.

Mission Highlights
At 5 1/2 minutes after liftoff, John Swigert, Fred Haise and James Lovell felt a little vibration. Then the center engine of the S-II stage shut down two minutes early. This caused the remaining four engines to burn 34 seconds longer than planned, and the S-IVB third stage had to burn nine seconds longer to put Apollo 13 in orbit.
Days before the mission, backup lunar module pilot, Charles Duke, inadvertently exposed the crew to German measles. Command Module Pilot Ken Mattingly had no immunity to measles and was replaced by backup command module pilot, John Swigert.
Ground tests before launch indicated the possibility of a poorly insulated supercritical helium tank in the lunar module, or LM, descent stage, so the flight plan was modified to enter the LM three hours early in order to obtain an onboard readout of helium tank pressure.
The No. 2 oxygen tank, serial number 10024X-TA0009, had been previously installed in the service module of Apollo 10, but was removed for modification and damaged in the process. The tank was fixed, tested at the factory, installed in the Apollo 13 service module and tested again during the Countdown Demonstration Test at NASA's Kennedy Space Center beginning March 16, 1970. The tanks normally are emptied to about half full. No. 1 behaved all right, but No. 2 dropped to only 92 percent of capacity. Gaseous oxygen at 80 pounds per square inch was applied through the vent line to expel the liquid oxygen, but to no avail. An interim discrepancy report was written, and on March 27, two weeks before launch, detanking operations resumed. No. 1 again emptied normally, but No. 2 did not. After a conference with contractor and NASA personnel, the test director decided to "boil off" the remaining oxygen in No. 2 by using the electrical heater within the tank. The technique worked, but it took eight hours of 65-volt DC power from the ground support equipment to dissipate the oxygen. Due to an oversight in replacing an underrated component during a design modification, this turned out to severely damage the internal heating elements of the tank.
Apollo 13 was to be the third lunar landing attempt, but the mission was aborted after rupture of service module oxygen tank. Still, it was classified as a "successful failure" because of the experience gained in rescuing the crew. The mission's spent upper stage successfully impacted the moon.
During the first two days, the crew ran into a couple of minor surprises, but generally Apollo 13 was looking like the smoothest flight of the program. At 46 hours, 43 minutes Joe Kerwin, the capsule communicator, or Capcom, on duty, said, "The spacecraft is in real good shape as far as we are concerned. We're bored to tears down here." It was the last time anyone would mention boredom for a long time.
At 55 hours, 46 minutes, as the crew finished a 49-minute TV broadcast showing how comfortably they lived and worked in weightlessness, Lovell said, "This is the crew of Apollo 13 wishing everybody there a nice evening, and we're just about ready to close out our inspection of Aquarius and get back for a pleasant evening in Odyssey. Good night."
Nine minutes later, oxygen tank No. 2 blew up, causing the No. 1 tank to also fail. The command module's normal supply of electricity, light and water was lost, and they were about 200,000 miles from Earth.
The message came in the form of a sharp bang and vibration at 9:08 p.m. April 13. Swigert saw a warning light that accompanied the bang and said, "Houston, we've had a problem here." Lovell came on and told the ground that it was a main B bus undervolt.
Next, the warning lights indicated the loss of two of three fuel cells, which were the spacecraft's prime source of electricity. With warning lights blinking, one oxygen tank appeared to be completely empty and there were indications that the oxygen in the second tank was rapidly depleting.
Thirteen minutes after the explosion, Lovell happened to look out of the left-hand window and saw the final evidence pointing toward potential catastrophe. "We are venting something out into the... into space," he reported to Houston. Capcom Jack Lousma replied, "Roger, we copy you venting." Lovell said, "It's a gas of some sort." It was oxygen gas escaping at a high rate from the second, and last, oxygen tank.
The first thing the crew did, even before discovering the oxygen leak, was try to close the hatch between the CM and the LM. They reacted spontaneously, similar to a submarine crew, closing the hatches to limit the amount of flooding. First Swigert, and then Lovell, tried to lock the reluctant hatch, but the stubborn lid wouldn't stay shut. Exasperated and realizing that there wasn't a cabin leak, they strapped the hatch to the CM couch.
The pressure in the No. 1 oxygen tank continued to drift downward; passing 300 pounds per square inch, then headed toward 200 pounds per square inch. Months later, after the accident investigation was complete, it was determined that when the No. 2 tank blew up, it either ruptured a line on the No. 1 tank or caused one of the valves to leak. When the pressure reached 200 pounds per square inch, the crew and ground controllers knew they would lose all oxygen, which meant that the last fuel cell also would die.
At one hour, 29 seconds after the bang, Lousma said after instructions from Flight Director Glynn Lunney, "It is slowly going to zero, and we are starting to think about the LM lifeboat." Swigert replied, "That's what we have been thinking about too."
Ground controllers in Houston faced a formidable task. Completely new procedures had to be written and tested in the simulator before being passed up to the crew. The navigation problem had to be solved; essentially how, when and in what attitude to burn the LM descent engine to provide a quick return home.
With only 15 minutes of power left in the CM, Lousma told the crew to make their way into the LM. Haise and Lovell quickly floated through the tunnel, leaving Swigert to perform the last chores in the command module. The first concern was to determine if there were enough consumables to get home. The LM was built for only a 45-hour lifetime and it needed to be stretch to 90. Oxygen wasn't a problem. The full LM descent tank alone would suffice. In addition, there were two ascent-engine oxygen tanks and two backpacks full of oxygen that would never be used on the lunar surface. Two emergency bottles on top of those packs each had six or seven pounds in them. At LM jettison just before re-entry 28.5 pounds of oxygen remained, more than half of what was available after the explosion.
Power also was a concern. There were 2,181 ampere hours in the LM batteries. Ground controllers carefully worked out a procedure where the CM batteries were charged with LM power. All noncritical systems were turned off and energy consumption was reduced to 1/5, which resulted in having 20 percent of LM electrical power left when Aquarius was jettisoned. There was one electrical close call during the mission. One of the CM batteries vented with such force that it momentarily dropped off the line. Had the battery failed, there would have been insufficient power to return the ship to Earth.
Water was the main consumable concern. It was estimated that the crew would run out of water about five hours before Earth re-entry, which was calculated at around 151 hours. However, data from Apollo 11, which had not sent its LM ascent stage crashing into the moon as in subsequent missions, showed that its mechanisms could survive seven or eight hours in space without water cooling. The crew conserved water. They cut down to six ounces each per day, 1/5 of normal intake, and used fruit juices; they ate hot dogs and other wet-pack foods when they ate at all. The crew became dehydrated throughout the flight and set a record that stood up throughout Apollo: Lovell lost 14 pounds and the crew lost a total of 31.5 pounds, nearly 50 percent more than any other crew. Those stringent measures resulted in the crew finishing with 28.2 pounds of water, about 9 percent of the total.
Removal of carbon dioxide also was a concern. There were enough lithium hydroxide canisters, which remove carbon dioxide from the spacecraft, but the square canisters from the command module were not compatible with the round openings in the lunar module environmental system. There were four cartridges from the LM and four from the backpacks, counting backups. However, the LM was designed to support two men for two days and was being asked to care for three men for about four days. After a day and a half in the LM, a warning light showed that the carbon dioxide had built up to a dangerous level. Mission control devised a way to attach the CM canisters to the LM system by using plastic bags, cardboard and to tape all materials carried on board.
One of the big questions was, "How to get back safely to Earth?" The LM navigation system wasn't designed to help in this situation. Before the explosion at 30 hours, 40 minutes, Apollo 13 had made the normal midcourse correction, which would take it out of a free-return-to-Earth trajectory and put it on a lunar landing course. Now the task was to get back on a free-return course. The ground computed a 35-second burn and fired it five hours after the explosion. As they approached the moon, another burn was computed; this time a long five-minute burn to speed up the return home. It took place two hours after rounding the far side of the moon.
The command module navigational platform alignment was transferred to the LM, but verifying alignment was difficult. Ordinarily the alignment procedure uses an onboard sextant device, called the Alignment Optical Telescope, or AOT, to find a suitable navigation star. Then with the help of an onboard computer, it verifies the guidance platform's alignment. However, due to the explosion, a swarm of debris from the ruptured service module made it impossible to sight real stars. An alternate procedure was developed to use the sun as an alignment star. Lovell rotated the spacecraft to the attitude Houston had requested and when he looked through the AOT, the sun was just where it was expected. The alignment with the sun proved to be less than 1/2 a degree off. The ground and crew then knew they could do the five-minute P.C. + 2 burn with assurance, cutting the total time of their voyage to about 142 hours. At 73 hours, 46 minutes into the mission, the air-to-ground transcript describes the event:
Lovell: OK. We got it. I think we got it. What diameter was it?
Haise: Yes. It's coming back in. Just a second.
Lovell: Yes, yaw's coming back in. Just about it.
Haise: Yaw is in....
Lovell: What have you got?
Haise: Upper-right corner of the sun....
Lovell: We've got it! If we raised our voices, I submit it was justified.
Flight Director Gerald Griffin, a man not easily shaken, recalled: "Some years later I went back to the log and looked up that mission. My writing was almost illegible, I was so damned nervous. And I remember the exhilaration running through me: My God, that's the last hurdle - if we can do that, I know we can make it. It was funny because only the people involved knew how important it was to have that platform properly aligned." Yet Griffin barely mentioned the alignment in his change-of-shift briefing - "That check turned out real well" is all he said an hour after his penmanship failed him.
The trip was marked by discomfort beyond the lack of food and water. Sleep was almost impossible because of the cold. When the electrical systems were turned off, the spacecraft lost an important source of heat. The temperature dropped to 38 degrees Fahrenheit and condensation formed on all the walls.
The most remarkable achievement of mission control was quickly developing procedures for powering up the CM after its long, cold sleep. Flight controllers wrote the documents for this innovation in three days, instead of the usual three months. The command module was cold and clammy at the start of power-up. The walls, ceiling, floor, wire harnesses and panels were all covered with droplets of water. It was suspected conditions were the same behind the panels. The chances of short circuits caused apprehension, but thanks to the safeguards built into the command module after the disastrous Apollo 1 fire in January 1967, no arcing took place. Lovell recalled the descent to Earth, "The droplets furnished one sensation as we decelerated in the atmosphere: it rained inside the CM."
Four hours before landing, the crew shed the service module; mission control had insisted on retaining it until then because everyone feared what the cold of space might do to the un-sheltered CM heat shield. Photos of the service module showed one whole panel missing and wreckage hanging out, it was a mess as it drifted away. Three hours later, the crew left the lunar module Aquarius and then splashed down gently in the Pacific Ocean near Samoa.
After an intensive investigation, the Apollo 13 Accident Review Board identified the cause of the explosion. In 1965, the CM had undergone many improvements that included raising the permissible voltage to the heaters in the oxygen tanks from 28 to 65 volts DC. Unfortunately, the thermostatic switches on these heaters weren't modified to suit the change. During one final test on the launch pad, the heaters were on for a long period of time. This subjected the wiring in the vicinity of the heaters to very high temperatures (1000 F), which have been subsequently shown to severely degrade teflon insulation. The thermostatic switches started to open while powered by 65 volts DC and were probably welded shut. Furthermore, other warning signs during testing went unheeded and the tank, damaged from eight hours of overheating, was a potential bomb the next time it was filled with oxygen. That bomb exploded on April 13, 1970 - 200,000 miles from Earth.
.
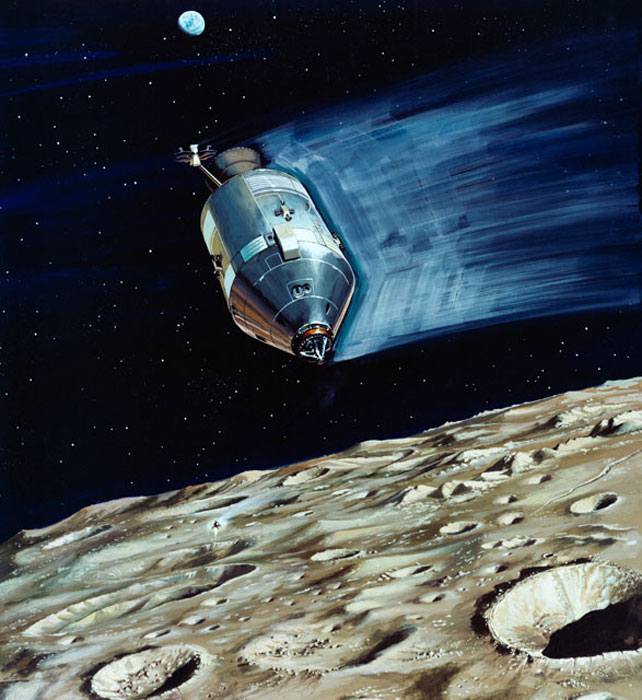

S70-31898 (March 1970) --- A North American Rockwell artist's concept depicting the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) descending to the Fra Mauro landing site as the Command and Service Module (CSM) remains in lunar orbit. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, will photograph the LM's descent from the CSM. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, will descend in the LM to explore the moon. Apollo 13 will be NASA's third lunar landing mission.
-
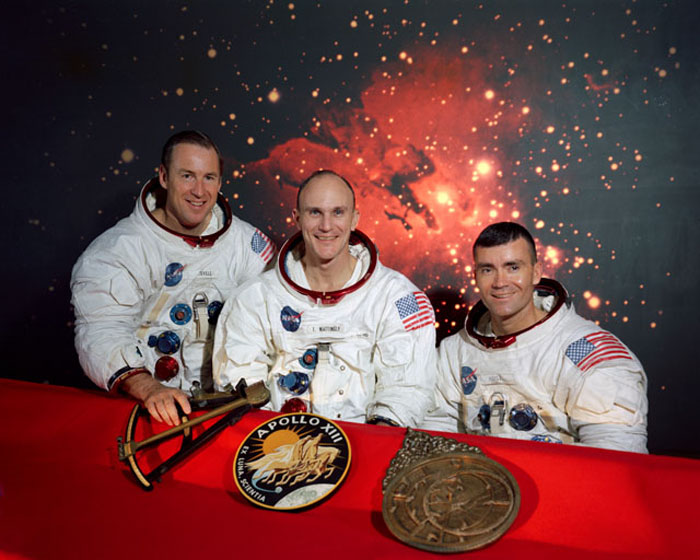

S69-62224 (December 1969) --- The members of the prime crew of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission (left to right) are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. They are seated in front of a scene of the Lagoon Nebula, with the mission insignia and two items of early navigation in the foreground. Represented in the Apollo 13 emblem (center) is Apollo, the sun god of Greek mythology, symbolizing that the Apollo flights have extended the light of knowledge to all mankind. The Latin phrase Ex Luna, Scientia means "From the Moon, Knowledge." The Hindu astrolabe in Sanskrit (on right) was used to predict the position of celestial bodies before the invention of the octant (on left) was used in 1790 to determine the altitude of celestial bodies from aboard ship.
.
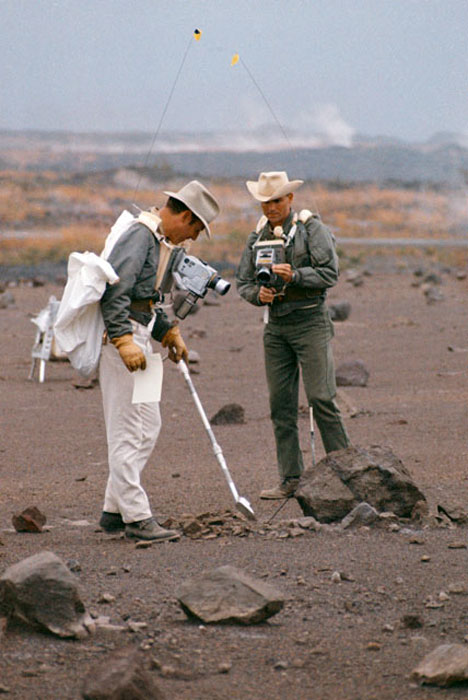

S70-20253 (December 1969) --- Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. (left) commander, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, carry out a simulation of a lunar traverse at Kilauea, Hawaii, site. Both crew members of NASA's third team of Moon explorers were carrying cameras and communications equipment during the simulated traverse. They maintained contact with men in the roles of spacecraft throughout the traverse. Lovell holds a scoop for the Apollo Lunar Hand Tools (ALHT) and a gnomon, also for the ALHT is deployed in front of Haise. The ALHT carrier is at left background, (almost obscured by Lovell).
.
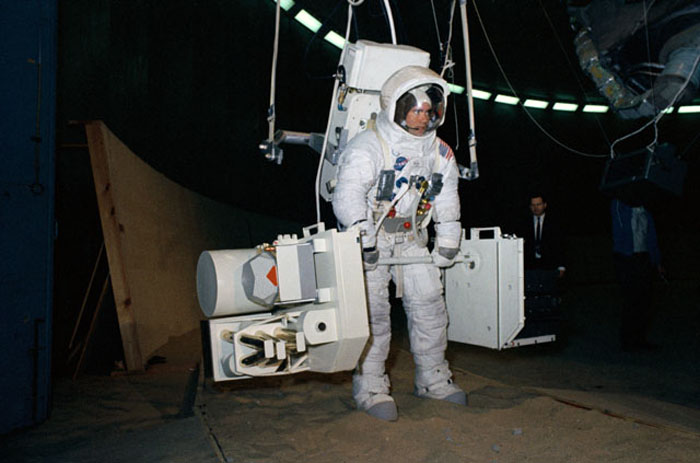

S70-24009 (19 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., Apollo 13 lunar module pilot, trains for his scheduled April lunar space walk at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Haise carries a training version of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), while connected to a "Six Degrees of Freedom" simulator. Out of frame is astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander, who will share the lunar extravehicular activity (EVA) with Haise. EDITOR'S NOTE: In April 1970 the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) experienced an explosion en route to the Moon. The three-man crew was forced to circumnavigate the Moon and return to Earth.
.

S70-24010 (17 Jan. 1970) --- The three prime crew members of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission stand by to participate in water egress training in a water tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). They are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., (left) commander; Fred W. Haise Jr., (right) lunar module pilot; and Thomas K. Mattingly II (in background, obscured by Haise), command module pilot.
.
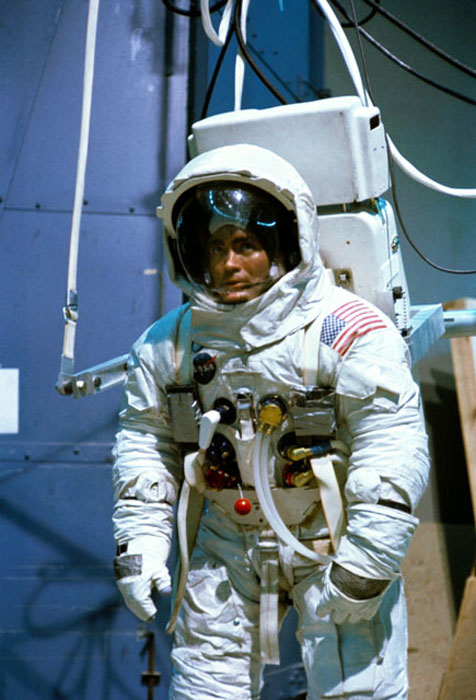

S70-24012 (19 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in lunar surface simulation training at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Haise is attached to a Six Degrees of Freedom Simulator.
.
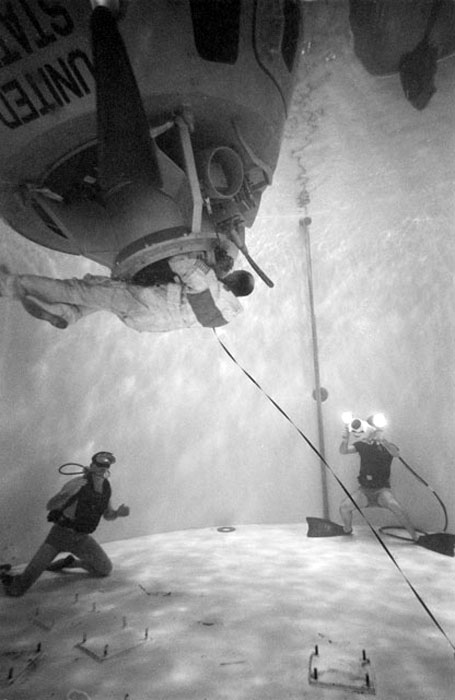

S70-24016 (17 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in water egress training in a water tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center.
-
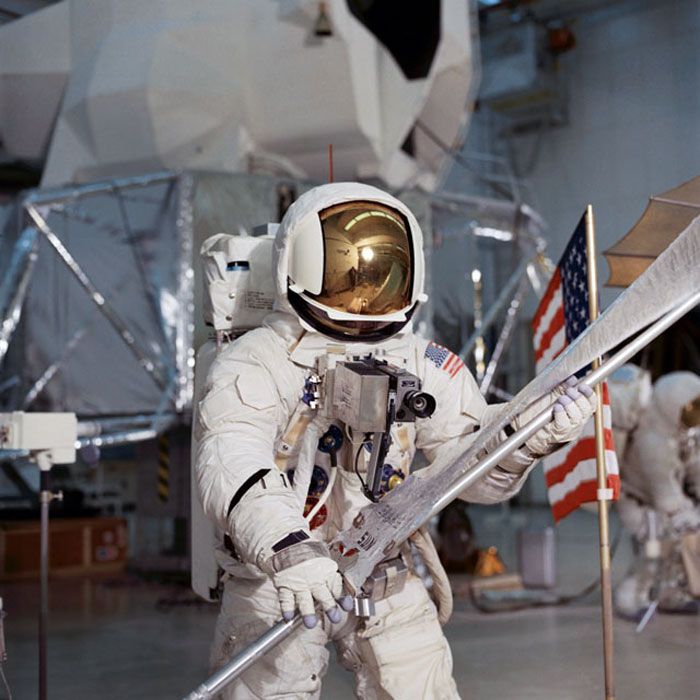

S70-27034 (4 Feb. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, simulates lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) during training exercises in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Flight Crew Training Building (FCTB). Haise, wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), is holding a Solar Wind Composition (SWC) experiment.
.
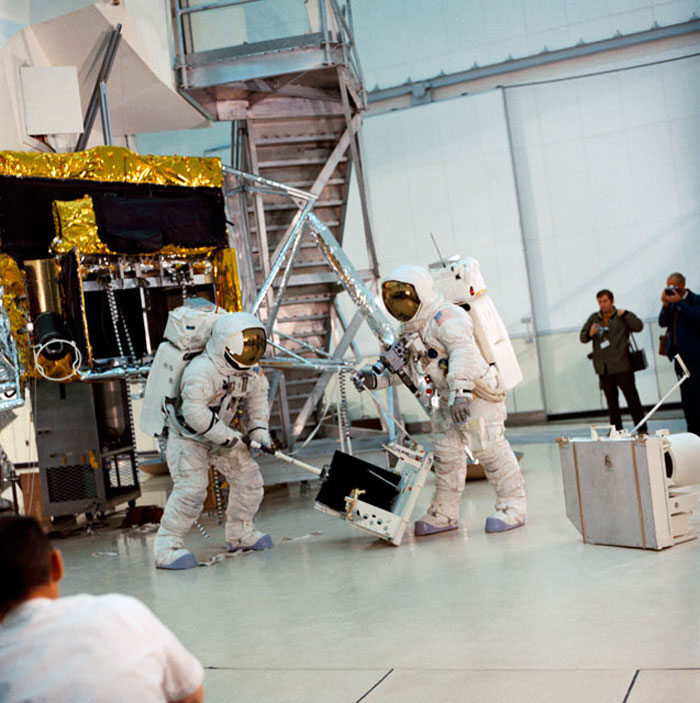

S70-27036 (4 Feb. 1970) --- Two crew men of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission simulate lunar surface Extravehicular Activity (EVA) during training exercises in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Flight Crew Training Building. They are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
.
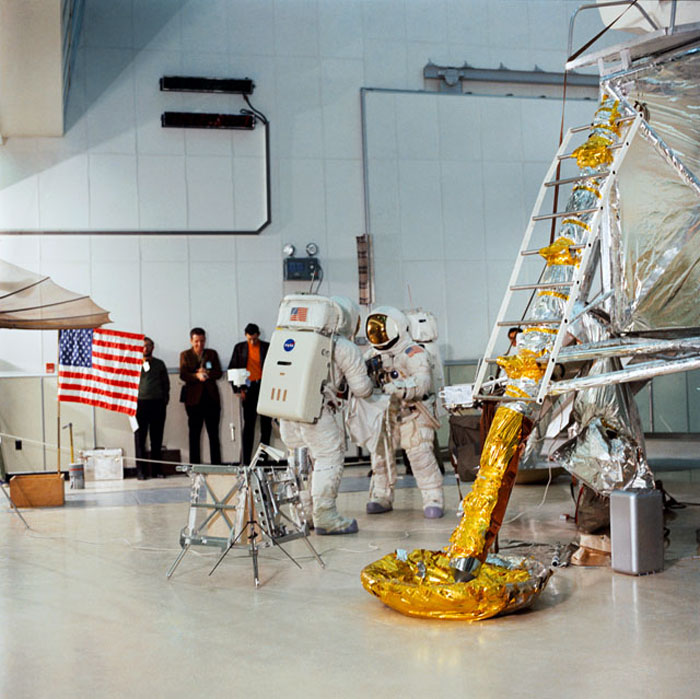

S70-27038 (4 Feb. 1970) --- Two crew men of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission simulate lunar surface Extravehicular Activity (EVA) during training exercises in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Flight Crew Training Building. They are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. (on left, back to camera) commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
.
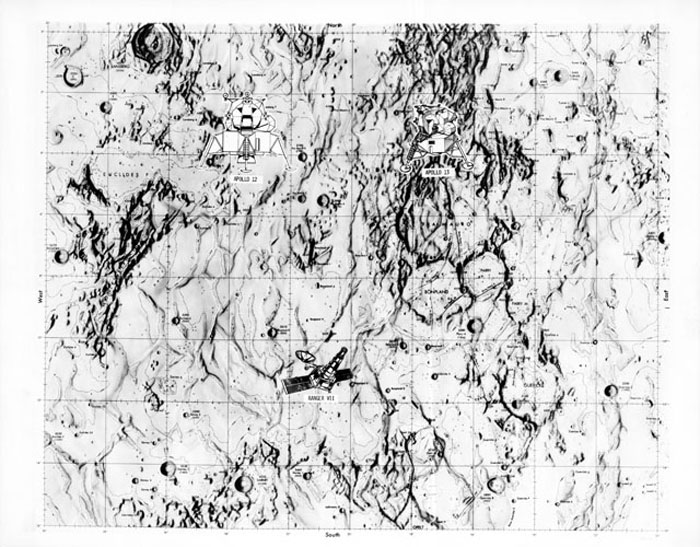
S70-28115 (January 1970) --- This overlay map of terrain on the lunar nearside shows the area of the landing site of the upcoming Apollo 13 mission, in relation to two previous NASA landings. The proposed Apollo 13 landing site is located in the highlands north of Fra Mauro. The coordinates of the planned site are 17.550 degrees west longitude and 3.617 degrees south latitude. The landing site of the Apollo 12 mission, which was highlighted by a lunar landing on November 19, 1969, is located approximately 105 nautical miles west of the Apollo 13 site. The landing site of the unmanned Ranger VII space vehicle, which impacted on the Moon on July 31, 1964, at 10.74 degrees south latitude and 20.7 degrees west longitude, is approximately 130 nautical miles south-southwest of the Apollo 13 site, and approximately 140 nautical miles south-southeast of the Apollo 12 site.
.
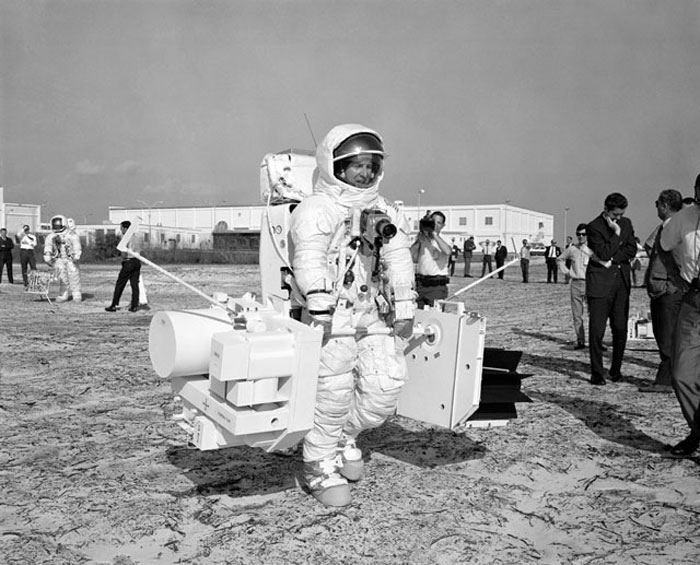

S70-29672 (28 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in a walk-through of the extravehicular activity timeline at the Kennedy Space Center. Here, Lovell, using mock-ups, traverses with the two subpackages of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP). Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, is standing in the left background.
.
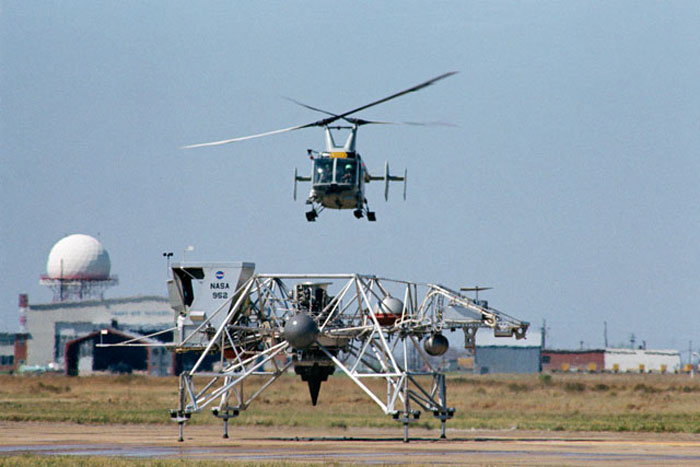

S70-30534 (9 March 1970) --- A Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV), piloted by astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., sets down on the runway at the conclusion of a test flight at Ellington Air Force Base. Lovell is the commander of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Lovell used the LLTV to practice lunar landing techniques in preparation for his scheduled mission. Lovell will be at the controls of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) when it lands on the moon in the highlands just north of Fra Mauro. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, will remain with the Apollo 13 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Lovell and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, descend in the LM to explore the moon. A hovering helicopter watches the LLTV landing.
.
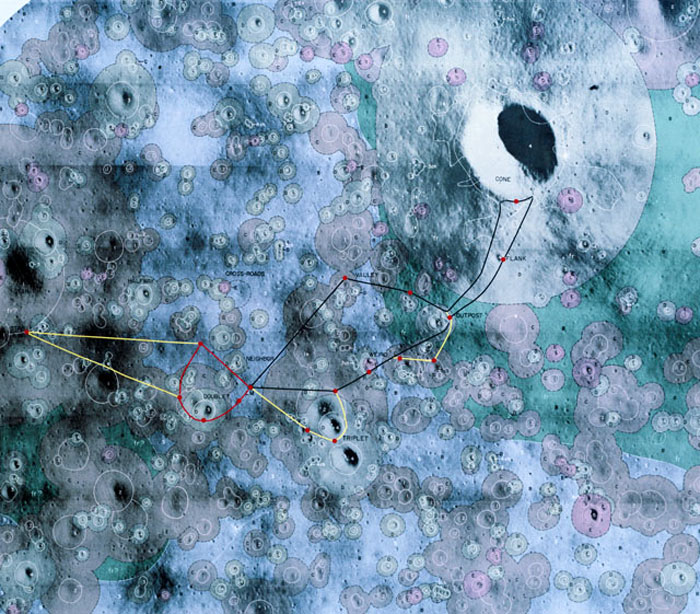

S70-30828 (March 1970) --- A photographic illustration of the Fra Mauro area showing the scheduled traverses planned for the extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. The larger red dot marked LM indicates the landing point of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM). The red line shows the path of the first EVA traverse. The second EVA traverse is marked with a black line. The yellow line denotes the extension of each traverse in the event a decision is made to do so. The red dots indicate the points of interest for samples and for observation. Participating in the Apollo 13 EVA will be astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II , command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
.
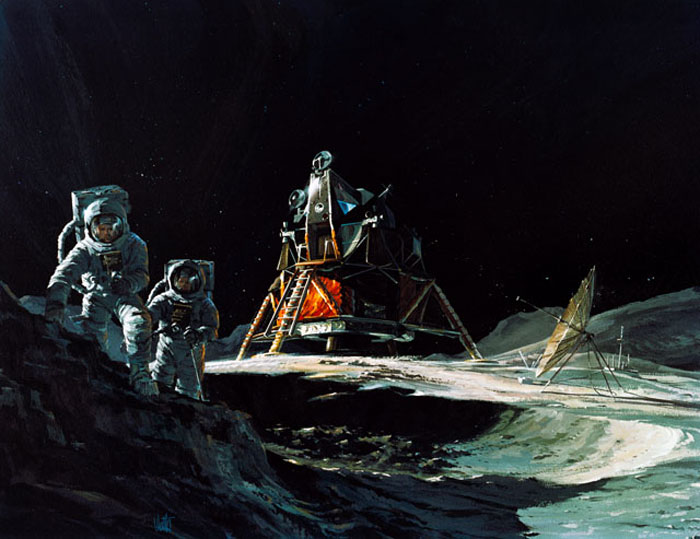

S70-31774 (March 1970) --- An artist's concept by Teledyne Ryan Aeronautical, San Diego, California, showing two Apollo 13 astronauts exploring the surface of the moon. In the center background is the Lunar Module (LM). Apollo 13 will land in the rugged highlands just north of Fra Mauro. The crew of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission will be astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Lovell and Haise are represented by the two men in this picture.
.

S70-34412 (4 April 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., Apollo 13 lunar module pilot, participates in simulation training in preparation for the scheduled lunar landing mission. He is in the Apollo Lunar Module Mission Simulator in the Kennedy Space Center's Flight Crew Training building.
.
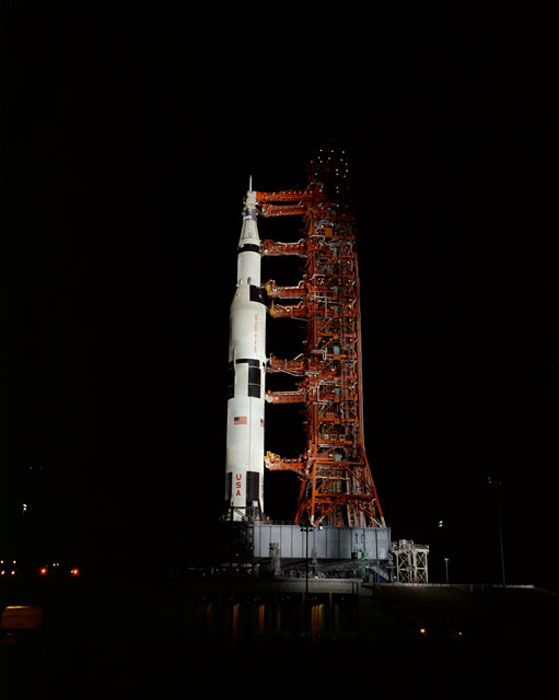

S70-32989 (24 March 1970) --- Nighttime, ground level view of Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), showing the Apollo 13 (Spacecraft 109/Lunar Module 7/Saturn 508) space vehicle during Countdown Demonstration Test (CDDT). The crew of NASA's third lunar landing mission includes astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The Apollo 13 launch has been scheduled for 2:13 p.m. (EST), April 11, 1970.
.
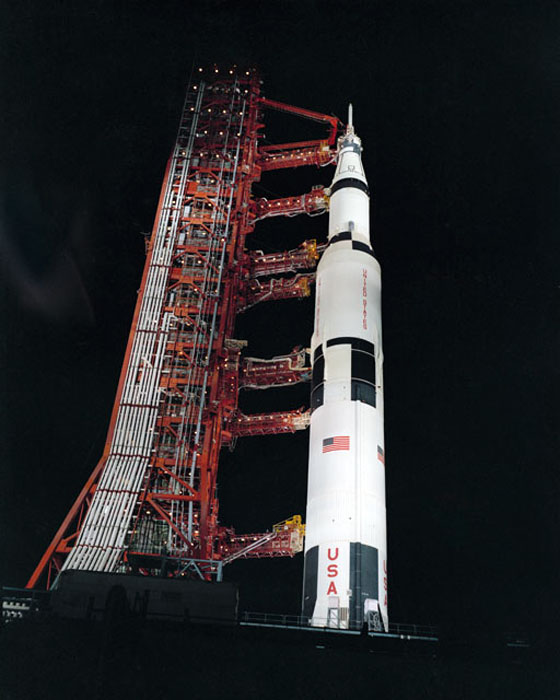

S70-32990 (24 March 1970) --- Nighttime, ground level view of Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), showing the Apollo 13 (Spacecraft 109/Lunar Module 7/Saturn 508) space vehicle during Countdown Demonstration Test (CDDT). The crew of NASA's third lunar landing mission includes astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The Apollo 13 launch has been scheduled for 2:13 p.m. (EST), April 11, 1970.
.
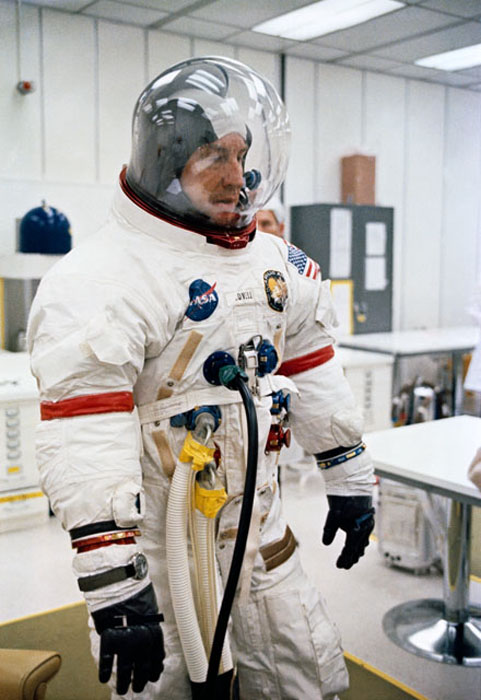

S70-34848 (11 April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander for NASA's Apollo 13 mission, undergoes space suit checks a few hours before launch. Other members of the crew are astronauts Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, and John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot. Swigert replaced astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II when it was learned he had been exposed to measles.
.
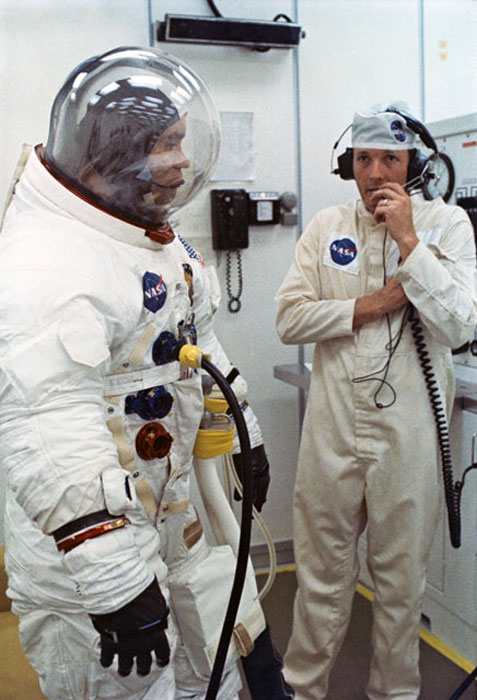

S70-34851 (11 April 1970) --- A space suit technician talks with astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot for NASA's Apollo 13 mission, during suiting up procedures at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Other members of the crew are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot. Swigert replaced astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II as a member of the crew when it was learned he had been exposed to measles.
.
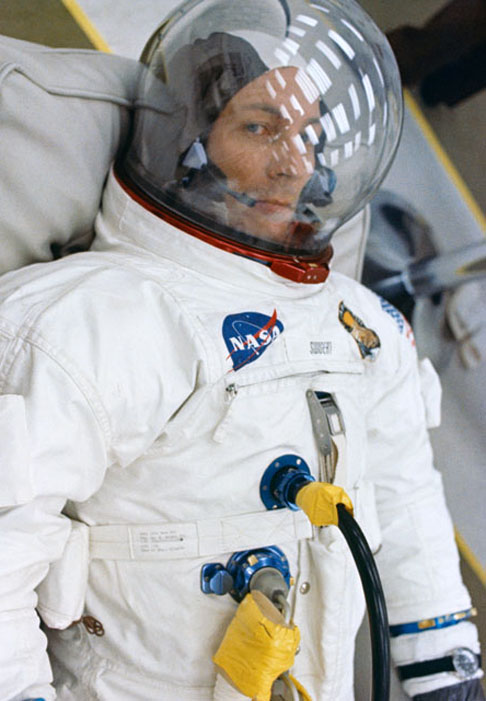

S70-34847 (11 April 1970) --- Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot for NASA's third lunar landing mission, appears to be relaxing in the suiting room at Kennedy Space Center prior to launch. Other members of the Apollo 13 crew include astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Swigert replaced astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II when it was discovered that Mattingly had been exposed to the measles.
.

S70-34685 (April 1970) --- A photographic replica of the plaque which the Apollo 13 astronauts will leave behind on the moon during their lunar landing mission. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, will descend to the lunar surface in the Lunar Module (LM) "Aquarius". Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The plaque will be attached to the ladder of the landing gear strut on the LM's descent stage. Commemorative plaques were also left on the moon by the Apollo 11 and Apollo 12 astronauts.
.


S70-34852 (11 April 1970) --- The Apollo 13 (Spacecraft 109/Lunar Module 7/Saturn 508) space vehicle is launched from Pad A Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), at 2:13 p.m. (EST), April 11, 1970. The crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) third lunar landing mission are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
-
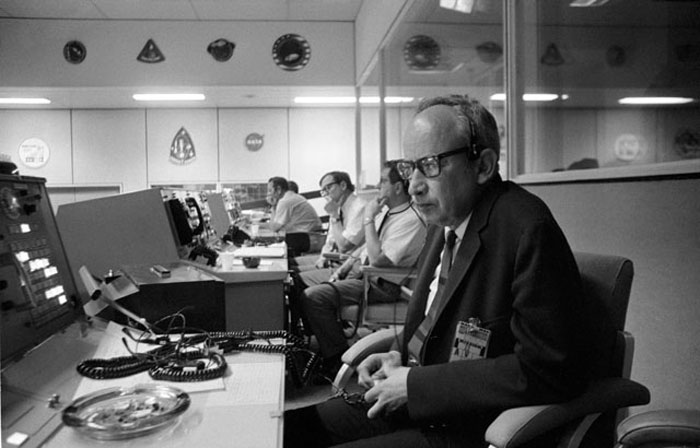

S70-34627 (11 April 1970) --- Sigurd A. Sjoberg, director of flight operations, at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), views the Apollo 13 liftoff from a console in the MSC Mission Control Center (MCC), Building 30. Apollo 13 lifted off at 1:13 p.m. (CST) April 11, 1970.
-

S70-34857 (13 April 1970) --- A telescopic photograph showing the Apollo 13 spacecraft in trans-lunar trajectory in the distant sky. Arrows point to the spacecraft, to the oxygen cloud, and to the expended Saturn V third stage. Apollo 13 was tracked at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) using a 16 inch Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope with an IO television camera with an S-20 type IO tube, mounted in place of the eyepiece. The TV camera information is stored first on a data disc and played back on a viewing monitor from which this photograph was taken.
.

S70-34902 (14 April 1970) --- Several persons important to the Apollo 13 mission, at consoles in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) of the Mission Control Center (MCC). Seated at consoles, from left to right, are astronauts Donald K. Slayton, director of flight crew operations; astronaut Jack R. Lousma, Shift 3 spacecraft communicator; and astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 13 backup crew. Standing, left to right, are astronaut Tom K. Mattingly II, who was replaced as Apollo 13 command module pilot after it was learned he may come down with measles, and astronaut Vance D. Brand, Shift 2 spacecraft communicator. Several hours earlier, in the late evening hours of April 13, crew members of the Apollo 13 mission reported to MCC that trouble had developed with an oxygen cell on their spacecraft.
.
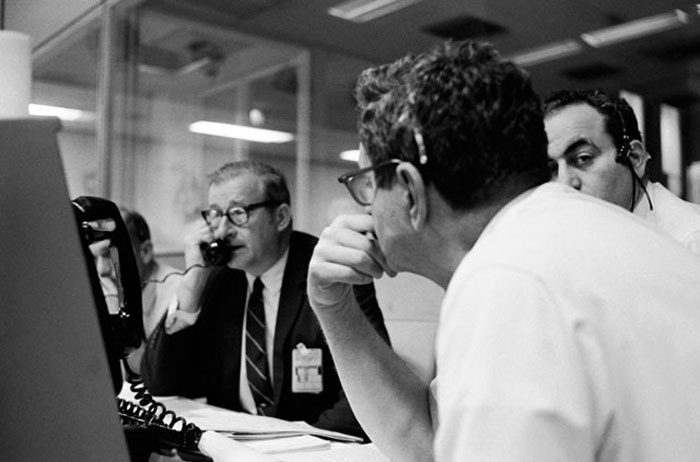

S70-34903 (14 April 1970) --- Dr. Thomas O. Paine, Administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), talks on the telephone to President Richard M. Nixon. Dr. Paine is seated at his console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) at the Mission Control Center (MCC), Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Also pictured are Dr. Rocco Petrone, Apollo program director, Office Manned Spaceflight, NASA Headquarters (facing camera); and Chester M. Lee, Apollo mission director, Office of Manned Spaceflight, NASA Headquarters (HQ). Dr. Paine and the President were discussing the revised Apollo 13 flight plan following discovery of an oxygen cell failure in the Apollo 13 spacecraft several hours earlier.
.
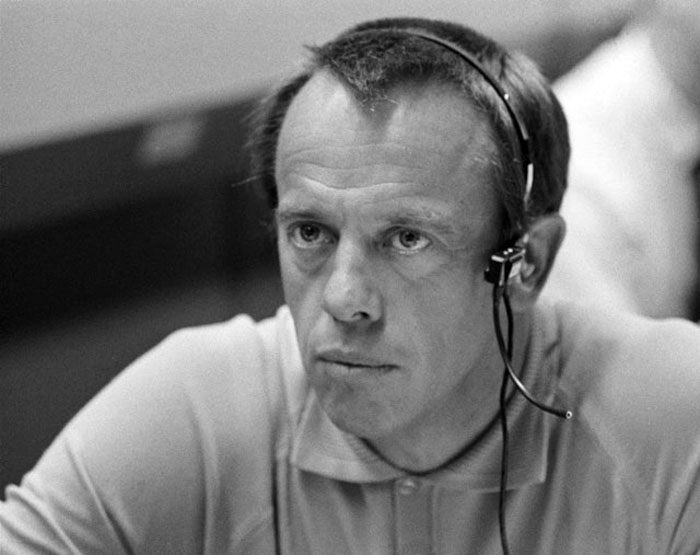

S70-34904 (14 April 1970) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., prime crew commander of the Apollo 14 mission, monitors communications between the Apollo 13 spacecraft and Mission Control Center. He is seated at a console in the Mission Operations Control Room of the MCC, Manned Spacecraft Center. The main concern of the moment was action taken by the three Apollo 13 crewmen - astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., John L. Swigert Jr. and Fred W. Haise Jr. - to make corrections inside the spacecraft following discovery of an oxygen cell failure several hours earlier.
.
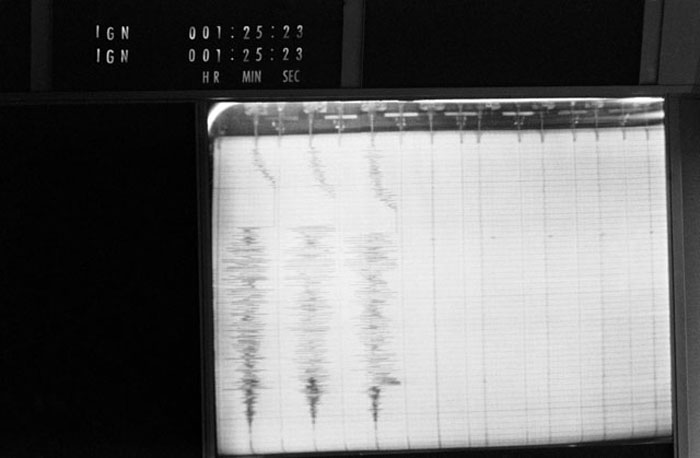

S70-34985 (14 April 1970) --- A seismic reading taken from instruments at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) recording the impact of the Apollo 13 S-IVB/Instrument Unit with the lunar surface. The expended Saturn third stage and instrument unit slammed into the moon at 7:09 p.m. (CST), April 14, 1970. The location of the impact was at 2.4 degrees south latitude and 27.9 degrees west longitude, about 76 nautical miles west-northwest of the Apollo 12 Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) deployment site. The S-IVB/IU impact was picked up by the Passive Seismic Experiment (PSE), a component of the Apollo 12 ALSEP, and transmitted to instruments at the Mission Control Center (MCC).
-
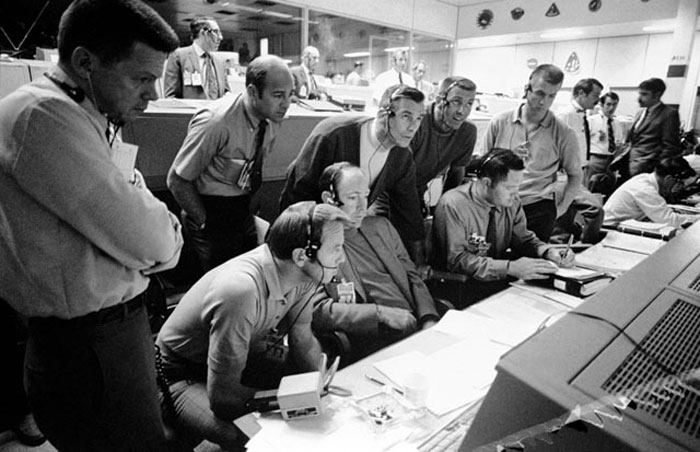

S70-34986 (14 April 1970) --- A group of six astronauts and two flight controllers monitor the console activity in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) of the Mission Control Center (MCC) during the problem-plagued Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Seated, left to right, are MOCR Guidance Officer Raymond F. Teague; astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, Apollo 14 prime crew lunar module pilot; and astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., Apollo 14 prime crew commander. Standing, left to right, are scientist-astronaut Anthony W. England; astronaut Joe H. Engle, Apollo 14 backup crew lunar module pilot; astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 14 backup crew commander; astronaut Ronald E. Evans, Apollo 14 backup crew command module pilot; and M.P. Frank, a flight controller. When this picture was made, the Apollo 13 moon landing had already been canceled, and the Apollo 13 crew men were in trans-Earth trajectory attempting to bring their damaged spacecraft back home.
.
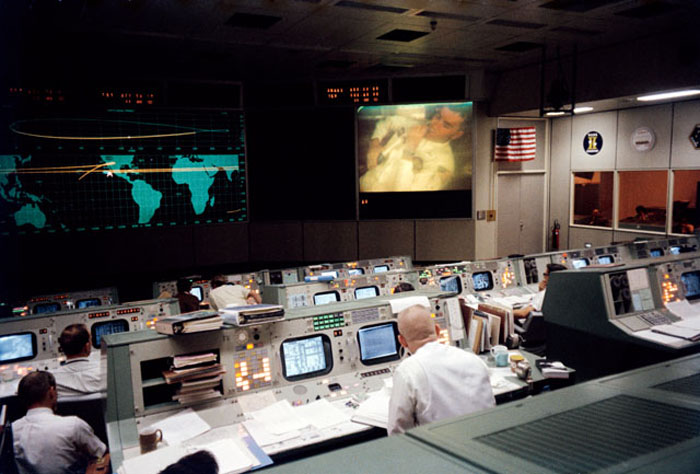

S70-35139 (13 April 1970) --- Overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC) at Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), during the fourth television transmission from the Apollo 13 mission in space. Eugene F. Kranz (foreground, back to camera), one of four Apollo 13 flight directors, views the large screen at front of MOCR, astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, is seen on the screen. The fourth TV transmission from the Apollo 13 mission was on the evening of April 13, 1970.
.

AS13-62-8929 (11-17 April 1970) --- Interior view of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) showing the "mail box," a jury-rigged arrangement which the Apollo 13 astronauts built to use the Command Module (CM) lithium hydroxide canisters to purge carbon dioxide from the LM. Lithium hydroxide is used to scrub CO2 from the spacecraft's atmosphere. Since there was a limited amount of lithium hydroxide in the LM, this arrangement was rigged up to utilize the canisters from the CM. The "mail box" was designed and tested on the ground at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) before it was suggested to the problem-plagued Apollo 13 crew men. Because of the explosion of one of the oxygen tanks in the Service Module (SM), the three crew men had to use the LM as a "lifeboat".
.
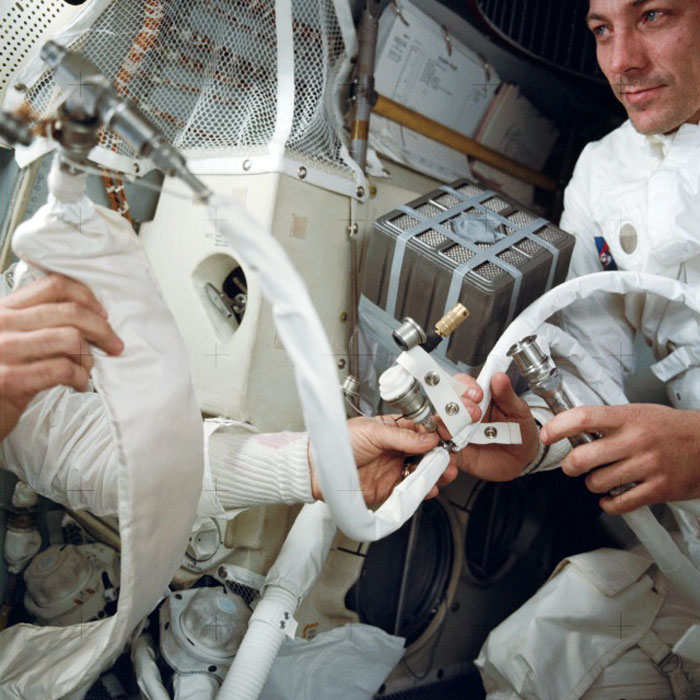

AS13-62-9004 (April 1970) --- An interior view of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) during the trouble-plagued journey back to Earth. This photograph shows some of the temporary hose connections and apparatus which were necessary when the three Apollo astronauts moved from the Command Module (CM) to use the LM as a "lifeboat". Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, is on the right. An unidentified astronaut on the left holds in his right hand the feed water bag from the Portable Life Support System (PLSS). It is connected to a hose (center) from the Lunar Topographic (Hycon) Camera. In the background is the "mail box," a jury-rigged arrangement which the crew men built to use the CM lithium hydroxide canisters to scrub CO2 from the spacecraft's atmosphere. Since there was a limited amount of lithium hydroxide in the LM, this arrangement was rigged up to utilize the canisters from the CM. The "mail box" was designed and tested on the ground at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) before it was suggested to the Apollo 13 astronauts. An explosion of an oxygen tank in the Service Module (SM) caused the cancellation of the scheduled moon landing, and made the return home a hazardous journey for astronauts Swigert, James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
.
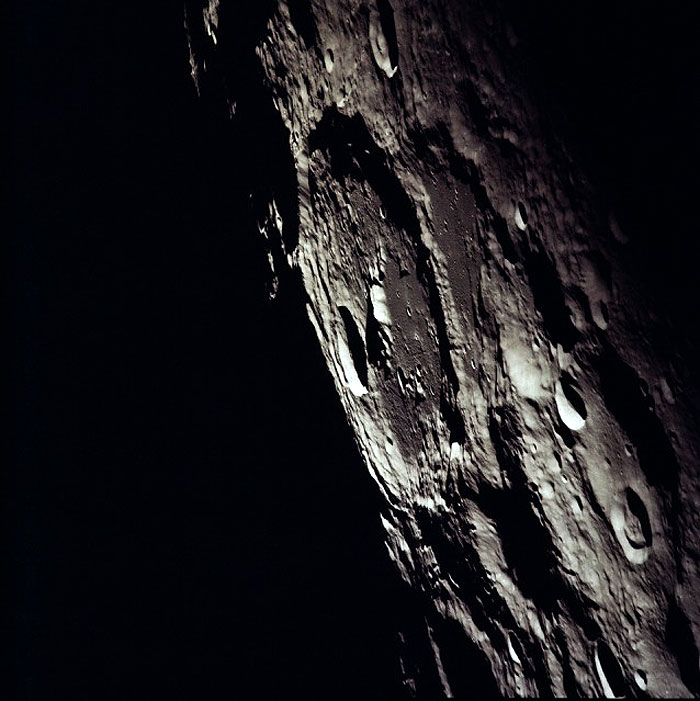
AS13-60-8635 (April 1970) --- An oblique view of the International Astronomical Union Crater No. 302 on the lunar farside as photographed from the Apollo 13 spacecraft during its pass around the moon. This large crater is located at 162 degrees east longitude and 10 degrees south latitude. The smaller crater, I.A.U. No. 301, is in the foreground. I.A.U. No. 302 has ridges in its center and a smaller crater near its inner edge. This view is looking southeast.
.
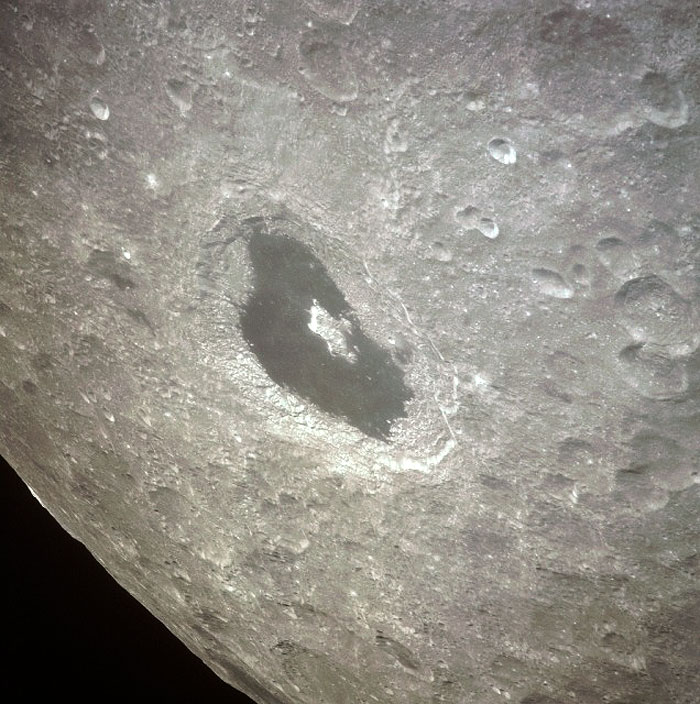

AS13-60-8659 (14 April 1970) --- Excellent view of the lunar farside showing the crater Tsiolkovsky, as photographed by the crew of the Apollo 13 mission during their lunar pass. The view is looking southeast toward the lunar horizon. The approximate coordinates of Tsiolkovsky are 128.5 degrees east longitude and 20.5 degrees south latitude. The Apollo 13 crew members were forced to cancel their scheduled lunar landing because of an apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two in the Service Module (SM).
.
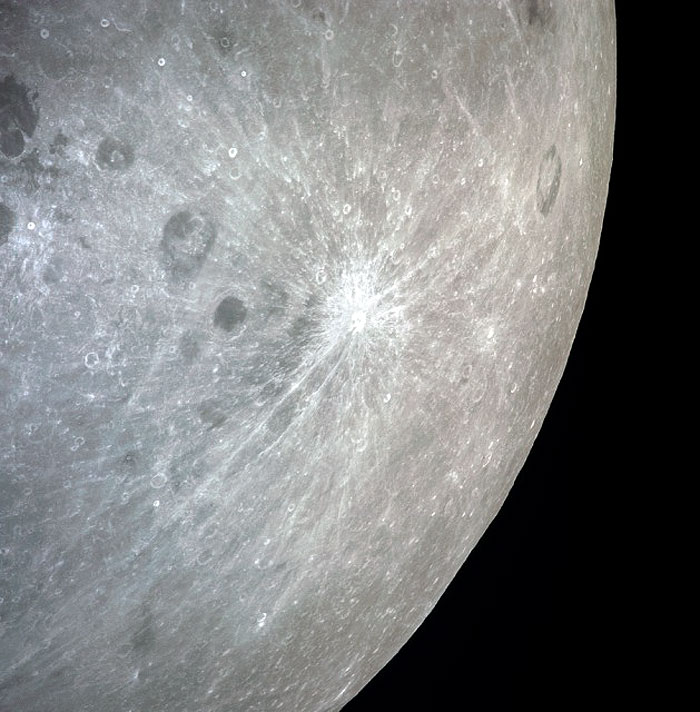
AS13-60-8675 (April 1970) --- This bright-rayed crater on the lunar farside was photographed from the Apollo 13 spacecraft during its pass around the moon. This area is northeast of Mare Marginus. The bright-rayed crater is located at about 105 degrees east longitude and 45 degrees north latitude. The crater Joliot-Curie is located between Mare Marginus and the rayed crater. This view is looking generally toward the northeast.
.
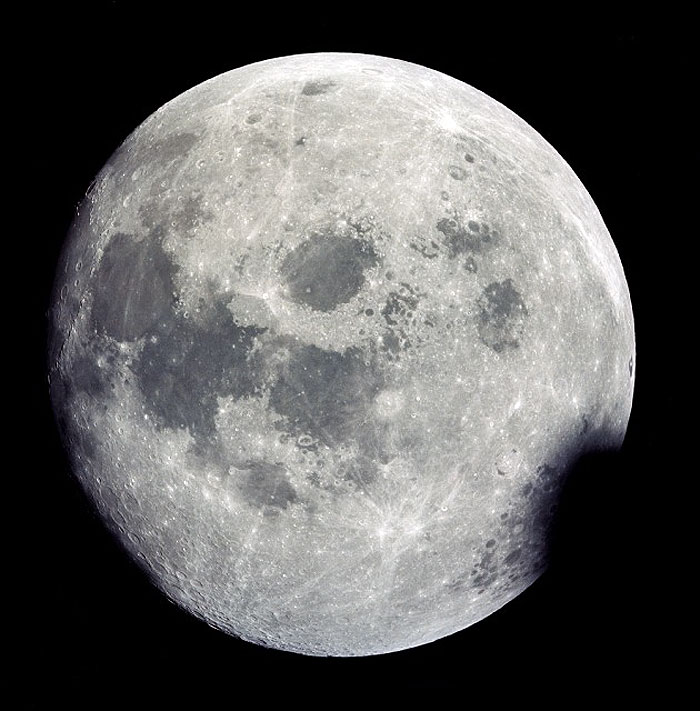

AS13-60-8703 (11-17 April 1970) --- This outstanding view of a near full moon was photographed from the Apollo 13 spacecraft during its trans-Earth journey homeward. Though the explosion of the oxygen tank in the Service Module (SM) forced the cancellation of the scheduled lunar landing, Apollo 13 made a pass around the moon prior to returning to Earth. Some of the conspicuous lunar features include the Sea of Crisis, the Sea of Fertility, the Sea of Tranquility, the Sea of Serenity, the Sea of Nectar, the Sea of Vapors, the Border Sea, Smyth's Sea, the crater Langrenus, and the crater Tsiolkovsky.
.
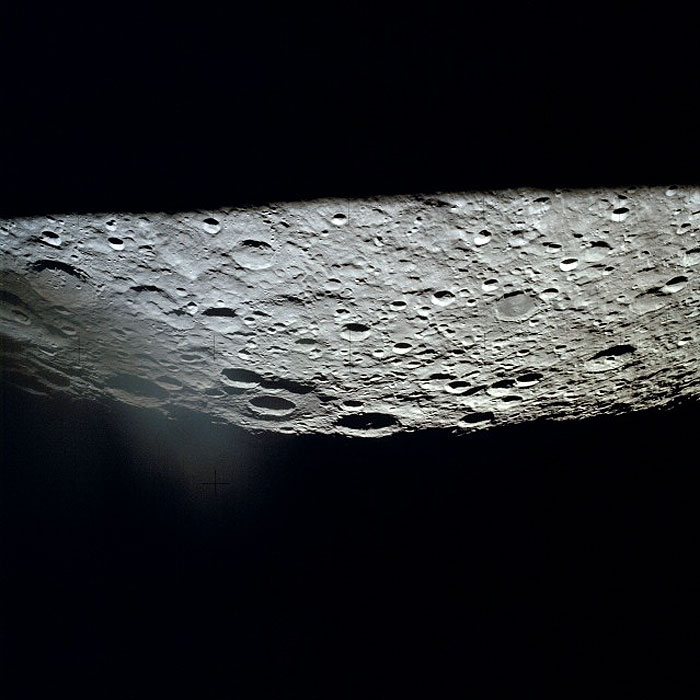
AS13-62-8918 (April 1970) --- This oblique view of the lunar farside was photographed from the Apollo 13 spacecraft as it passed around the moon on its hazardous journey homeward. This view is looking east. The large crater in the center at the horizon is International Astronomical Union Crater No. 221. The next larger crater just south of I.A.U. No. 221 is I.A.U. 220. This area of the moon is located southeast of Mare Moscoviense. I.A.U. 221 is located at 164 degrees east longitude and 10 degrees north latitude.
.
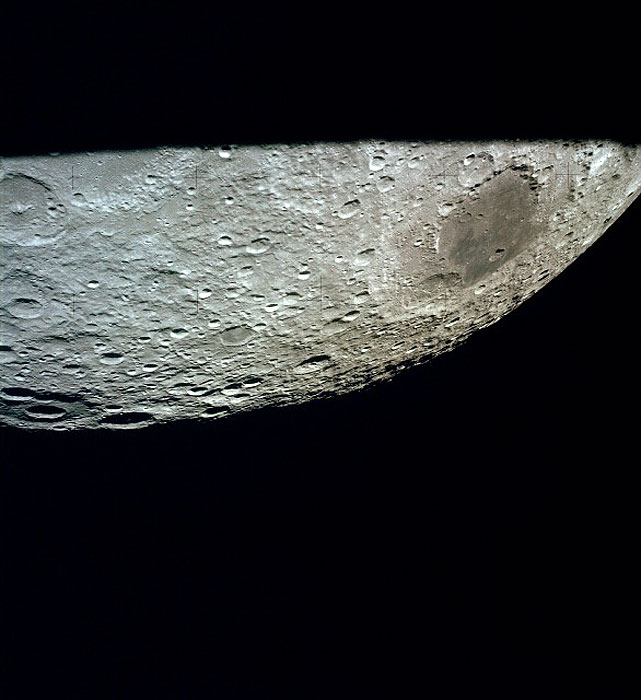

AS13-62-8923 (11-17 April 1970) --- This oblique view of the lunar farside was photographed from the Apollo 13 spacecraft as it passed around the moon on its hazardous journey home. The large conspicuous mare area is Mare Moscoviense which is located at 146 degrees east longitude and 25 degrees north latitude. The large crater at the horizon is International Astronomical Union Crater No. 221. This view is looking northeast from the spacecraft.
-
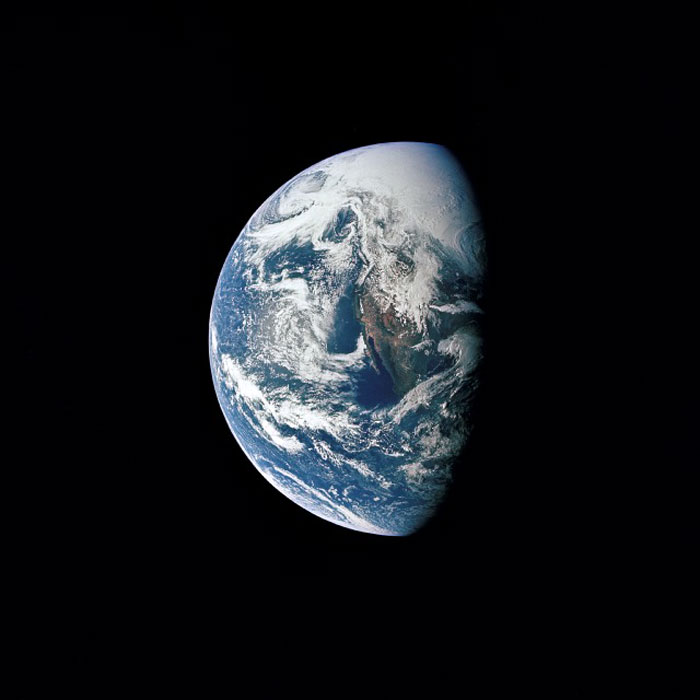

AS13-60-8588 (17 April 1970) --- This photograph of Earth was taken from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Apollo 13 spacecraft during its trans-Earth journey home. The most visible land mass includes southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. The peninsula of Baja California is clearly seen. Most of the land area is under heavy cloud cover. The Apollo 13 crew consisted of astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
.

AS13-58-8458 (17 April 1970) --- This view of the severely damaged Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) was photographed from the Lunar Module/Command Module (LM/CM) following SM jettisoning. An entire SM panel was blown away by the apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two. Two of the three fuel cells are visible at the forward portion of the opening. The hydrogen tanks are located in Sector 4 of the Apollo 13 SM. The apparent rupture of the oxygen tank caused the Apollo 13 crew members to use the LM as a "lifeboat." The LM was jettisoned just prior to Earth re-entry by the CM.
.

AS13-58-8464 (17 April 1970) --- This view of the severely damaged Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) was photographed from the Lunar Module/Command Module (LM/CM) following SM jettisoning. Nearest the camera is the Service Propulsion System (SPS) engine and nozzle. An entire SM panel was blown away by the apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two located in Sector 4 of the SM. The apparent rupture of the oxygen tank caused the Apollo 13 crew men to use the Lunar Module (LM) as a "lifeboat".
.
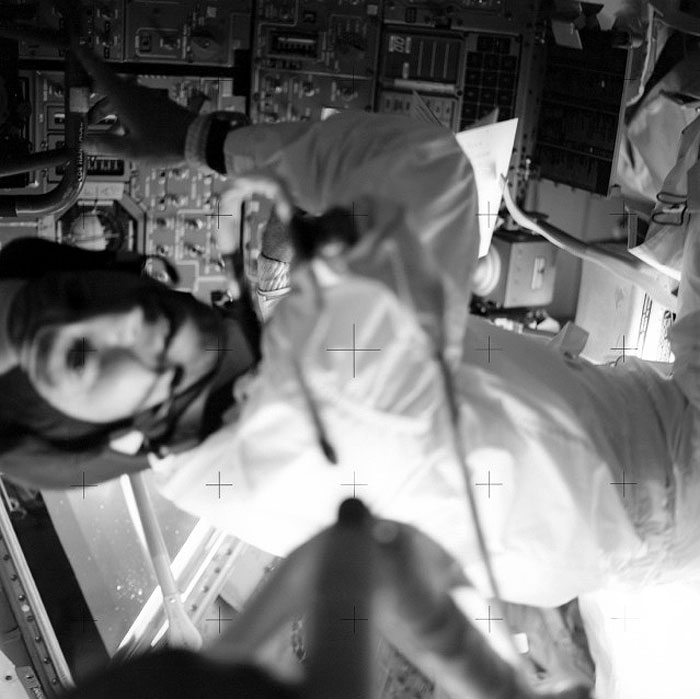

AS13-59-8484 (April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander, is pictured at his position in the Lunar Module (LM). The Apollo 13 crew of astronauts Lovell; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, relied on the LM as a "lifeboat". The dependence on the LM was caused by an apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two in the Service Module (SM). The LM was jettisoned just prior to Earth re-entry by the Command Module (CM).
.

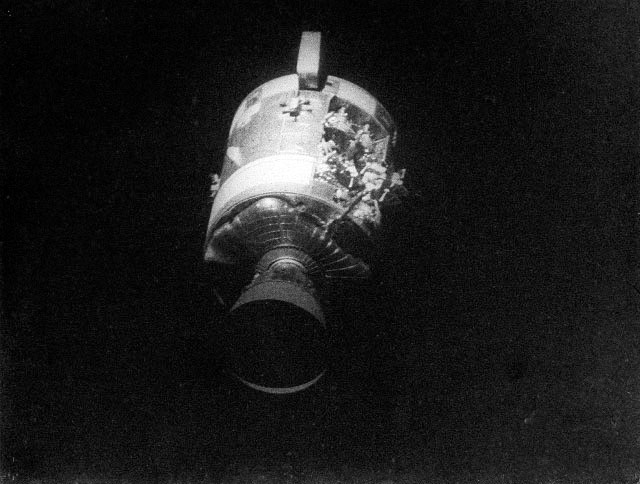
AS13-59-8501 (17 April 1970) --- This view of the severely damaged Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) was photographed from the Lunar Module/Command Module (LM/CM) following SM jettisoning. As seen here, an entire panel on the SM was blown away by the apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two located in Sector 4 of the SM. Two of the three fuel cells are visible just forward (above) the heavily damaged area. Three fuel cells, two oxygen tanks, and two hydrogen tanks are located in Sector 4. The damaged area is located above the S-Band high gain antenna. Nearest the camera is the Service Propulsion System (SPS) engine and nozzle. The damage to the SM caused the Apollo 13 crew men to use the LM as a "lifeboat." The LM was jettisoned just prior to Earth re-entry by the CM.
.

AS13-59-8500A (17 April 1970) --- This view of the severely damaged Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) was photographed from the Lunar Module/Command Module (LM/CM) following SM jettisoning. As seen in this cropped image, enlarged to provide a close-up view of the damaged area, an entire panel on the SM was blown away by the apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two located in Sector 4 of the SM. Two of the three fuel cells are visible just forward (above) the heavily damaged area. Three fuel cells, two oxygen tanks, and two hydrogen tanks are located in Sector 4. The damaged area is located above the S-Band high gain antenna. Nearest the camera is the Service Propulsion System (SPS) engine and nozzle. The damage to the SM caused the Apollo 13 crew members to use the LM as a "lifeboat". The LM was jettisoned just prior to Earth re-entry by the CM. Photo credit: NASA
-
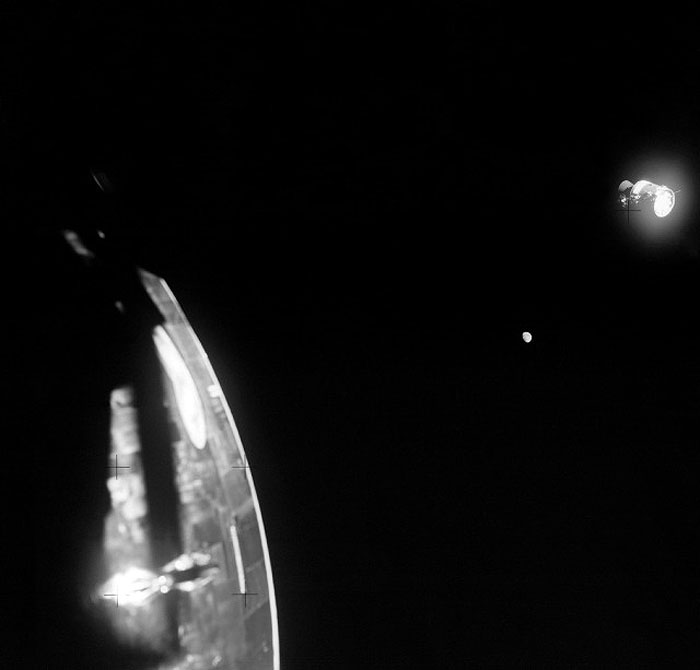
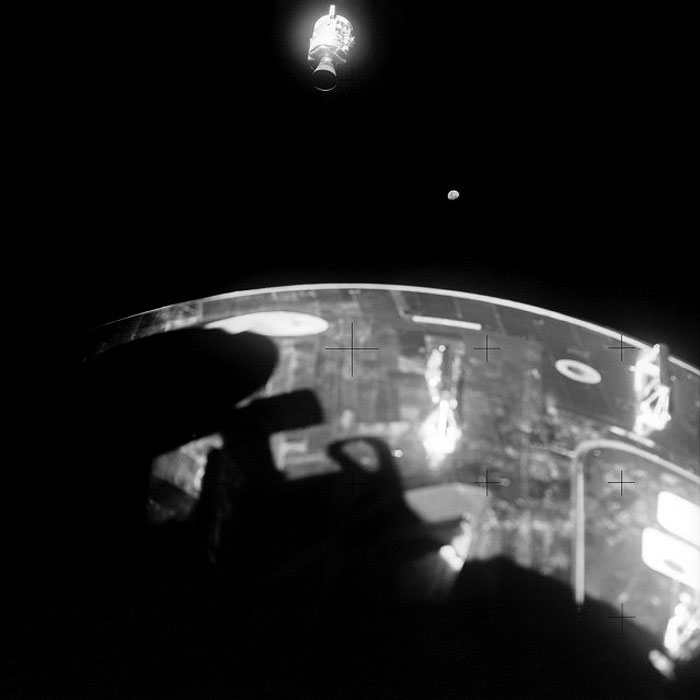
AS13-59-8513 (17 April 1970) --- This view of the severely damaged Apollo 13 Service Module (SM), with the moon in the distant background, was photographed from the Lunar Module (LM) following SM jettisoning. The Command Module (CM), still docked with the LM, is in the foreground. An entire panel on the SM was blown away by the apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two located in Sector 4 of the SM. Three fuel cells, two oxygen tanks, and two hydrogen tanks are located in Sector 4. The damaged area is forward (above) the S-Band high gain antenna. The damage to the SM caused the Apollo 13 crew members to use the LM as a "lifeboat." The LM was jettisoned just prior to Earth re-entry by the CM. The Apollo 13 crew consisted of astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
.
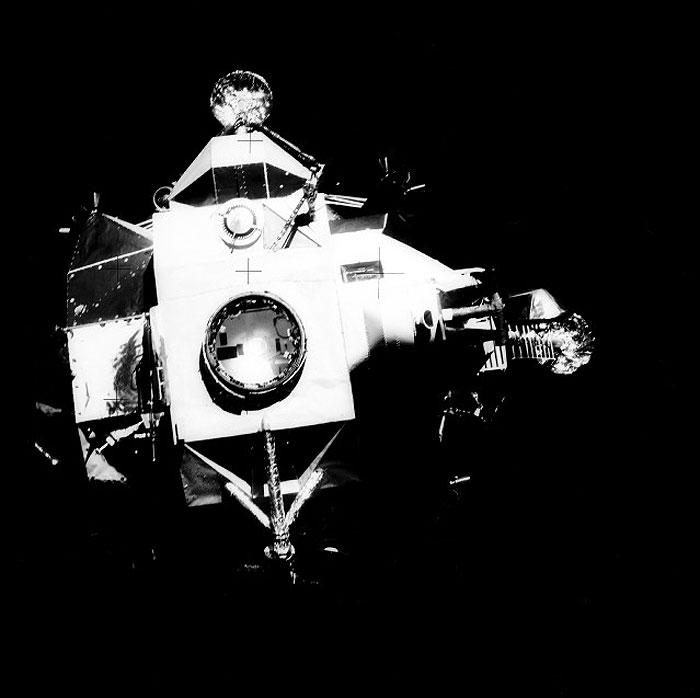

AS13-59-8562 (17 April 1970) --- This view of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) was photographed from the Command Module (CM) just after the LM had been jettisoned. The jettisoning occurred a few minutes before 11 a.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, just over an hour prior to splashdown of the CM in the south Pacific Ocean. The apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two in the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) caused the Apollo 13 crew members to rely on the LM as a "lifeboat".
.
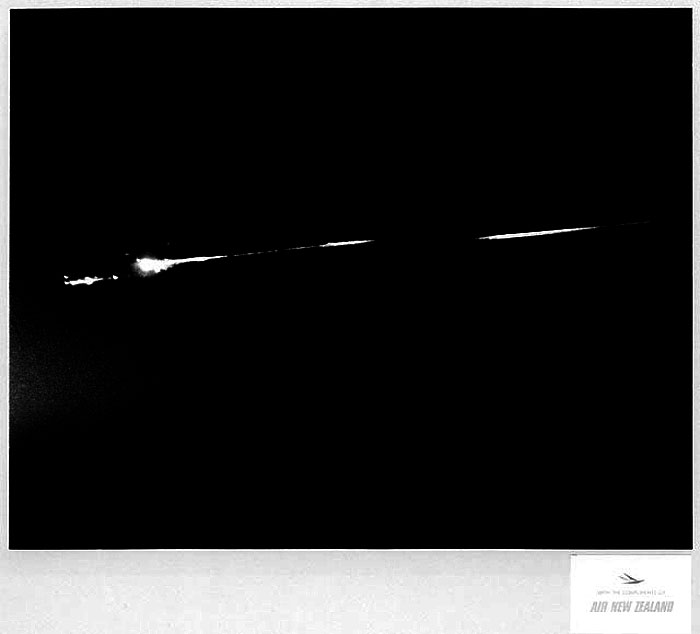

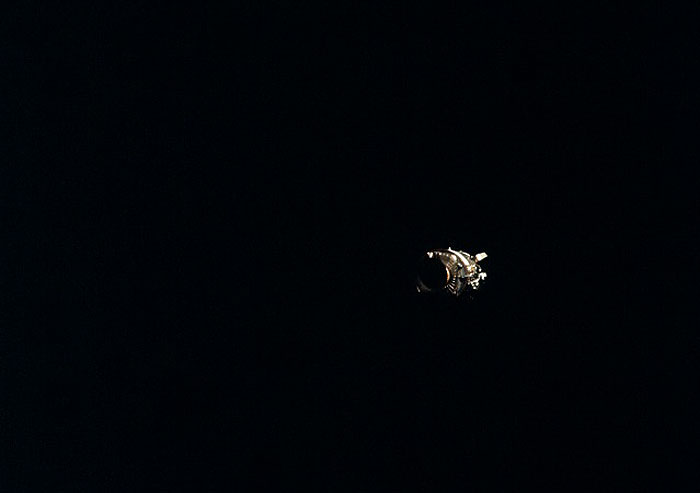
S70-17646 (18 April 1970) --- An unidentified airline passenger snapped these bright objects, believed to be the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) and Lunar Module (LM) as they entered Earth's atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean on April 18, 1970. The aircraft, an Air New Zealand DC-8 was midway between the Fiji Islands (Nandi Island to be specific) and Auckland, New Zealand, when the photograph was taken. The crew men of the problem plagued Apollo 13 mission jettisoned the LM and SM prior to entering Earth's atmosphere in the Apollo 13 Command Module (CM).
.
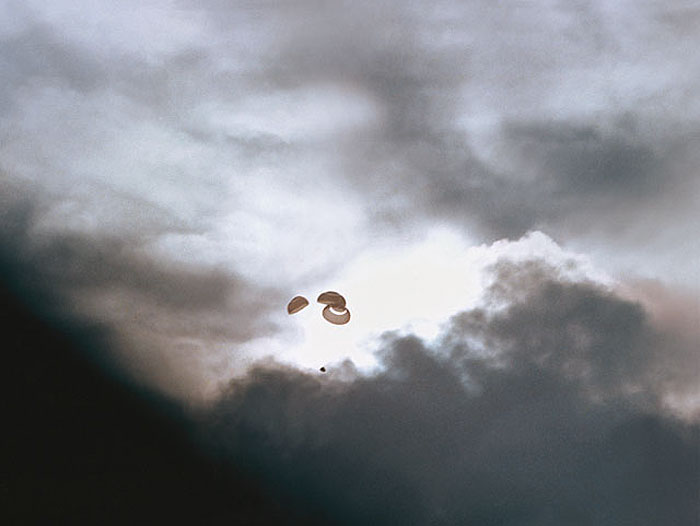

S70-35652 (17 April 1970) --- The Apollo 13 spacecraft heads toward a splashdown in the South Pacific Ocean. The Apollo 13 Command Module splashed down in the South Pacific at 12:07:44 p.m., April 17, 1970. Note the capsule and its parachutes just visible against a gap in the dark clouds.
.
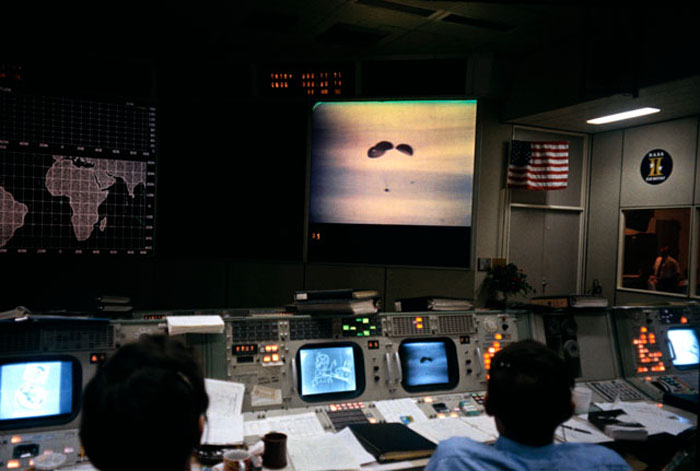

S70-35471 (17 April 1970) --- Two flight controllers man consoles in the Missions Operations Control Room (MOCR) of the Mission Control Center (MCC) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), Houston, Texas, just before splashdown occurred in the south Pacific Ocean. Though the MOCR does not appear to be crowded in this photo, there was a very large crowd of persons on hand for the splashdown and recovery operations coverage. Most of the group crowded around in the rear of the room. Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970.
.
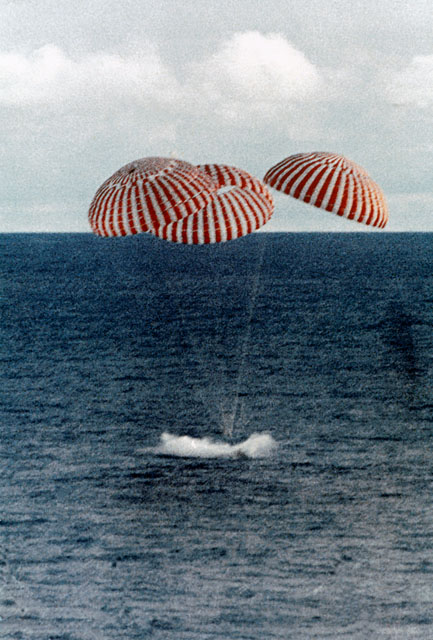

S70-35638 (17 April 1970) --- A perilous space mission comes to a smooth ending with the safe splashdown of the Apollo 13 Command Module (CM) in the South Pacific, only four miles from the prime recovery ship. The spacecraft with astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., John L. Swigert Jr., and Fred W. Haise Jr. aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST) April 17, 1970, to conclude safely the problem-plagued flight. The crewmen were transported by helicopter from the immediate recovery area to the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery vessel.
.
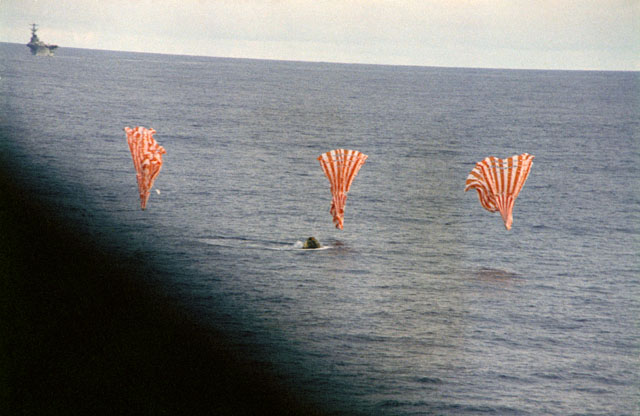

S70-35644 (17 April 1970) --- The Apollo 13 Command Module (CM) splashes down and its three main parachutes collapse, as the week-long problem-plagued Apollo 13 mission comes to a premature, but safe end. The spacecraft, with astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, aboard splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST) April 17, 1970, in the South Pacific Ocean, only about four miles from the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship.
-
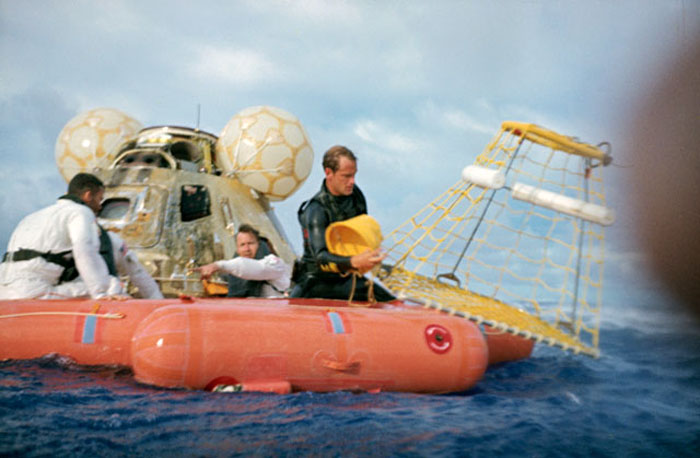

S70-35631 (17 April 1970) --- A water-level view of recovery operations for the Apollo 13 mission in the South Pacific Ocean. The three crewmen have egressed their spacecraft, and are awaiting the readying of the "Billy Pugh" net which will hoist them to a helicopter hovering above. The crewmembers (from the left) are astronauts Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; (only partially visible between Haise and the Command Module (CM)), and James A. Lovell Jr., commander. A U.S. Navy underwater demolition team swimmer prepares to assist Haise into the net. Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, in the South Pacific, about four miles from the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship.
-
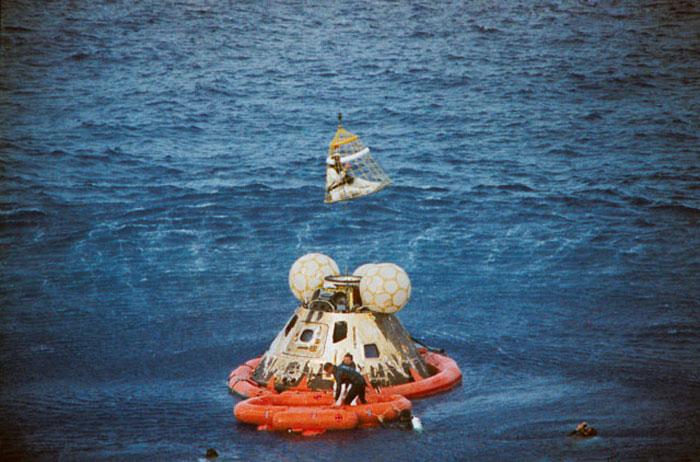

S70-35651 (17 April 1970) --- Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, is lifted aboard a helicopter in a "Billy Pugh" net while astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander, awaits his turn. Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, is already aboard the helicopter. In the life raft with Lovell, and in the water are several U.S. Navy underwater demolition team swimmers, who assisted in the recovery operations. The crew was taken to the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship, several minutes after the Apollo 13 spacecraft splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970.
-
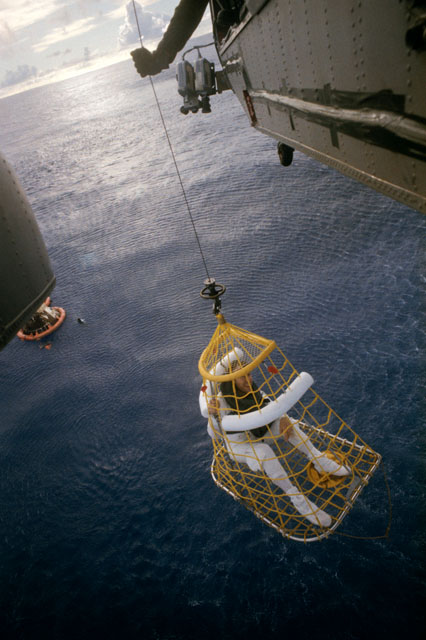

S70-35645 (17 April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander, is hoisted aboard a helicopter from the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery vessel for the mission. Lovell was the last of the three Apollo 13 crewmembers to egress the Command Module (CM) and the last to be lifted aboard the helicopter. He was preceded by astronauts John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The CM and a U.S. Navy underwater demolition team swimmer can be seen in the ocean background. Apollo 13 splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970.
-
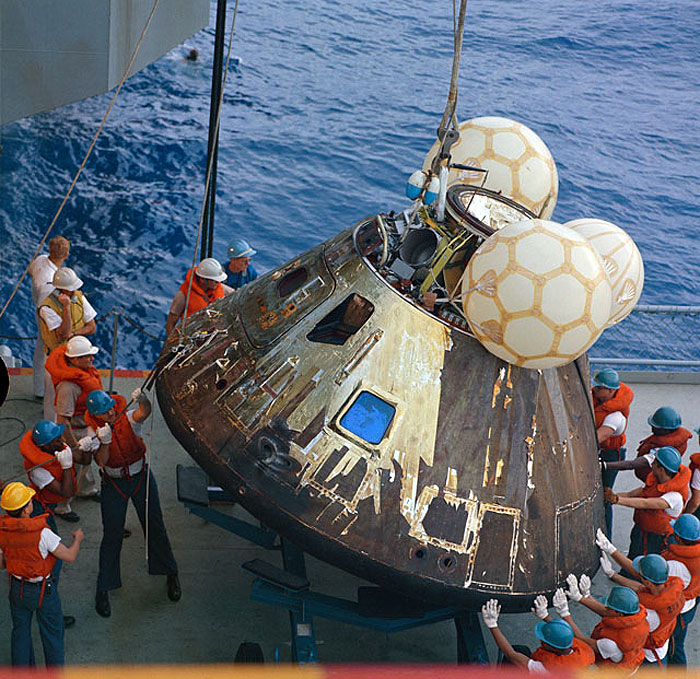

S70-35632 (17 April 1970) --- Crewmen aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission, guide the Command Module (CM) atop a dolly onboard the ship. The CM is connected by strong cable to a hoist on the vessel. The Apollo 13 crewmembers, astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, were already aboard the USS Iwo Jima when this photograph was made. The CM, with the three tired crewmen aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, only about four miles from the recovery vessel in the South Pacific Ocean.
.
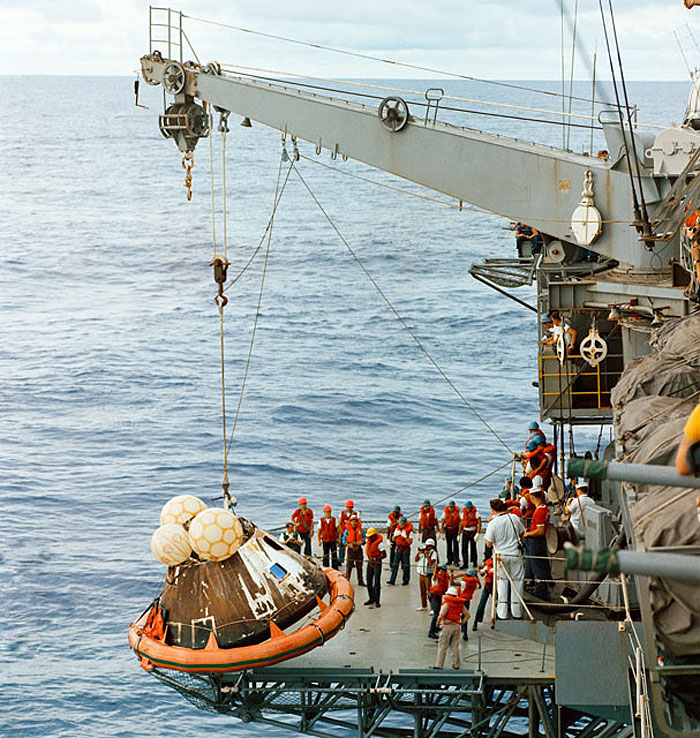

S70-15530 (17 April 1970) --- Crew men aboard the U.S.S. Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission, hoist the Command Module (CM) aboard ship. The Apollo 13 crew men, astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., John L. Swigert Jr. and Fred W. Haise Jr., were already aboard the Iwo Jima when this photograph was taken. The CM, with the three tired crew men aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, only about four miles from the recovery vessel in the South Pacific Ocean.
-

S70-15531 (17 April 1970) --- Crew men aboard the U.S.S. Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission, guide the Command Module (CM) atop a dolly on board the ship. The CM is connected by strong cable to a hoist on the vessel. The Apollo 13 astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, were already aboard the U.S.S. Iwo Jima when this photograph was taken. The CM, with the three tired crew men aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, only about four miles from the recovery vessel in the South Pacific Ocean.
-

S70-35472 (17 April 1970) --- Overall view of the crowded Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) during post-recovery ceremonies aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission. The Apollo 13 spacecraft, with astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, aboard, splashed down in the South Pacific at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970. The smooth splashdown and recovery operations brought an end to a perilous spaceflight for the crewmembers, and a tiring one for ground crew in MCC.
.
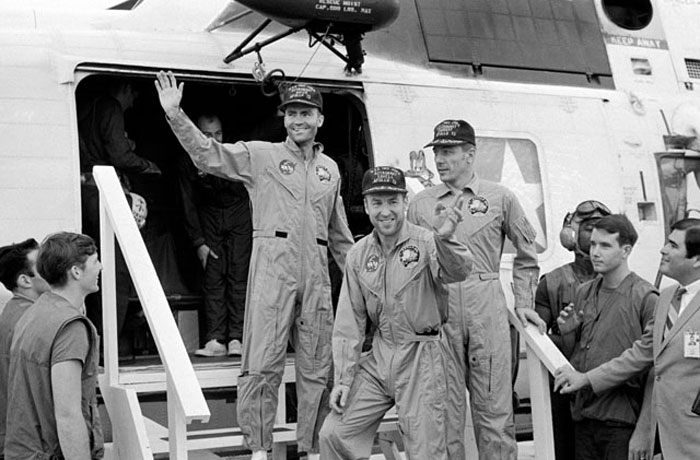

S70-35614 (17 April 1970) --- The crewmembers of the Apollo 13 mission, step aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the mission, following splashdown and recovery operations in the South Pacific Ocean. Exiting the helicopter which made the pick-up some four miles from the Iwo Jima are (from left) astronauts Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot; James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot. The crippled Apollo 13 spacecraft splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970.
-
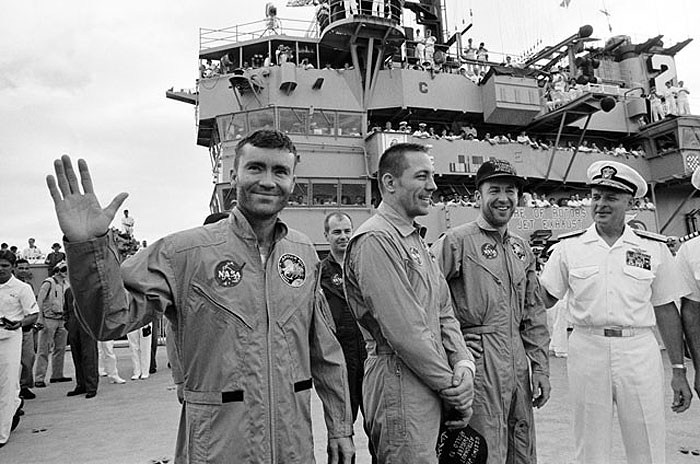

S70-35606 (17 April 1970) --- Rear Admiral Donald C. Davis, Commanding Officer of Task Force 130, the Pacific Recovery Forces for the Manned Spacecraft Missions, welcomes the Apollo 13 crewmembers aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission. The crewmembers (from the left) astronauts Fred W. Haise Jr. (waving), lunar module pilot; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and James A. Lovell Jr., commander; were transported by helicopter to the ship following a smooth splashdown only about four miles from the USS Iwo Jima. Splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, to conclude safely a perilous space flight.
.

S70-15501 (17 April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 13 mission commander, reads a newspaper account of the safe recovery of the problem plagued mission. Lovell is on board the U.S.S. Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for Apollo 13, which was on a course headed for Pago Pago. From Pago Pago the astronauts flew to Hickham Air Force Base, Hawaii, where they were presented the Presidential Medal of Freedom by President Richard M. Nixon. Other Apollo 13 crew members were astronauts John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
-
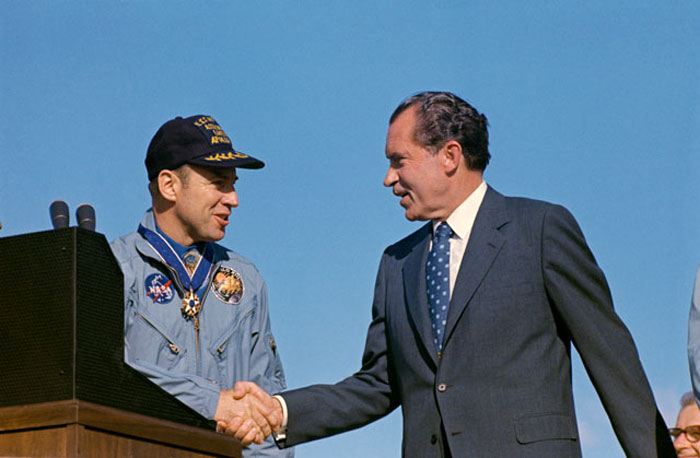

S70-15506 (18 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon and astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 13 commander, shake hands at special ceremonies at Hickham Air Force Base, Hawaii. President Nixon was in Hawaii to present the Apollo 13 crew with the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the nations highest civilian honor. The wives of astronauts Lovell and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot; and the parents of astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, flew with the Chief Executive to Hickam Air Force Base. The Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, a day and a half prior to the awards ceremony.
-
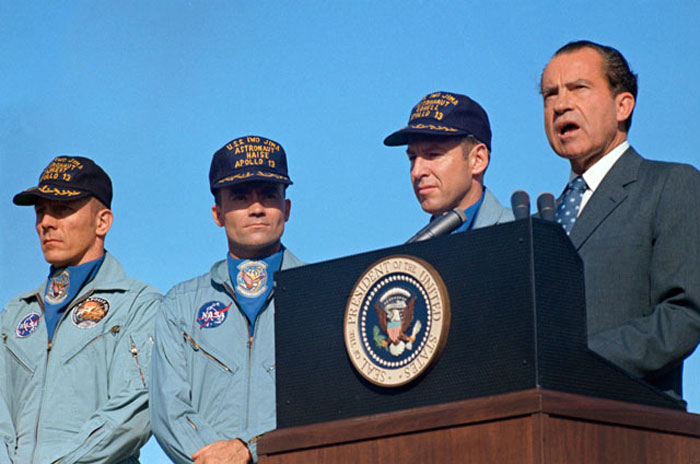

S70-15511 (19 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon speaks at Hickham Air Force Base prior to presenting the nation's highest civilian award to the Apollo 13 crew. Receiving the Presidential Medal of Freedom were astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., (next to the Chief Executive), commander; John L. Swigert Jr. (left), command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Wives of Lovell and Haise and the parents of Swigert accompanied the President to Hawaii. The Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, about a day and a half prior to the Hickam Air Force Base ceremonies.
.

S70-35562 (April 1970) --- A photographic replica of the Presidential Medal of Freedom Award which President Richard M. Nixon presented to the Apollo 13 Missions Operations Team (MOT). The presentation was made by the Chief Executive during a visit to the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) in April 1970.
-

S70-35601 (18 April 1970) --- A wide-angle, overall view of the large crowd of people who were on hand to see President Richard M. Nixon present the Presidential Medal of Freedom to the Apollo 13 Mission Operations Team. The honor is the nation's highest civilian award. A temporary speaker's platform was erected beside Building 1 for the occasion.
-
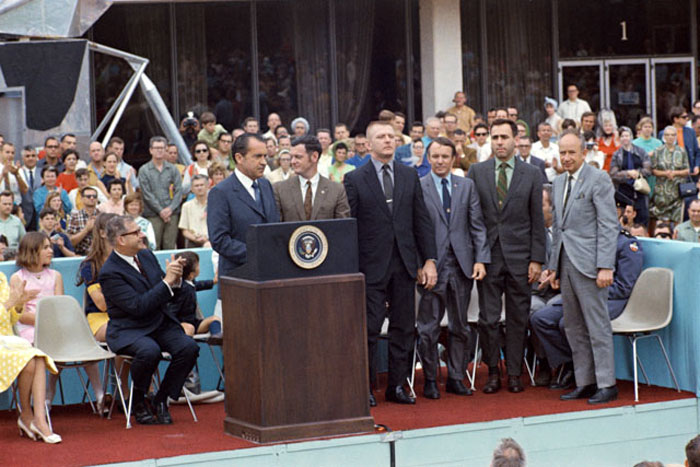

S70-35600 (18 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon introduces Sigurd A. Sjoberg (far right), director of Flight Operations at Manned Spacecraft Center, and the four Apollo 13 flight directors during the President's post-mission visit to the Manned Spacecraft Center. The flight directors are, from left to right, Glynn S. Lunney, Eugene A. Kranz, Gerald D. Griffin and Milton L. Windler. Dr. Thomas O. Paine, Administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, is seated at left. President Nixon was on the site to present the Presidential Medal of Freedom - the nation's highest civilian honor - to the Apollo 13 Mission Operations Team.
-

S70-35748 (20 April 1970) --- Dr. Donald K. Slayton (center foreground), MSC director of flight crew operations, talks with Dr. Wernher von Braun (right), famed rocket expert, at an Apollo 13 postflight debriefing session. The three crewmen of the problem-plagued Apollo 13 mission (left to right) in the background are astronauts James A Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The apparent rupture of oxygen tank number two in the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) and the subsequent damage forced the three astronauts to use the Lunar Module (LM) as a "lifeboat" to return home safely after their moon landing was canceled. Dr. von Braun is the deputy associate administrator for planning of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
-
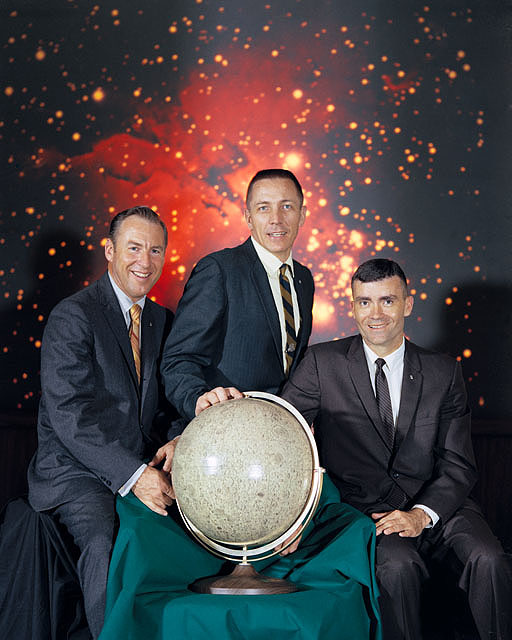

S70-36485 (April 1970) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Left to right, are James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Apollo 13 will be the United States' third lunar landing mission.
-
Fotos: NASA
.
5449 Views
