.
A team of astronomers has used the High Dispersion Spectrograph on the Subaru Telescope to conduct spectroscopic observations of Sun-like "superflare" stars first observed and cataloged by the Kepler Space Telescope. The investigations focused on the detailed properties of these stars and confirmed that Sun-like stars with large starspots can experience superflares.
The team, made up of astronomers from Kyoto University, University of Hyogo, the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ), and Nagoya University, targeted a set of solar-type stars emitting very large flares that release total energies 10-10000 times greater than the biggest solar flares. Solar flares are energetic explosions in the solar atmosphere and are thought to occur by intense releases of magnetic energy around the sunspots. Large flares often cause massive bursts of high-speed plasma called coronal mass ejections (CMEs), can lead to geomagnetic storms on Earth. Such storms can have severe impacts on our daily life by affecting such systems as communications and power grids.
This work follows up on observations made in 2012 (Maehara et al. Nature on 2012 May 24), where the team reported finding several hundred superflares on solar-type stars by analyzing stellar observation data from Kepler Space Telescope. This discovery was very important since it enabled the astronomers to conduct statistical analysis of superflares for the first time. However, more detailed observations were needed to investigate detailed properties of superflare stars and whether such massive flares can occur on ordinary single stars similar to our Sun.
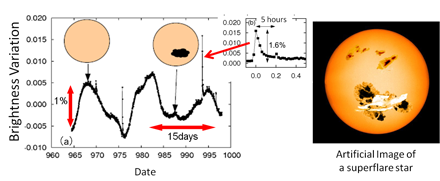
Figure 1: Left: The brightness variation of solar-type superflare stars (from Kepler data). In addition to the sudden brightenings caused by flares, quasi-periodic brightness variations with periods of about 15 days are seen. Right: An artificial image of a superflare star seen with visible light. This figure shows a large superflare (shown in white) occurring in the large starspot area. (Credit: Kyoto University)
.
Based on the initial discovery, the team carried out spectroscopic observations on 50 solar-type superflare stars selected from the Kepler Space Telescope's data. From the investigation of the detailed properties of spectral lines, the team obtained the following results:
More than half the observed 50 stars show no evidence of binarity (that is, they are not binary stars). The team confirmed the characteristics of the target stars as similar to those of the Sun.
On the basis of the Kepler data, superflare stars show somewhat regular, periodic changes in their brightnesses. The typical periods range from one day to a few tens of days. Such variations are explained by the rotation of the star and its starspots. As shown in Figure 1, the stars seem to become dimmer when their starspots are on their visible sides. Moreover, the timescales of the brightness variations should correspond to the stars' rotation speeds. Spectroscopic observations allow observers to estimate the rotation velocity from the broadening of absorption lines (Figure 2), and confirm that a velocity derived from spectroscopic data matches the brightness variation timescale as the star rotates. In addition, the measured rotation velocity of some target superflare stars is as slow as that of the Sun.
Based on solar observations, astronomers know that if there are large dark star spots on a stellar surface, the "core depth" (the depth and width of a spectral line) of the Ca II 854.2[nm] (ionized Calcium) absorption line becomes shallow. Using this, they investigated the core depth of Ca II 854.2 [nm] line, and found that superflare stars have large starspots compared to sunspots (Figure 3).
The results of these observations and analysis confirm that stars similar to the Sun can have superflares if they have large starspots. In the future, in addition to the continuing spectroscopic observations with Subaru Telescope, the team will conduct observations with the Kyoto University's Okayama 3.8m telescope, which is now under construction. This will allow them to investigate more detailed properties and changes in long-term activity of superflare stars.
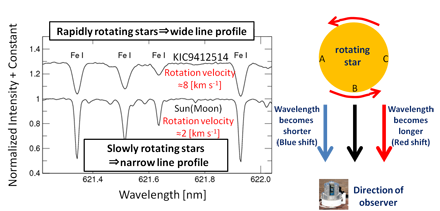
Figure 2: Left: Four neutral iron (Fe I) absorption lines are shown. As mentioned above, spectral lines show some broadening because of the Doppler effect on the light from the rotating stellar surface. Slowly rotating stars like the Sun have a narrow line profile, while rapidly rotating stars have a wide line profile. Measuring these broadenings allows an estimate of the stellar rotation velocity. Right: The wavelength of light from the surface of a rotating star shifts because of the Doppler effect. For example, the wavelength of light from point A becomes a bit short (is blue-shifted) since this point is approaching us (the observer). By contrast, the wavelength of light from point C is a bit long (is red-shifted) since this point moves away from us. The wavelengths of light from point B have no shifts since this point moves perpendicular to the line of sight. Finally, this line-shift effect results in broadening of spectral lines. (Credit: Kyoto University)
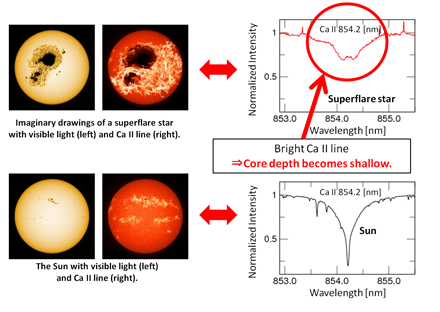
Figure 3: Left: The bottom two images show the Sun in visible light (left) and the Ca II line (right) (These two pictures are from the Big Bear Solar Observatory). The upper two images are imaginary drawings of a superflare star in visible light (left) and the Ca II line (right) where the areas around the starspots are bright. Right:Absorption line of Ca II 854.2[nm] (ionized calcium). Superflare stars (the upper two spectra, shown in red and blue) have a shallow (bright) core depth compared to the Sun (the bottom spectrum, in black). This suggests that these two superflare stars have large starspots. (Credit: Kyoto University)
Research Team Members
Yuta Notsu (Department of Astronomy, Kyoto University)
Satoshi Honda (Center for Astronomy, University of Hyogo)
Hiroyuki Maehara (Okayama Astrophysical Observatory, NAOJ)
Shota Notsu (Department of Astronomy, Kyoto University)
Takuya Shibayama (Solar-Terrestrial Environment Laboratory, Nagoya University)
Daisaku Nogami (Department of Astronomy, Kyoto University)
Kazunari Shibata (Kwasan and Hida Observatories, Kyoto University)
This research is based on the following two research papers.
Paper 1:
"High Dispersion Spectroscopy of Solar-type Superflare Stars. I. Temperature, Surface Gravity, Metallicity, and v sin i"
Paper 2:
"High Dispersion Spectroscopy of Solar-type Superflare Stars. II. Stellar Rotation, Starspots, and Chromospheric Activities"
Authors of both papers:
Notsu, Y., Honda, S., Maehara, H., Notsu, S., Shibayama, T., Nogami, D., and Shibata, K.
To be published on Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan June 25, 2015 issue (Online versions are published in February 22, 2015 and March 29, 2015, respectively)
This work was supported by the Grant-in-Aids from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (No.25287039, 26400231, and 26800096).
Quelle: Subaro Telescope
5283 Views
