.
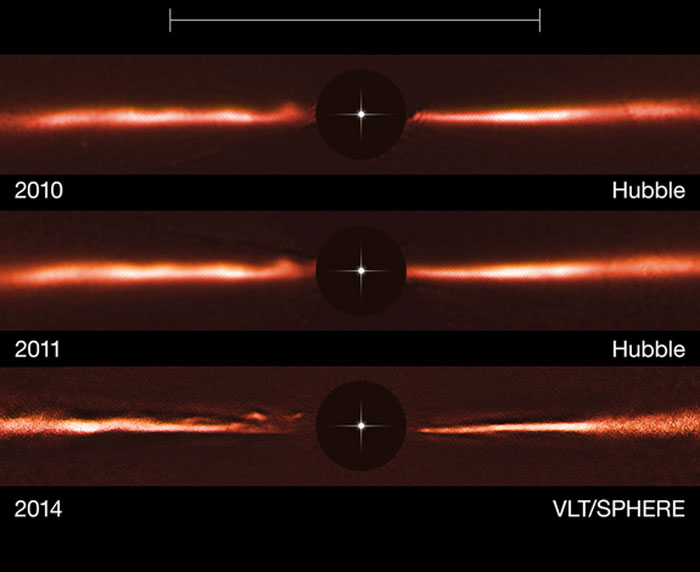
Researchers have spotted strange, fast-traveling ripples speeding around the disk of dust surrounding the young star AU Microscopii. Images from the Hubble Space Telescope and ESA's Very Large Telescope show the ripples' movement over the course of four years. The scale bar at the top of the image stretches the length of Neptune's orbit around the sun.
.
"We reprocessed images from the Hubble data and ended up with enough information to track the movement of these strange features over a four-year period," Christian Thalmann, a team member from ETH Zurich, in Switzerland, said in the statement. "By doing this, we found that the arches are racing away from the star at speeds of up to 40,000 km/h [24,855 mph]!"
The red dwarf star AU Microscopii, called AU Mic for short, is 32 light-years from Earth and half the mass of the sun. Because of its heavy, uneven disk of debris, which Earth observers see edge-on, researchers have kept a careful eye on the star to watch for planets coalescing from the dust (noticing fluffy, "dryer-lint" evidence of planetary precursors in 2007, for instance).
The newly spotted features are racing away at terrific speeds. The outermost ones are moving faster, and at least three appear to be moving quickly enough to escape the star's gravitational pull, officials said in the statement. The waves are likely not caused by the collision of large asteroidlike objects or changes in the star's gravity, the researchers said.
"One explanation for the strange structure links them to the star's flares," co-author Glenn Schneider, of Steward Observatory in Arizona, said in the statement. "AU Mic is a star with high flaring activity — it often lets off huge and sudden bursts of energy from on or near its surface."
"One of these flares could perhaps have triggered something on one of the planets — if there are planets — like a violent stripping of material which could now be propagating through the disk, propelled by the flare's force," Schneider said.
The scenario is still speculative; it will take a lot of continued observation with the Very Large Telescope and other instruments to work out exactly what's causing the racing waves. The research paper suggests the huge Acatama Large Millimeter/submillimeter array in Chile, for instance, to monitor the gas movement in the system. An accompanying "News and Views" column points out that the Gemini South telescope in Chile has also observed the system, but with a different field of view. Researchers may have to pool measurements from a number of perspectives to get to the bottom of the ripples.
"Cases such as that of AU Mic, in which disks can be imaged in great detail but any planets present are unseen, are likely to remain more common than directly imaged planets," Marshall Perrin, a researcher at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Maryland, who was not involved with the study, wrote in the "News and Views" column. "Lucky for astronomers, then, that circumstellar disks still turn out to have surprises such as the fast-moving dust features of AU Mic."
Quelle: SC
4628 Views
