.

Mission Highlights
Apollo 9 launched from Cape Kennedy on March 3, 1969, into a nominal 117 by 119-mile Earth orbit with Commander James McDivitt, Command Module Pilot David Scott and Lunar Module Pilot Russell Schweickart aboard.
On the first day, and after orbit injection of the combined S-IVB stage and its SLA-LM-CSM payload, venting of the S-IVB propellant tanks changed the orbit to 123 by 127 miles. The CSM separated and the SLA panel walls jettisoned, transposing the CSM to 180 degrees toward the LM atop the S-IVB. The CSM docked with the LM in the second orbit. The linked modules ejected from the S-IVB, and the thrust placed the CSM-LM a safe distance away for a 62-second restart of the S-IVB, which raised the apogee to 1,895 miles. To achieve a hyperbolic orbit for the planned escape trajectory, the S-IVB restarted a second time for four minutes, two seconds. It resulted in a less than desired maximum velocity increase and was off nominal by about 11 percent. While this did not affect the Apollo 9 flight, a lunar mission might have been aborted. Before the third S-IVB burn, the CSM SPS fired for five seconds, placing the CSM in an orbit of 125 by 145 miles. The firing improved orbital lifetime, checked the capability of the guidance and navigation system to control the burn, and performed a hard check of the LM's ability to withstand thrust acceleration and vibration.
The second SPS firing for one minute, five seconds occurred on March 4. It changed Apollo 9's orbit to 123 by 213 miles and tested the structural dynamics of the docked CSM-LM under loads about those of a lunar mission. A third SPS firing the same day for four minutes, 42 seconds, changed the orbit to 126 by 313 miles. The fourth burn, which lasted for 28.2 seconds, was an out-of-plane change.
On Flight Day 3, McDivitt and Schweickart put on spacesuits and transferred to the LM through the tunnel connection to perform a systems checkout. This included a 367-second firing of the LM descent engine to simulate the throttle pattern to be used during a lunar landing mission. McDivitt controlled the final 59 seconds, varying the thrust from 10 to 40 percent and shutting it off manually. This was the first crewed throttling of an engine in space and increased the spacecraft's orbit to 130 by 300 miles. After nine hours, McDivitt and Schweickart transferred back to the CSM with Scott. Then, the SPS fired for the fifth time as the final shaping maneuver prior to the rendezvous exercises to be performed two days later. The firing placed Apollo 9 into an orbit of 142 by 149 miles.
On Flight Day 4, McDivitt and Schweickart re-entered the LM. Because of nausea, Schweickart's scheduled two-hour EVA to simulate external transfer rescue techniques was canceled. Instead, he climbed out of the LM porch for a 37.5 minute EVA, testing the EVA mobility unit, including the portable life support system backpack.
On Flight Day 5, with McDivitt and Schweickart again aboard the LM, it separated from Scott's CSM. The LM descent engine fired once for 24.9 seconds to place the spacecraft into a 137 by 167 mile orbit. If fired again for 24.4 seconds to circularize the orbit about 154 by 160 miles, some 12 miles higher than the CMS. Four hours later, horizontally 113 miles away from the CSM, the LM descent stage jettisoned for a first-time firing in space of the ascent stage engine. It lowered the LM orbit by 11 miles and placed it 75 miles behind and 10 miles below the CSM, leaving it able to commence a rendezvous. Six hours later, the CSM and LM redocked. The LM ascent stage jettisoned and was commanded to fire its engine to fuel depletion.
Although postponed by one revolution on Flight Day 6, a sixth firing of the CSM SPS lowered the orbit to 121 by 138 miles. On the seventh day, the crew performed Earth landmark tracking over the U.S. and the South Atlantic. On the eighth day, a seventh burn of the SPS altered the orbit of Apollo 9 to 113 by 288 miles. No major mission activities were scheduled for the ninth day.
Two telecasts were made to Earth from Apollo 9. The first, on March 5, lasted for almost seven minutes. The second telecast on the following day lasted about 13 minutes, and only showed interior views of the LM. Photographs taken as part of the multi-spectral terrain photographic experiment were successful.
On March 13, the tenth day, re-entry was extended by one revolution because of heavy seas in the primary recovery area. Six hundred miles into its 152nd revolution, Apollo 9 splashed down at 23.25 degrees north, 68 degrees west. The crew was within three miles and in full view of their recovery ship, about 341 miles north of Puerto Rico. The flight totaled 241 hours, 53 seconds - 10 seconds longer than planned. The S-IVB stage reached heliocentric orbit and the LM ascent stage reached Earth orbit. The LM descent stage decayed March 22.
.
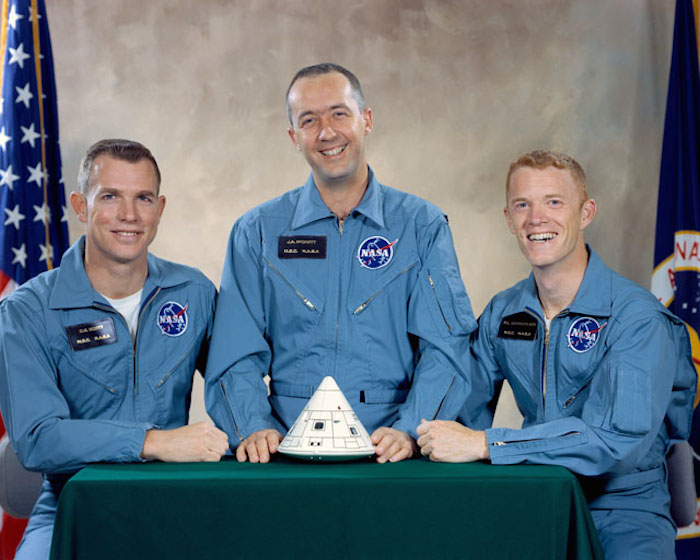

S66-30237 (March 1966) --- These three astronauts have been named as the prime crew of the Apollo 9 mission. They are (left to right) David R. Scott, command module pilot; James A. McDivitt, commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot.
.
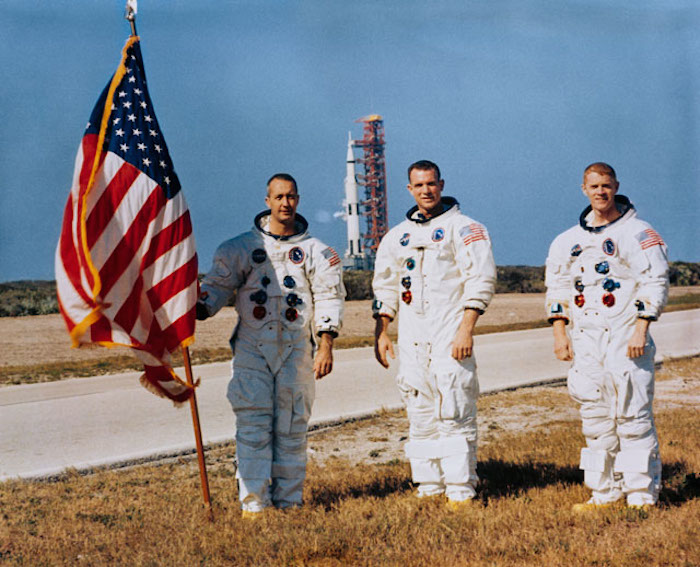

S68-56621 (18 Dec. 1968) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew of the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space mission. Left to right, are James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot: and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 launch is scheduled no earlier than February 28, 1969. In the background is the Apollo 8 space vehicle on Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, which was launched on December 21, 1968. (Gaseous liquid oxygen is venting from the vehicle’s first [S-1C] stage during a countdown demonstration test). McDivitt holds a U.S. flag.
.
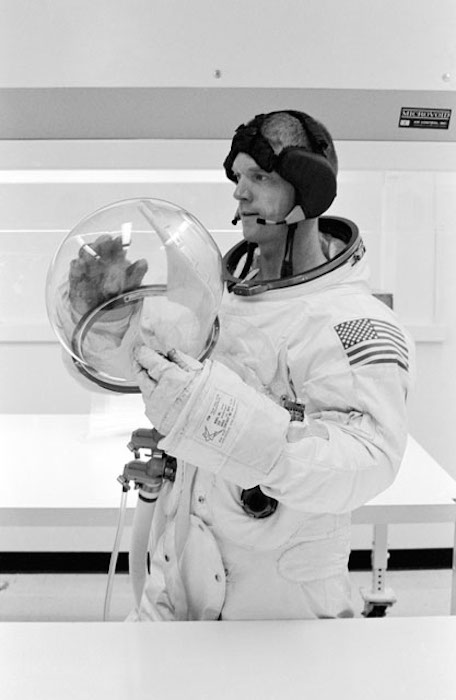

S68-38051 (29 June 1968) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart suits up to participate in an altitude verification test of the Apollo Portable Life Support System flight unit in Crew Systems Division's 8-ft altitude chamber in Building 7.
.
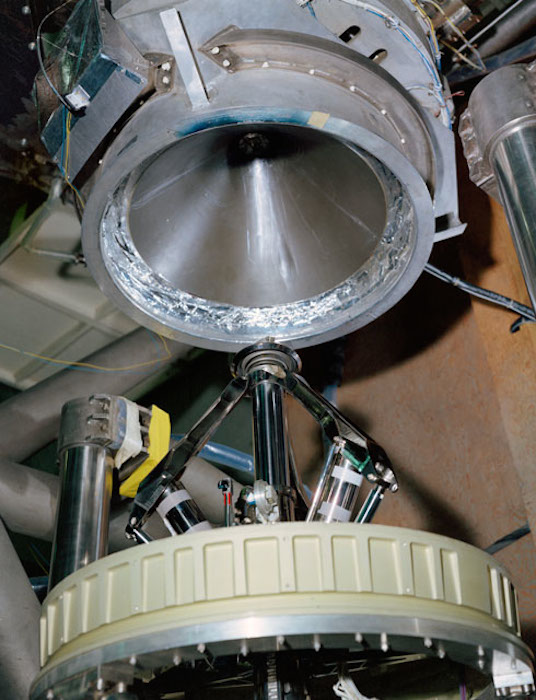
S68-50869 (1968) --- An engineering set up illustrating the docking system of the Apollo spacecraft. During docking maneuvers the docking probe on the Command Module engages the cone-shaped drogue of the Lunar Module. The primary docking structure is the tunnel through which the astronauts transfer from one module to the other. This tunnel is partly in the nose of the Command Module and partly in the top of the Lunar Module. Following CSM/LM docking the drogue and probe are removed to open the passageway between the modules.
.
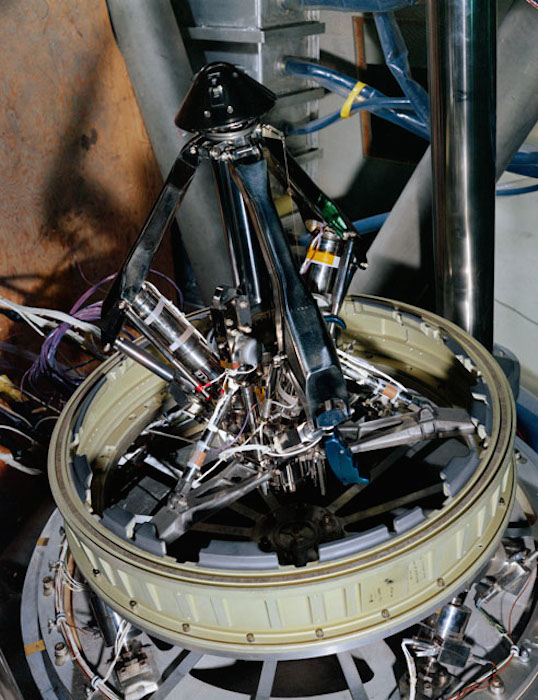

S68-50870 (1968) --- An engineering set up illustrating the probe portion of the docking system of the Apollo spacecraft. During docking maneuvers the docking probe on the Command Module (CM) engages the cone shaped drogue of the Lunar Module (LM). The primary docking structure is the tunnel through which the astronauts transfer from one module to the other. This tunnel is partly in the nose of the CM and partly in the top of the LM. Following CSM/LM docking the drogue and probe are removed to open the passageway between the modules.
.
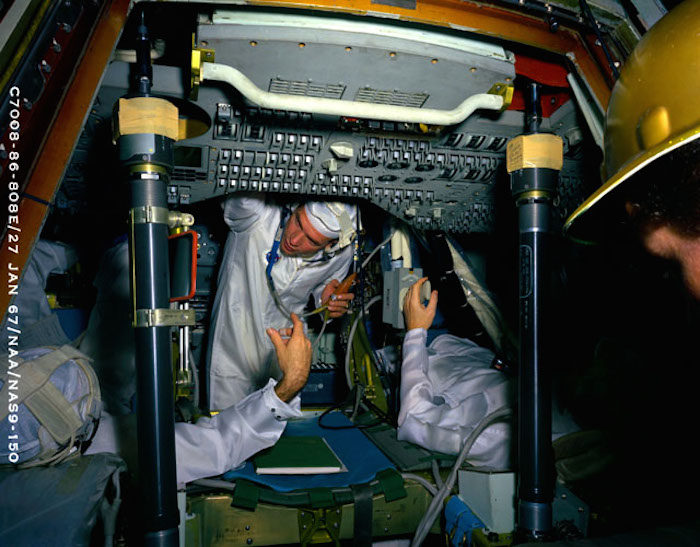

S67-23078 (27 Jan. 1967) --- Three astronauts (later to be named the Apollo 9 prime crew) in Apollo spacecraft 101 Command module during Apollo crew compartment fit and function test. Left to right are astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart.
.
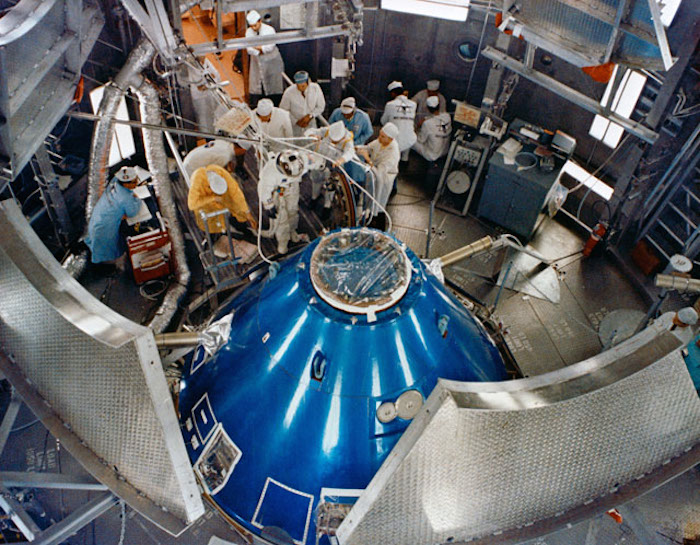

S68-55255 (6 Nov. 1968) --- Overhead view of Altitude Chamber "L" in the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building showing a member of the Apollo 9 backup crew preparing to ingress the Apollo 9 spacecraft for egress test and simulated altitude run. The Apollo 9 backup crew consists of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Richard F. Gordon Jr., and Alan L. Bean.
.
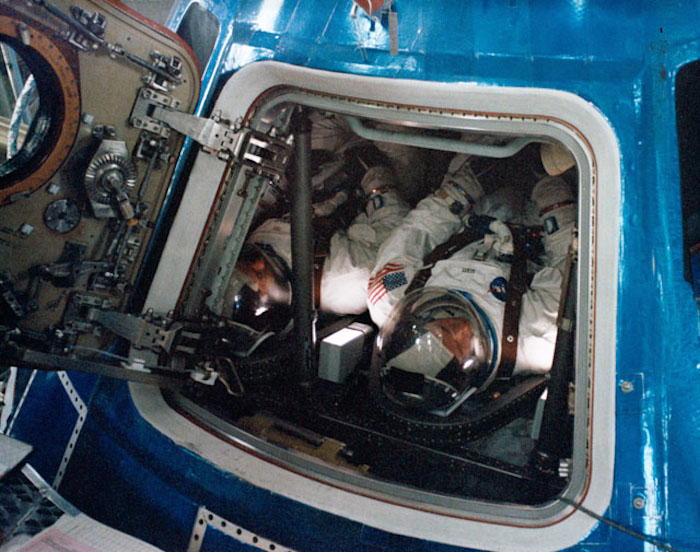

S68-55272 (15 Nov. 1968) --- The Apollo 9 prime crew is seen inside the Apollo 9 spacecraft in the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building during manned altitude chamber test activity. Left to right, are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart (out of view to far right), lunar module pilot.
.
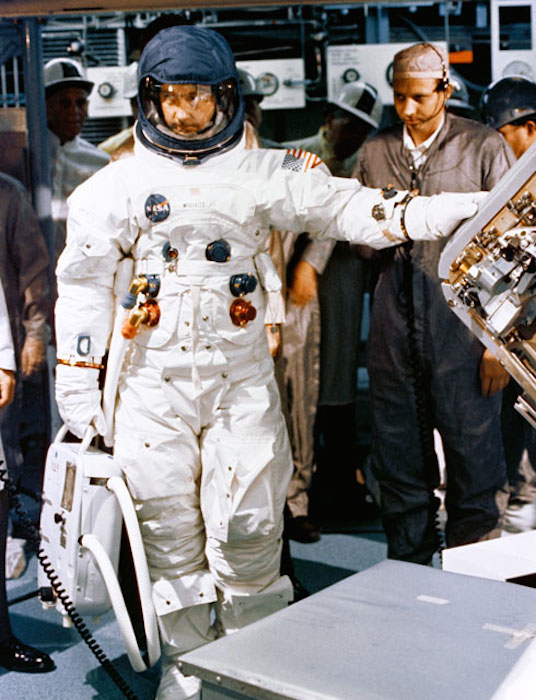

S69-18544 (19 July 1968) --- Astronaut James A. McDivitt, commander of the Apollo 9 prime crew, stands by to participate in crew compartment fit and function test activity at North American Rockwell.
.
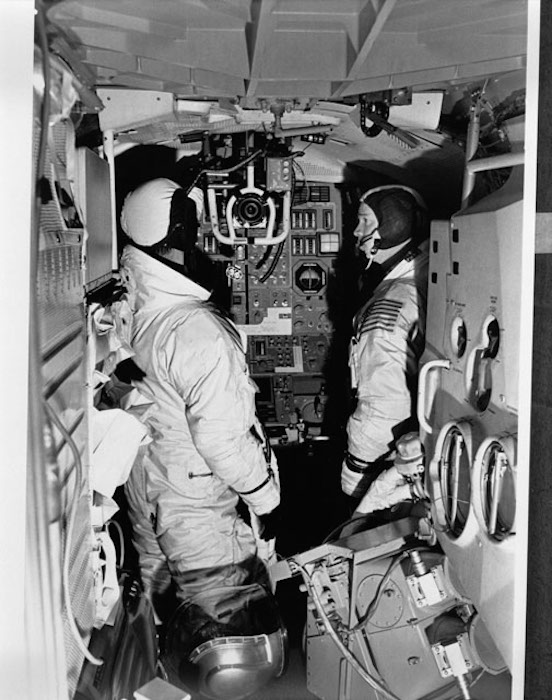

S69-19858 (December 1968) --- Two members of the Apollo 9 prime crew participate in simulation training in the Apollo Lunar Module Mission Simulator (LMMS) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). On the left is astronaut James A. McDivitt, commander; and on the right is astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot.
.
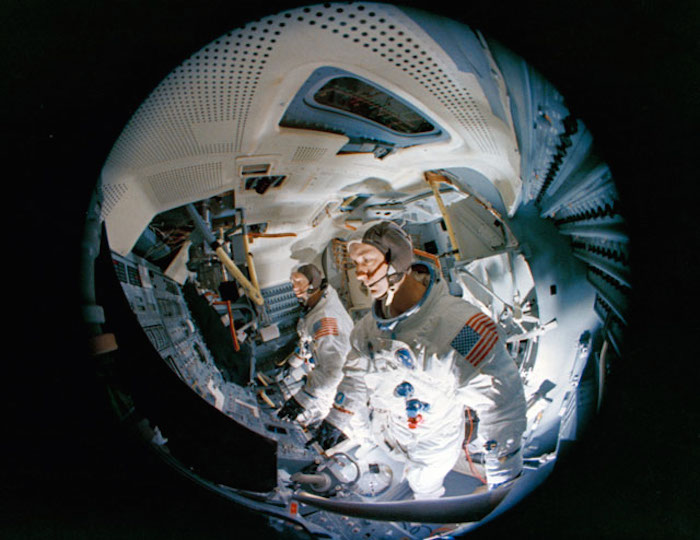

S69-19981 (23 Feb. 1969) --- Fish-eye camera lens view of the interior of the Apollo Lunar Module Mission Simulator (LMMS) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) during Apollo 9 simulation training. In the foreground is astronaut James A. McDivitt, prime crew commander; and in background is astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot.
.
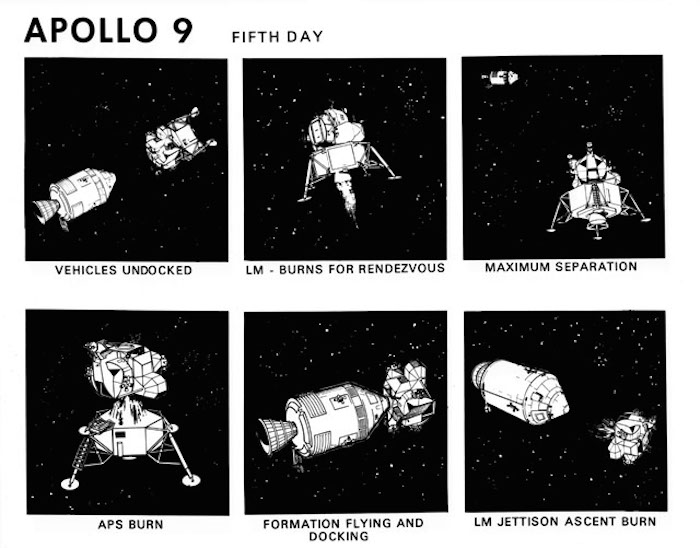
S69-19796 (February 1969) --- Composite of six artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 mission, including vehicles undocked, Lunar Module burns for rendezvous, maximum separation, ascent propulsion system burn, formation flying and docking, and Lunar Module jettison ascent burn. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
.
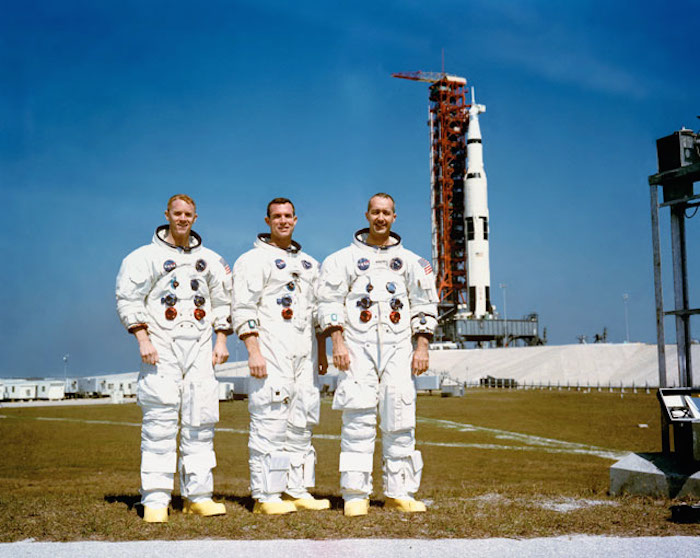

S69-25478 (23 Feb. 1969) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital space mission. Left to right, are Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and James A. McDivitt, commander. In the right background is the Apollo 9 space vehicle on Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC). They are pausing momentarily during training for their scheduled 10-day mission.
.
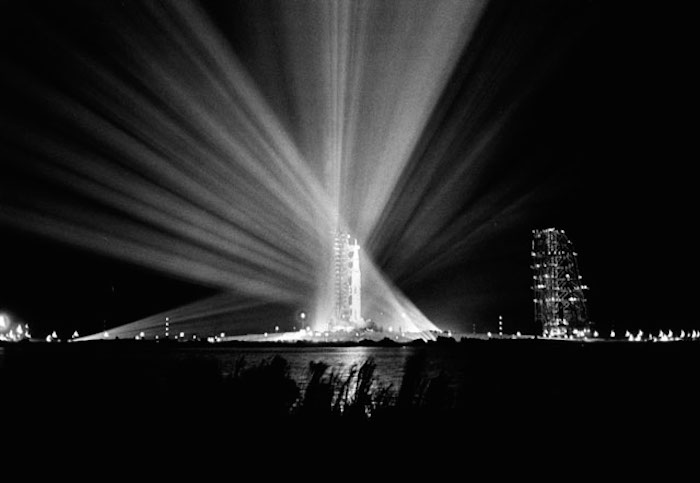

S69-25879 (23 Feb. 1969) --- Nighttime view of the 363-feet-high Apollo 9 space vehicle at Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, during preparations for the scheduled 10-day Earth-orbital space mission. The crew of the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space flight will be astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart.
.
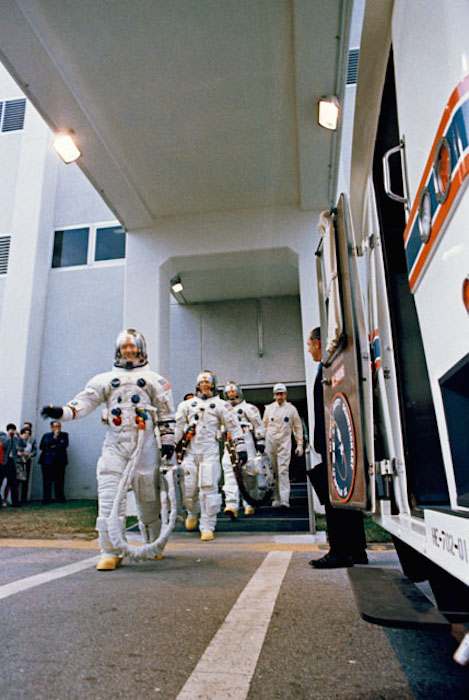

S69-25883 (3 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 crew leaves the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building during the Apollo 9 prelaunch countdown. Leading is astronaut James A. McDivitt, commander; followed by astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Moments later they entered the special transfer van which transported them to their waiting spacecraft at Pad A, Launch Complex 39. Apollo 9 was launched at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969, on a 10-day Earth-orbital mission.
.
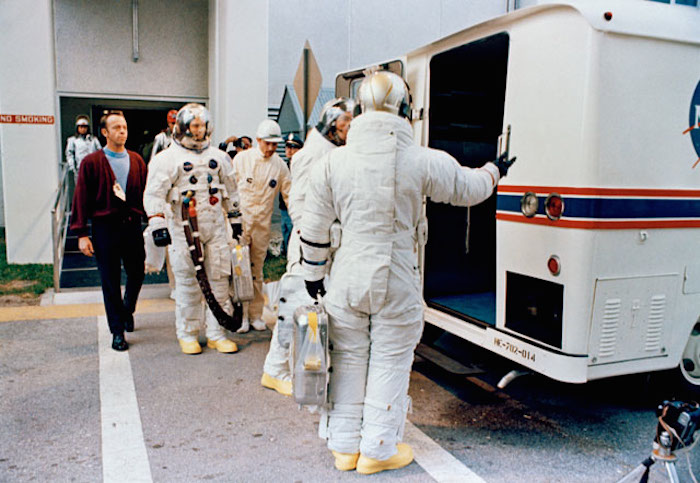

S69-25881 (3 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 crew leaves the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building during the Apollo 9 prelaunch countdown. The crewman entered the special transfer van which transported them to their waiting spacecraft at Pad A, Launch Complex 39. Astronaut James A. McDivitt (back to camera) is the commander. McDivitt appears to be inviting astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, to step first into van. In background is astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Walking along almost behind Schweickart is astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., chief, Astronaut Office, Manned Spacecraft Center. Apollo 9 was launched at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969, on a 10-day Earth-orbital mission.
.
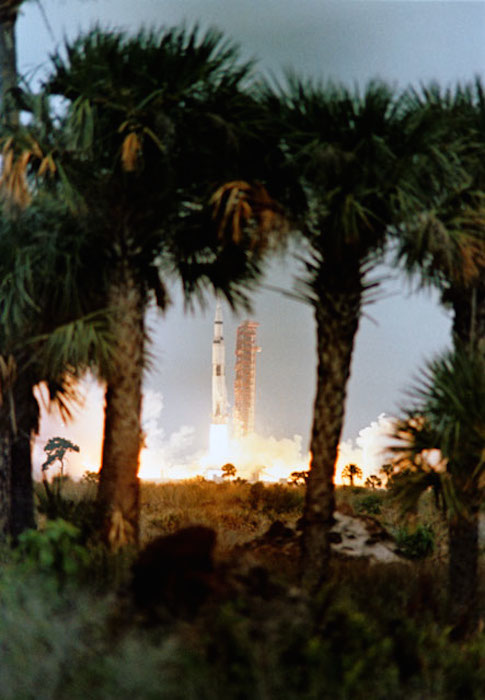

S69-25862 (3 March 1969) --- Framed by palm trees in the foreground, the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/ Saturn 504) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 is the second manned Saturn V mission.
.
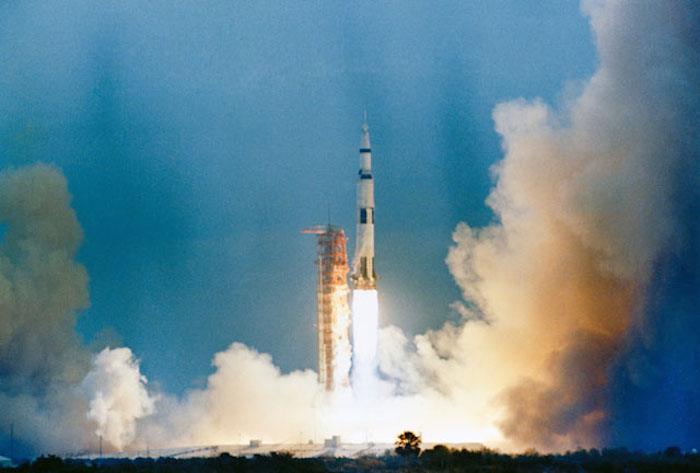

S69-25861 (3 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/ Saturn 504) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 is the second manned Saturn V mission.
.
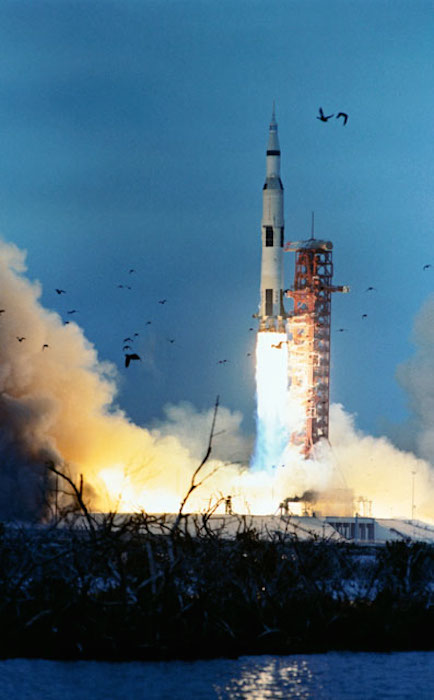

S69-25863 (3 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 is the second manned Saturn V mission.
.

AS09-19-2994 (6 March 1969) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, is photographed from the Command Module (CM) "Gumdrop" during his extravehicular activity (EVA) on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. He holds, in his right hand, a thermal sample which he is retrieving from the Lunar Module (LM) exterior. The Command and Service Modules (CSM) and LM "Spider" are docked. Schweickart, wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), is standing in "golden slippers" on the LM porch. Visible on his back are the Portable Life Support System (PLSS) and Oxygen Purge System (OPS). Astronaut James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, was inside the "Spider". Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the CM "Gumdrop".
.
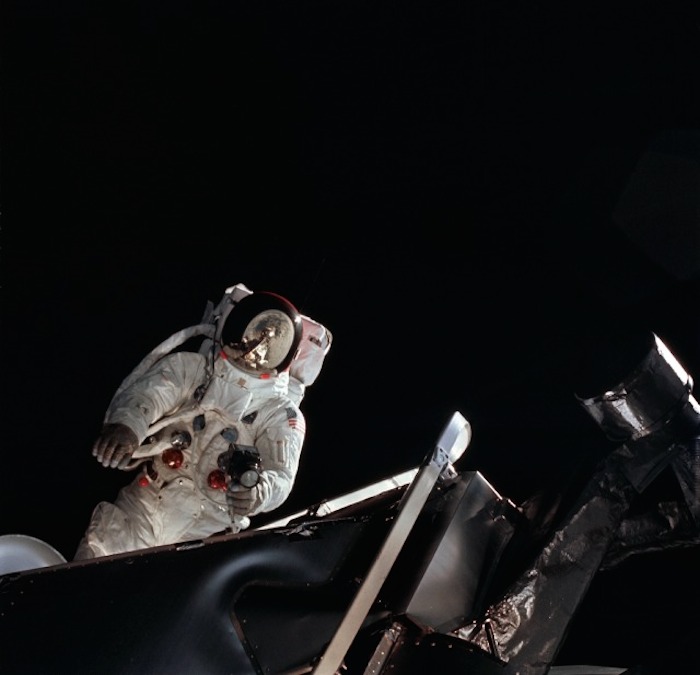

AS09-19-2983 (6 March 1969) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, operates a 70mm Hasselblad camera during his extravehicular activity (EVA) on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The Command and Service Modules (CSM) and Lunar Module (LM) "Spider" are docked. This view was taken from the Command Module (CM) "Gumdrop". Schweickart, wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), is standing in "golden slippers" on the LM porch. On his back, partially visible, are a Portable Life Support System (PLSS) and an Oxygen Purge System (OPS). Astronaut James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, was inside the "Spider". Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the CM.
.
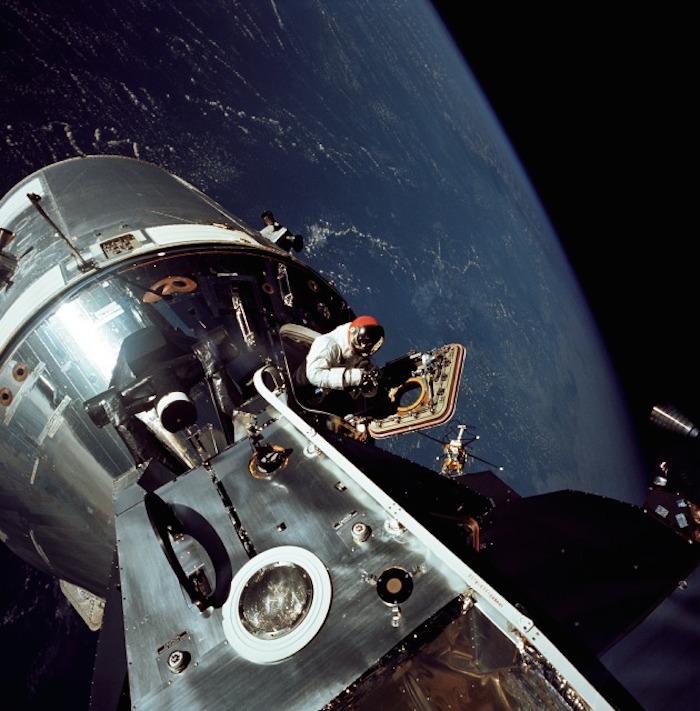

AS09-20-3064 (6 March 1969) --- Excellent view of the docked Apollo 9 Command and Service Modules (CSM) and Lunar Module (LM), with Earth in the background, during astronaut David R. Scott's stand-up extravehicular activity (EVA), on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. Scott, command module pilot, is standing in the open hatch of the Command Module (CM). Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, took this photograph of Scott from the porch of the LM. Inside the LM was astronaut James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander.
.
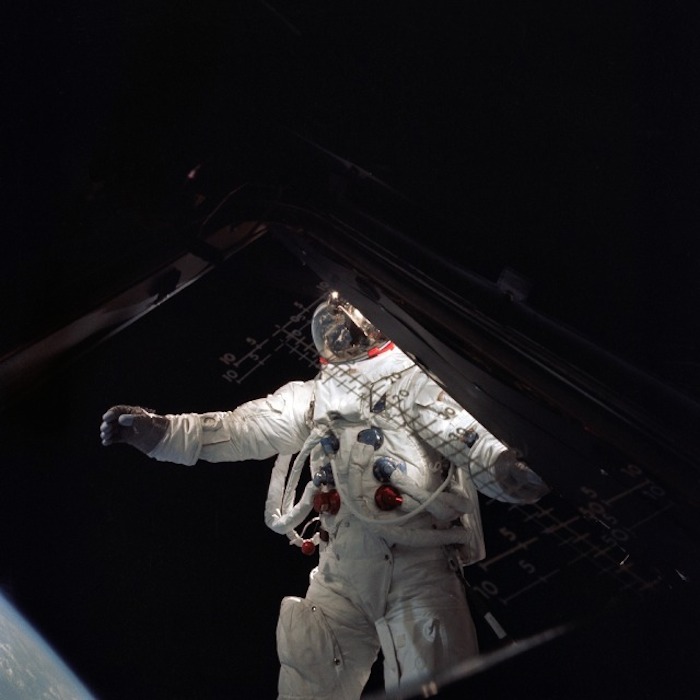

AS09-20-3094 (6 March 1969) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, stands in "golden slippers" on the Lunar Module porch during his extravehicular activity on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. This photograph was taken from inside the Lunar Module "Spider". The Command and Service Modules were docked to the LM. Schweickart is wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU). Inside the "Spider" was astronaut James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 crew commander. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls of the Command Module, "Gumdrop."
.
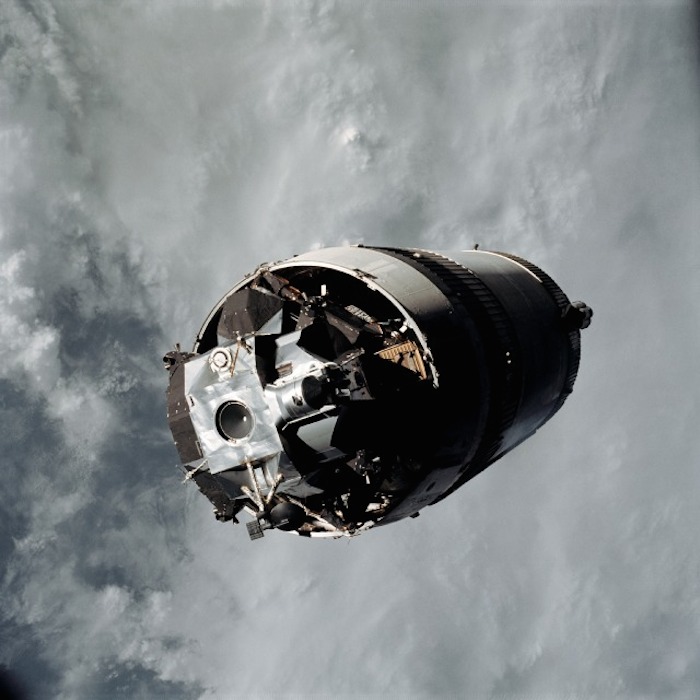

AS09-19-2919 (3 March 1969) --- The Lunar Module (LM) "Spider", still attached to the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage, is photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Gumdrop" on the first day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. This picture was taken following CSM/LM-S-IVB separation and prior to LM extraction from the S-IVB. The Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) panels have already been jettisoned. Inside the Command Module were astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot.
.
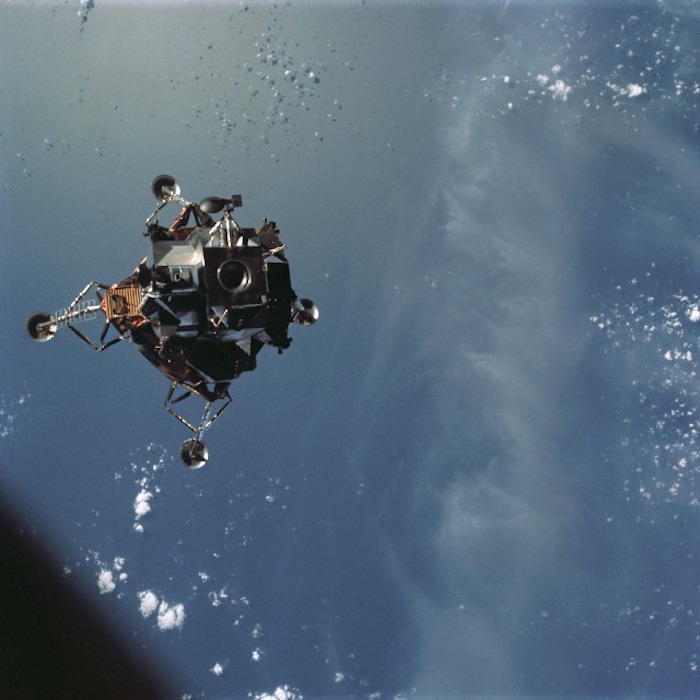

AS09-21-3181 (7 March 1969) --- A View of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module (LM), "Spider," in a lunar lading configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module (CM), "Gumdrop," while the other two astronauts checked out the LM.
.
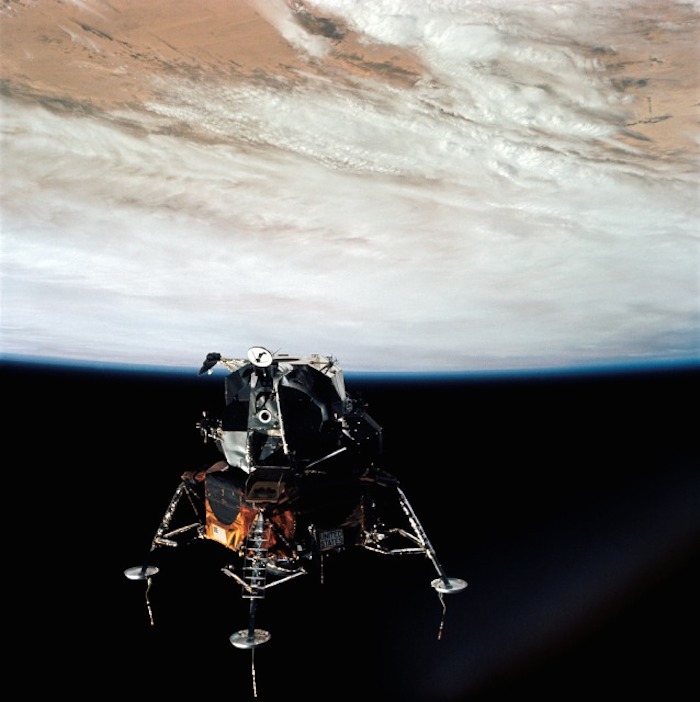

AS09-21-3212 (7 March 1969) --- A view of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module (LM), "Spider", in a lunar landing configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Lunar surface probes (sensors) extend out from landing gear foot pads. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module (CM), "Gumdrop", while the other two astronauts checked out the Lunar Module.
.
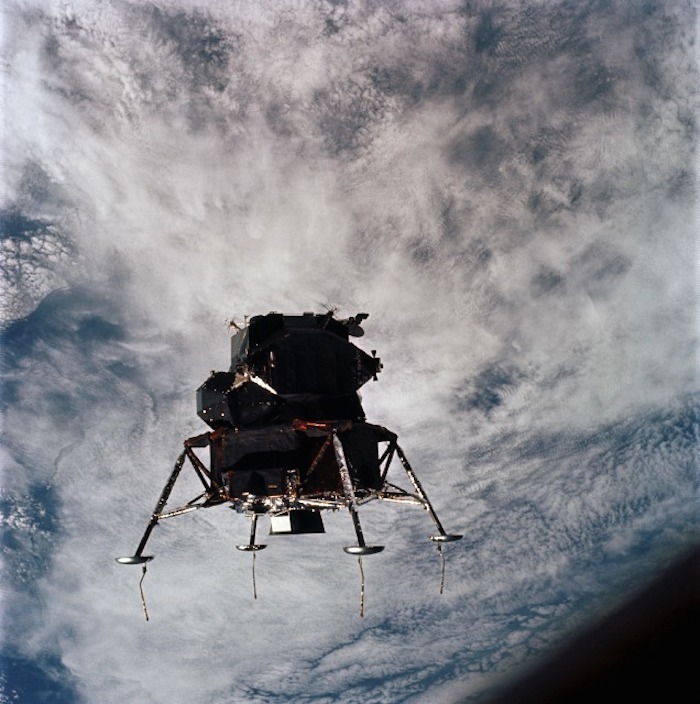

AS09-21-3199 (7 March 1969) --- Excellent view of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module, "Spider," in a lunar landing configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Lunar surface probes (sensors) extend out from the landing gear foot pads. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module, "Gumdrop," while the other two astronauts checked out the Lunar Module.
.
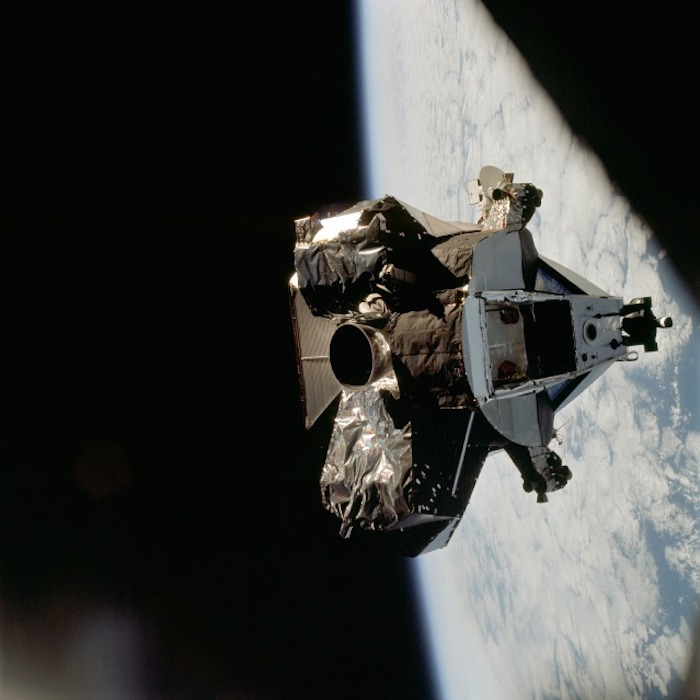

AS09-21-3236 (7 March 1969) --- The Lunar Module (LM) "Spider" ascent stage is photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. While astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the CSM "Gumdrop," astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, checked out the "Spider." The LM's descent stage had already been jettisoned.
.
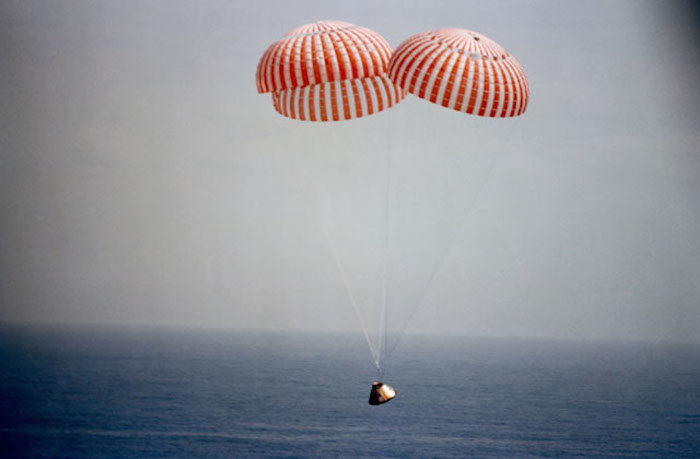

S69-20364 (13 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 spacecraft, with astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart aboard, approaches touchdown in the Atlantic recovery area to conclude a successful 10-day Earth-orbital space mission. Splashdown occurred at 12:00:53 p.m. (EST), March 13, 1969, only 4.5 nautical miles from the prime recovery ship, USS Guadalcanal.
.
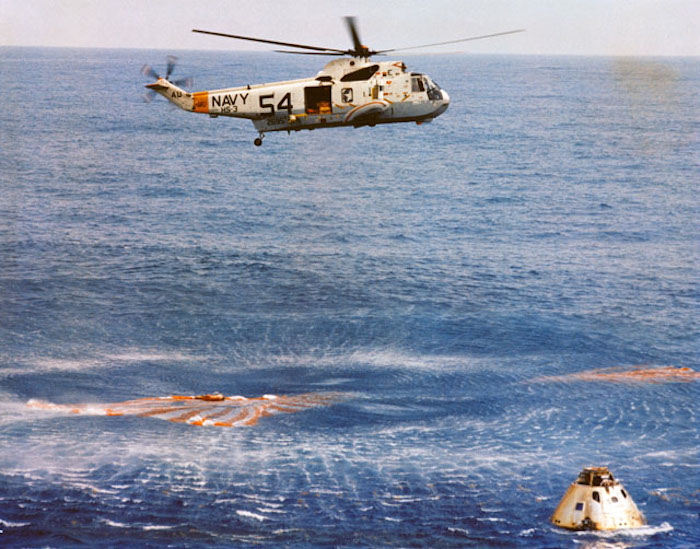

S69-27919 (13 March 1969) --- Immediately after splashdown a recovery helicopter from the USS Guadalcanal hovers over the Apollo 9 spacecraft. Still inside the Command Module (CM) are astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart. Splashdown occurred at 12:00:53 p.m. (EST), March 13, 1969, only 4.5 nautical miles from the USS Guadalcanal, the prime recovery ship, to conclude a successful 10-day Earth-orbital mission in space.
.
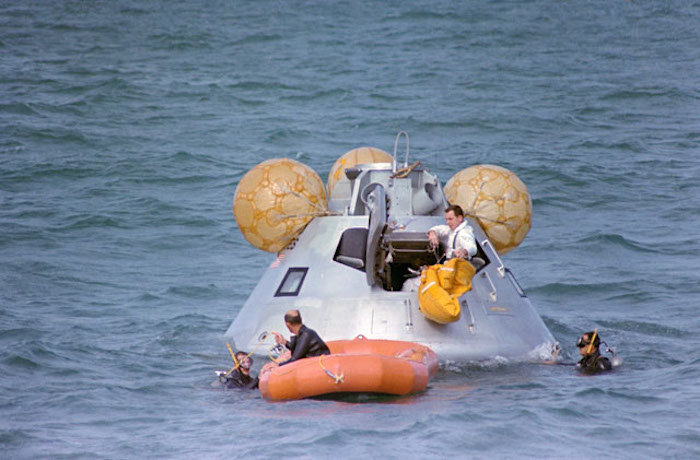

S68-50977 (20 Nov. 1968) --- The Apollo 9 prime crew participates in water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. Apollo Command Module Boilerplate 1102 was used in the training. Egressing the boilerplate is astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot. Inside the boilerplate, out of view, are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. A team of MSC swimmers assisted in the exercise. The inflated bags were used to upright the boilerplate prior to egress.
.
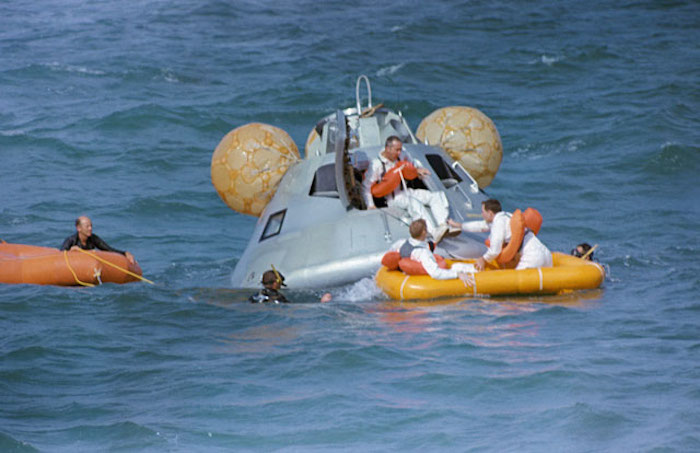

S68-50967 (20 Nov. 1968) --- The Apollo 9 prime crew participates in water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. Apollo Command Module (CM) Boilerplate 1102 was used in the training. Egressing boilerplate is astronaut James A. McDivitt, commander. In life raft are astronauts Russell L. Schweickart (on left), lunar pilot; and David R. Scott, command pilot. A team of MSC swimmers assisted in the exercise. The inflated bags were used to upright the boilerplate prior to egress.
.
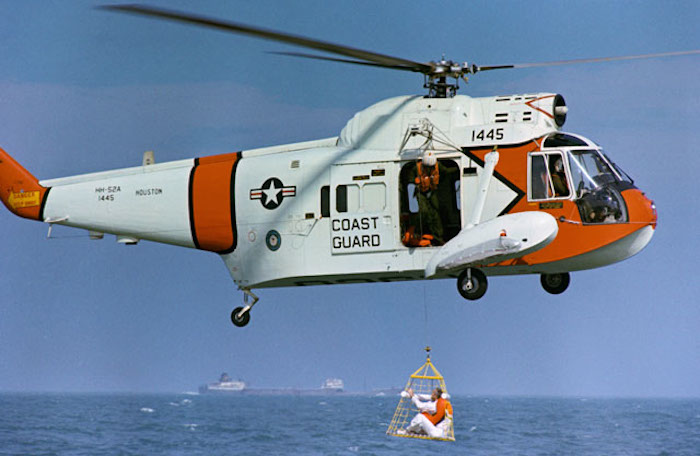

S68-50989 (20 Nov. 1968) --- Astronaut James A. McDivitt, commander of the Apollo 9 prime crew, is hoisted up to a U.S. Coast Guard helicopter in a new type rescue net during water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico.
.
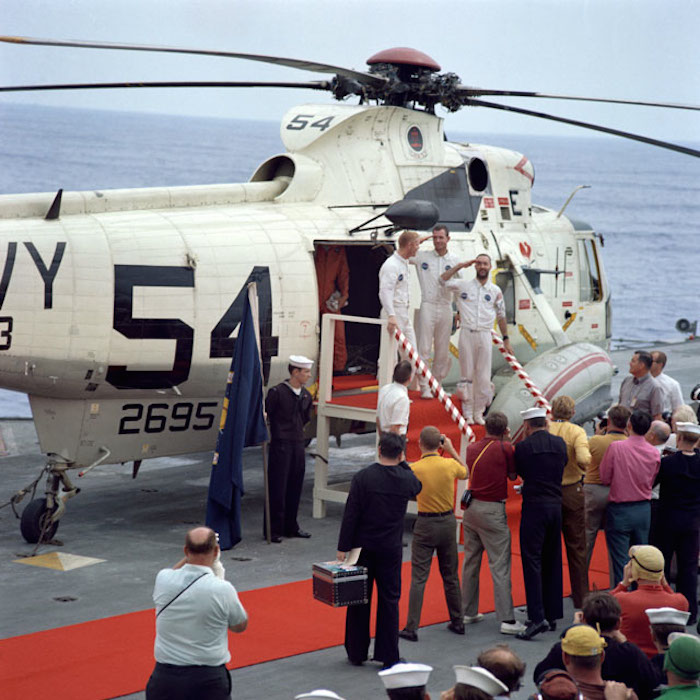

S69-20060 (13 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 crewmen arrive aboard the USS Guadalcanal as they step from a helicopter to receive a red-carpet welcome. Two of the crewmen salute the crowd of newsmen, Navy and NASA personnel gathered to greet them. Left to right, are astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot; David R. Scott (in back), command module pilot; and James A. McDivitt, commander. Splashdown occurred at 12:00:53 p.m. (EST), March 13, 1969, only 4.5 nautical miles from the USS Guadalcanal, prime recovery ship, to conclude a successful 10-day Earth-orbital space mission.
.
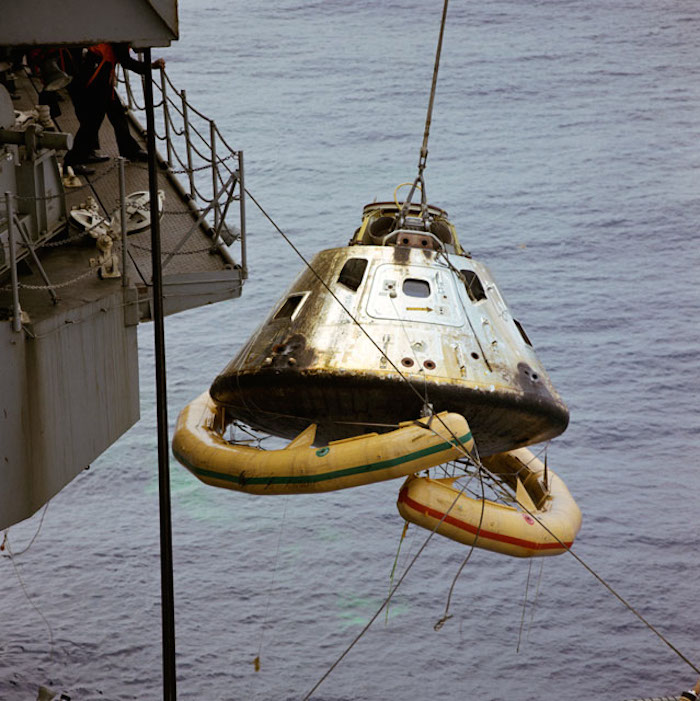

S69-20086 (13 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 Command Module (CM), with flotation collar still attached, is hoisted aboard the prime recovery ship, USS Guadalcanal, during recovery operations. The Apollo 9 crew, astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart, had already been picked up earlier by helicopter and flown to the dock of the carrier. Splashdown occurred at 12:00:53 p.m. (EST), March 13, 1969, only 4.5 nautical miles from the aircraft carrier, to conclude a successful 10-day Earth-orbital space mission.
.
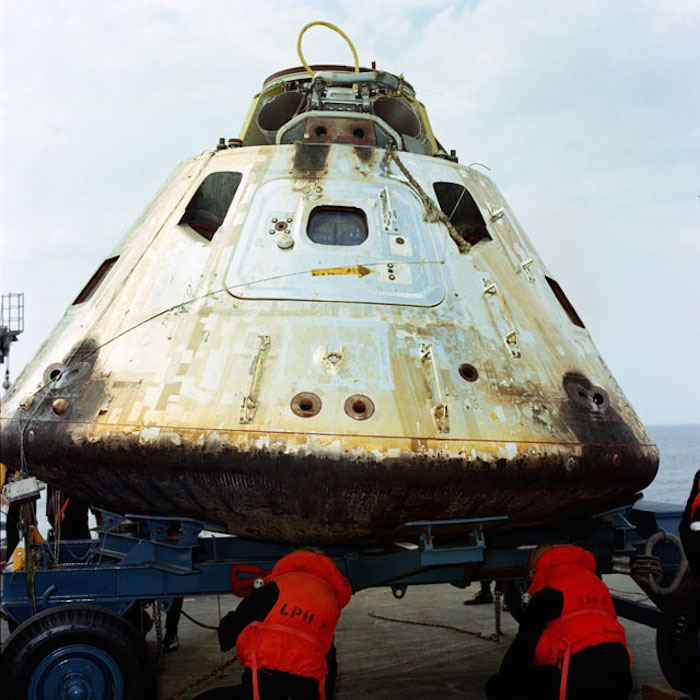

S69-20239 (13 March 1969) --- Close-up view of the Apollo 9 Command Module (CM) as it sets on dolly on the deck of the USS Guadalcanal just after being hoisted from the water. The Apollo 9 spacecraft, with astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart aboard, splashed down at 12:00:53 p.m. (EST), March 13, 1969, only 4.5 nautical miles from the aircraft carrier to conclude a successful 10-day Earth-orbital mission in space.
.
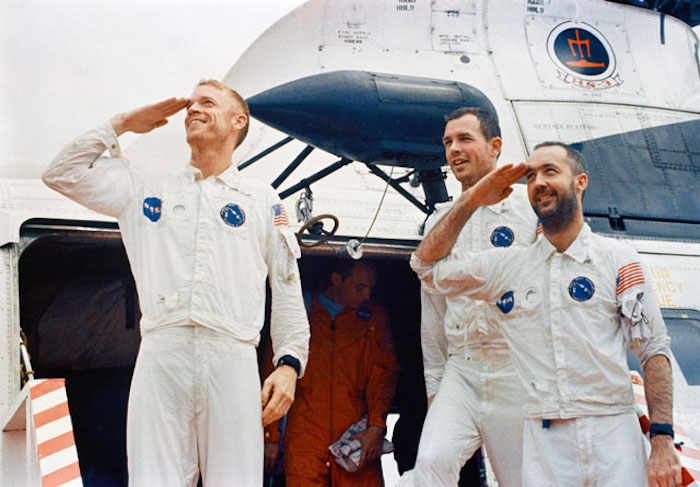

S69-27921 (13 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 crewmen arrive aboard the USS Guadalcanal as they step from a helicopter to receive a red-carpet welcome. Two of the crewmen salute the crowd of newsmen, Navy and NASA personnel gathered to greet them. Left to right, are astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, David R. Scott, and James A. McDivitt. Splashdown occurred at 12:00:53 p.m. (EST), March 13, 1969, only 4.5 nautical miles from the USS Guadalcanal, prime recovery ship, to conclude a successful 10-day Earth-orbital space mission.
.
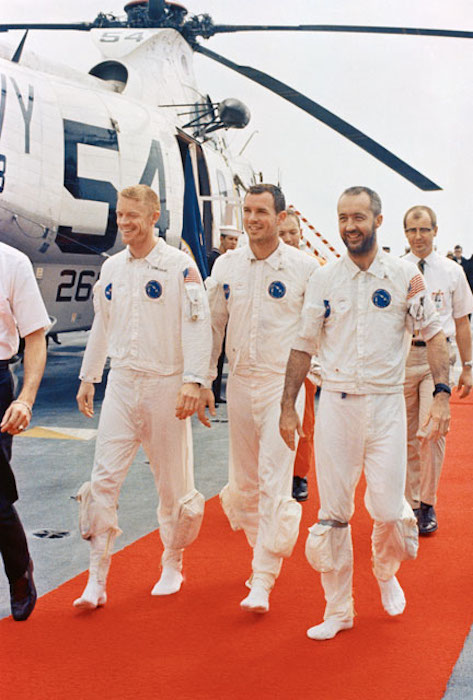

S69-27920 (13 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 crew men walk on a red carpet after arriving aboard the prime recovery ship, USS Guadalcanal. Left to right, are astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, David R. Scott, and James A. McDivitt. They are walking from the recovery helicopter which picked them up from the splashdown area. Splashdown occurred at 12:00:53 p.m. (EST), March 13, 1969, only 4.5 nautical miles from the USS Guadalcanal to conclude a successful 10-day Earth-orbital space mission.
.
Quelle: NASA
5488 Views
