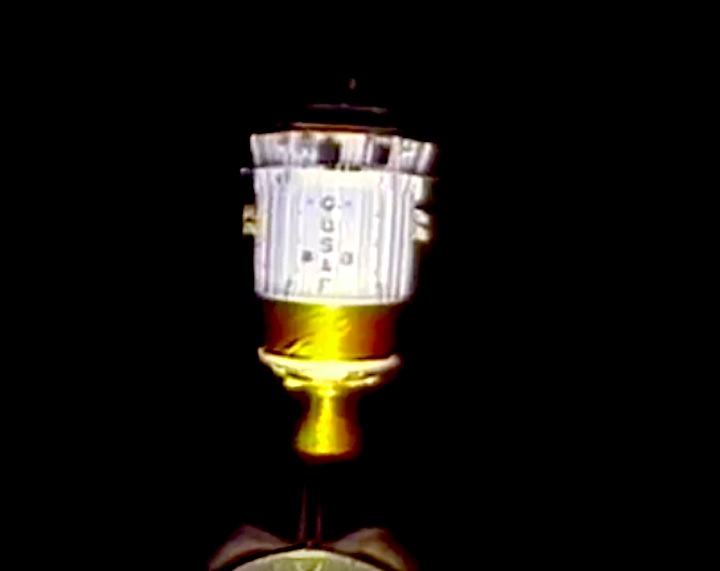
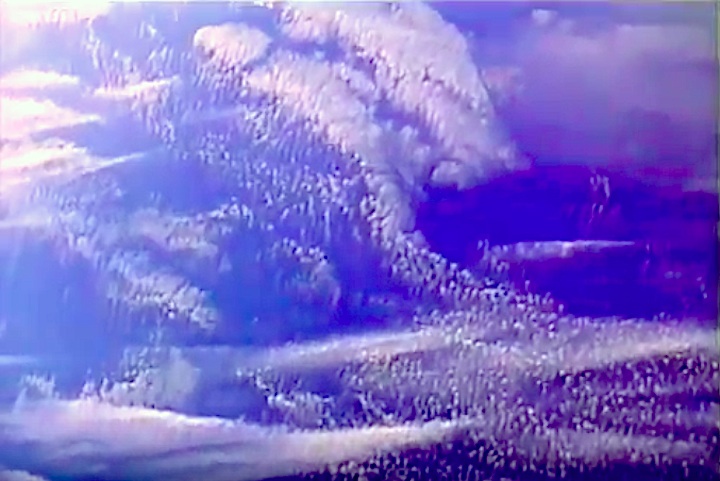
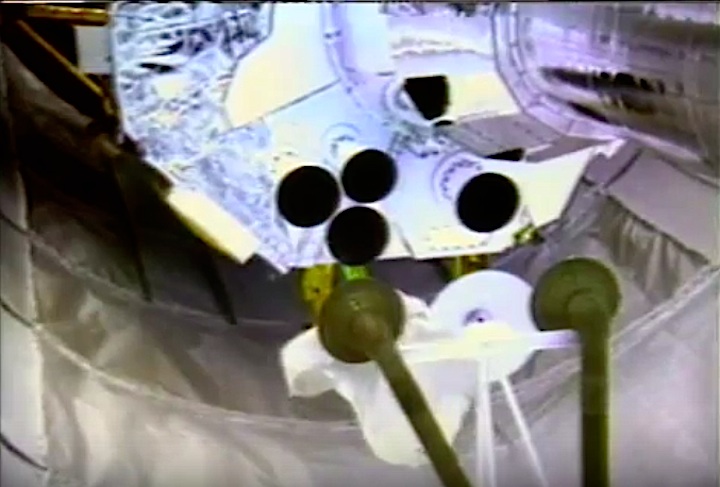
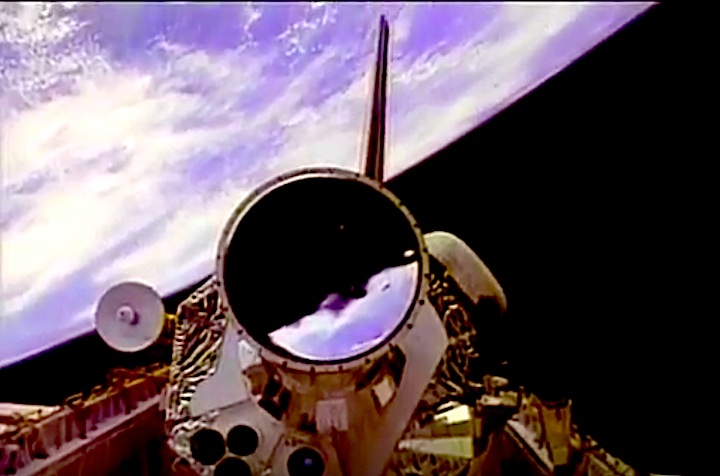
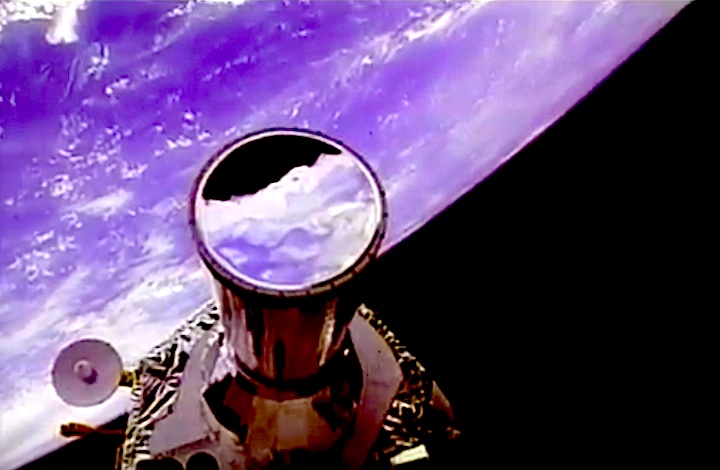
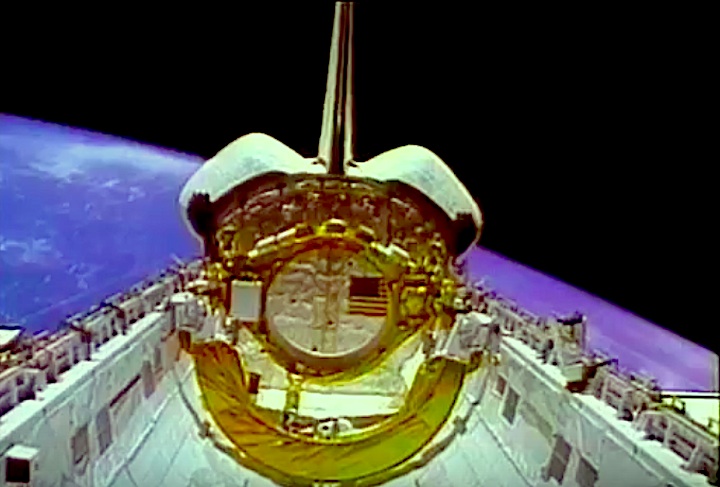
STS-44 Defense Support Program (DSP) / Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) spacecraft, with forward airborne support equipment (ASE) payload retention latch actuator released (foreground), is raised to a 29 degree predeployment position by the ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table in the payload bay (PLB) of Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104. Underneath the DSP / IUS combination, the umbilical boom is connected to the IUS. DSP components include Infrared (IR) sensor (top), AR I, SHF Antenna, EHF Antenna, Link 2 High-Gain Antenna, star sensor, and stowed solar paddles (box-like structure around the base). The Earth's limb and the blackness of space create the backdrop for this deployment scene.
---
Frams von STS-44 Atlantis Mission NASA-Video:









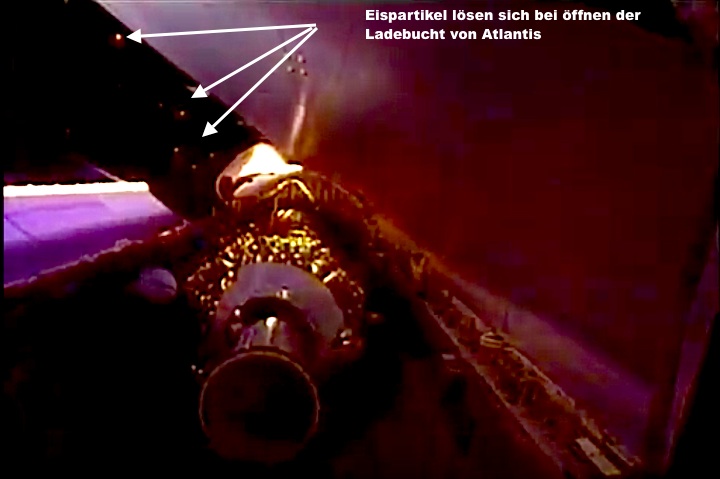
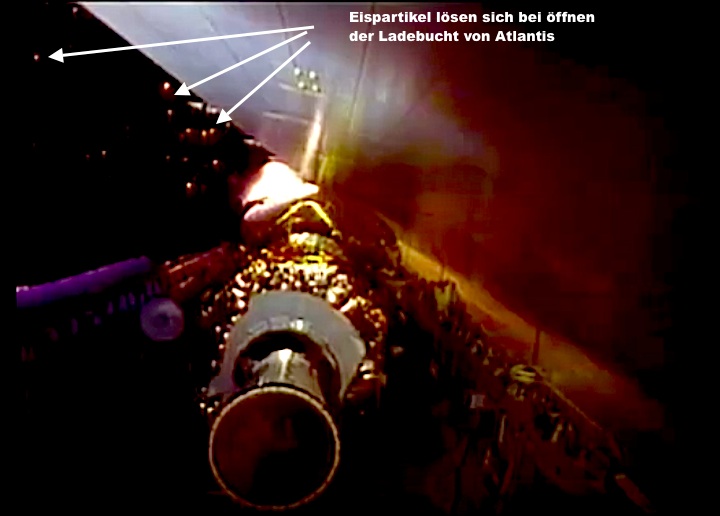
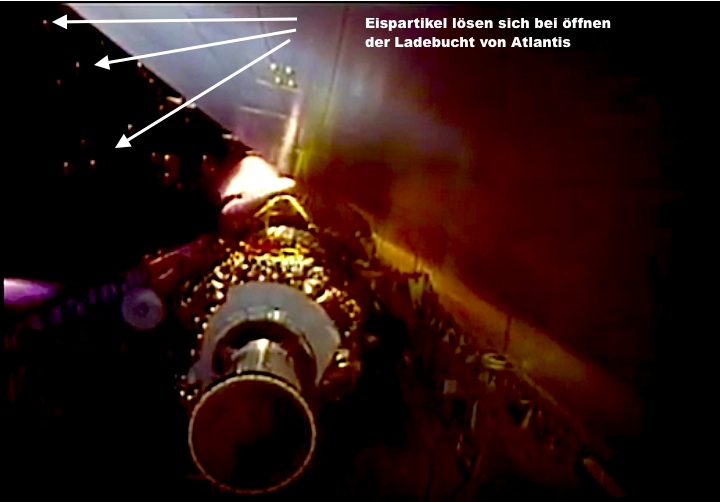

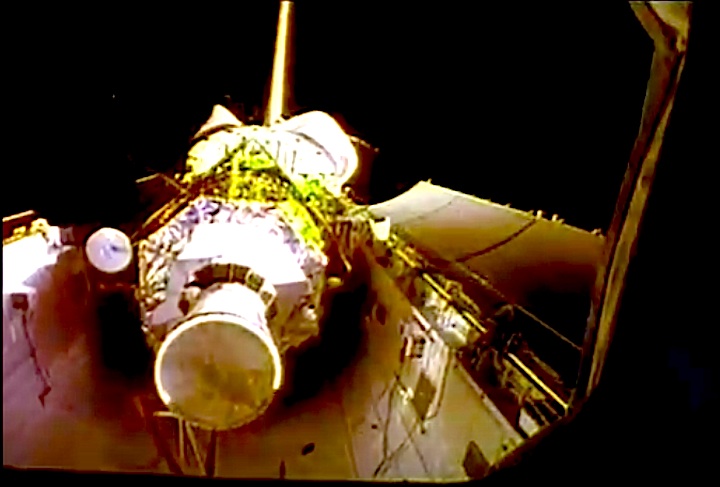
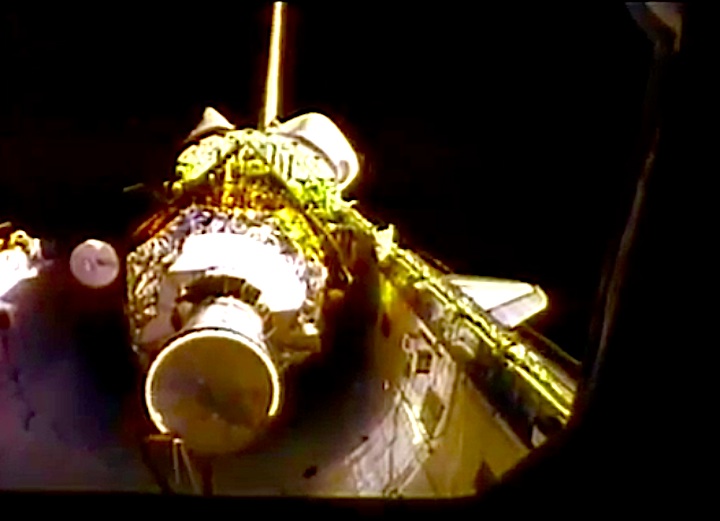
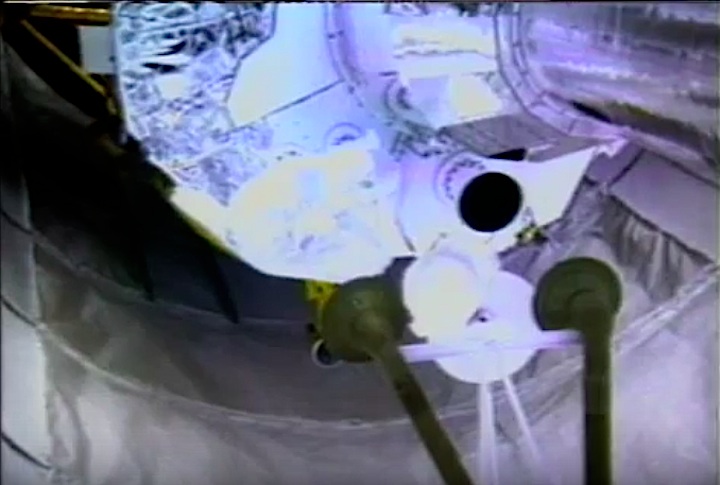














































Quelle: NASA
4101 Views

