4.12.2024
BepiColombo probe captures haunting Mercury image on 5th of 6 gravity assist flybys
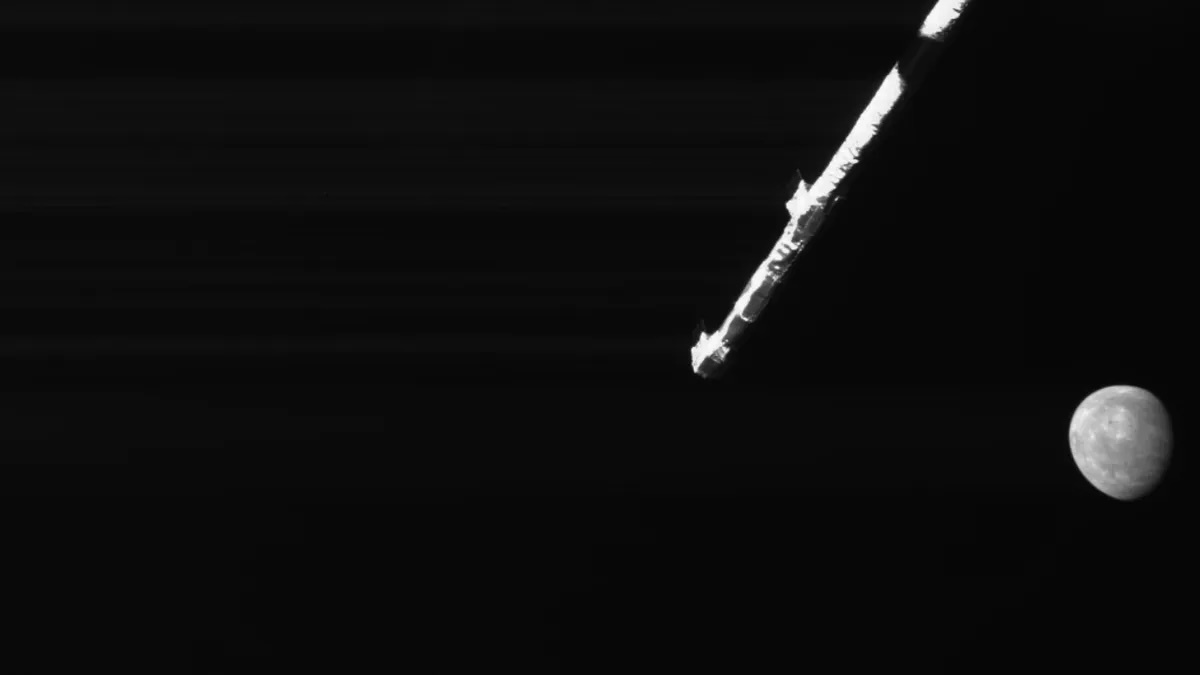

(Image credit: JAXA/ESA)
The BepiColombo Mercury probe flew close to our solar system's innermost planet this week, capturing another haunting image as it zoomed by.
On Sunday (Dec. 1), BepiColombo made its fifth of six flybys of Mercury. On this most recent rendezvous, the probe was 200 times farther from the planet than on its previous flyby, which saw it come within just 103 miles (165 kilometers) of Mercury's surface.
Despite the greater distance in this recent flyby, the probe was once again able to generate an eerie image of diminutive Mercury, shining alone in the darkness of space. This fifth flyby is the first during which the probe used its Mercury Radiometer and Thermal Infrared Spectrometer (MERTIS) instrument, which measures the temperature and composition of the planet's surface and reveals what types of minerals are found on the planet's surface, which the European Space Agency (ESA) says is "one of the key Mercury mysteries that BepiColombo is designed to tackle."
BepiColombo is operated by the ESA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The probe launched in 2018 atop an Ariane 5 rocket on an eight-year voyage that will place it in orbit around Mercury.

(Image credit: ESA/JAXA)
The original mission plan had the spacecraft arriving in December 2025, but BepiColombo experienced thruster glitches that slowed things down; the probe is now set to be inserted into Mercury's orbit in November 2026.
Once there, the spacecraft will separate into two separate orbiters: ESA's Mercury Planetary Orbiter and JAXA's Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter. The pair will then study the small, hot world with 16 different science instruments.
The spacecraft has been flying by Earth, Venus and Mercury since 2020, use the planets' gravity to help put it on the right course to enter Mercury's orbit.
BepiColombo made its first Earth and Venus flybys in 2020, and first swung past Mercury on Oct. 1, 2021. After one flyby in 2022 and 2023 each, the probe then made close approaches to Mercury on Sept. 4, 2024 and Dec. 1, 2024.
The probe's next Mercury flyby will occur on Jan. 8, 2025.
Quelle: SC
----
Update: 17.12.2024
.
BepiColombo’s fifth flyby of Mercury reveals planet’s surface in mid-infrared light

The European Space Agency’s BepiColombo spacecraft recently performed its fifth flyby of Mercury on Dec. 1, becoming the first spacecraft ever to observe the planet in mid-infrared light. BepiColombo’s observations from the flyby have revealed interesting new details on the Mercury’s surface, including temperature and composition variations.
BepiColombo is only the third mission to visit the smallest planet in our solar system, making Mercury the least-explored rocky planet in the solar system. In 2026, BepiColombo will enter orbit around Mercury and begin its primary mission, becoming the first spacecraft to orbit Mercury since NASA’s Messenger from 2011 to 2015.
BepiColombo’s long journey to Mercury began on Oct. 20, 2018, when the mission launched from French Guiana atop an Ariane 5 rocket. The mission was initially planned to arrive at the planet in December 2025. However, thruster issues discovered in September 2024 forced a one-year extension of the coast phase, bringing the arrival date to November 2024.
The mission’s coast phase has involved several flybys of Earth, Venus, and Mercury, using the gravitational pull from each planet to alter BepiColombo’s orbital trajectory around the Sun and bring the spacecraft closer to Mercury. BepiColombo’s recent Dec. 1 flyby saw the spacecraft fly within 38,000 km of the planet’s surface. The primary objective of this flyby was to gather additional data on Mercury’s surface and surrounding environment.

Infographic highlighting BepiColombo’s fifth flybys. (Credit: ESA)
The spacecraft measured particles and electromagnetic fields while in the planet’s vicinity and, for the first time, imaged the cratered surface in mid-infrared wavelengths with the Mercury Radiometer and Thermal Infrared Spectrometer (MERTIS) instrument.
“With MERTIS, we are breaking new ground and will be able to understand the composition, mineralogy, and temperatures on Mercury much better,” said MERTIS principal investigator Harald Hiesinger of the University of Münster in Germany.
“After about two decades of development, laboratory measurements of hot rocks similar to those on Mercury, and countless tests of the entire sequence of events for the mission duration, the first MERTIS data from Mercury is now available. It is simply fantastic!” added MERTIS co-principal investigator Jörn Helbert of the German Aerospace Center (DLR) in Berlin.
The first observations from MERTIS revealed that certain areas of Mercury’s surface shine brighter in the mid-infrared than others. More specifically, the Caloris Basin and parts of a large volcanic plain in Mercury’s northern hemisphere emit more mid-infrared light.
Mid-infrared light increases in these regions due to surface temperature, roughness, and composition. MERTIS’ imaging spectrometer is sensitive to mid-infrared light with wavelength between 7 and 14 nm. This wavelength range is known to be particularly suitable for observing and distinguishing rock-forming minerals in surface features.

MERTIS’s mid-infrared measurements of Mercury’s surface from the Dec. 1 flyby. (Credit: MERTIS/DLR/University of Münster/NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington)
“The moment when we first looked at the MERTIS flyby data and could immediately distinguish impact craters was breathtaking. There is so much to be discovered in this dataset — surface features that have never been observed in this way before are waiting for us. We have never been this close to understanding the global surface mineralogy of Mercury with MERTIS ready for the orbital phase of BepiColombo,” said project lead Solmaz Adeli of the DLR.
Mercury’s surface composition has long been a mystery in planetary science, and Messenger’s data on the planet’s surface and composition has proven lackluster in providing definitive results. When MERTIS and other BepiColombo instruments arrive in orbit around the planet in 2026, they will provide planetary scientists with better surface imaging resolution and elemental composition accuracy.
Messenger’s data has led scientists to believe that Mercury’s surface contains low amounts of iron — an interesting discovery given the planet’s large iron-nickel core. Messenger also showed that some chemical elements that easily evaporate are present in high concentrations on Mercury’s surface despite the planet’s tight orbit around the Sun.
Another mystery surrounding Mercury is its dark appearance. While the planet’s cratered surface may look similar to that of the Moon at first glance, it only reflects around two-thirds as much light as the Moon’s surface — a fascinating characteristic for a planet that orbits extremely close to our Sun.
MERTIS’s measurements rely on how different minerals glow in mid-infrared light and how the glow varies with temperature. Mission teams have been testing different material and mineral mixtures in a lab to train both the instrument and analysis programs for BepiColombo and MERTIS’s arrival at the planet in 2026. During the tests, the mixtures are heated to different temperatures so that they glow, and then measurements of their glow are made in mid-infrared wavelengths.
“Because Mercury’s surface is surprisingly poor in iron, we have been testing natural and synthetic minerals that lack iron. The materials tested include rock-forming minerals to simulate what Mercury’s surface might be made of,” Solmaz explained.
Shortly after entering orbit, MERTIS will create a global map of Mercury’s surface mineral distribution with a resolution down to 500 m.
Interestingly, MERTIS is currently partially blocked due to the stacked configuration of the BepiColombo spacecraft. BepiColombo is comprised of two satellites that have been stacked atop each other. Once in orbit around Mercury, the two halves, the Mercury Planetary Orbiter (MPO) and Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter (MMO), will separate and begin their missions.
MERTIS’s design features two “ports” for collecting and calibrating data. One of these ports is currently blocked due to BepiColombo’s stacked nature; however, scientists reworked the instrument to operate with only one open port for the flybys. Once in orbit around Mercury, both ports will be open and MERTIS will operate as planned.
“These fascinating and valuable results from the MERTIS instrument are only a tantalizing hint of the great results we’re expecting from the entire BepiColombo science payload once both orbiters are operating in orbit around Mercury,” says BepiColombo project scientist Geraint Jones
Quelle: NSF
----
Update: 3.01.2025
.
Wassereis und Diamanten?

Der Merkur ist der am wenigsten erforschte Planet des Sonnensystems. Das könnte sich jetzt ändern. Eine Sonde liefert völlig neue Daten.
Astronomen können zum ersten Mal einen genaueren Blick auf den Merkur werfen: Die Sonde "BepiColombo" hat bei ihrem fünften Vorbeiflug an dem Planeten wertvolle Messdaten gesammelt, wie die Universität Münster mitteilt, die mit einem Experiment an der Mission beteiligt ist.
Dieses Experiment wird mit dem Infrarotspektrometer Mertis durchgeführt, das bei dem Vorbeiflug von "BepiColombo" in einer Entfernung von 37.630 Kilometern die Oberfläche des Planeten im mittleren Infrarotbereich beobachtet. "Nie zuvor wurde der Merkur im von Mertis abgedeckten Wellenlängenbereich untersucht", heißt es.
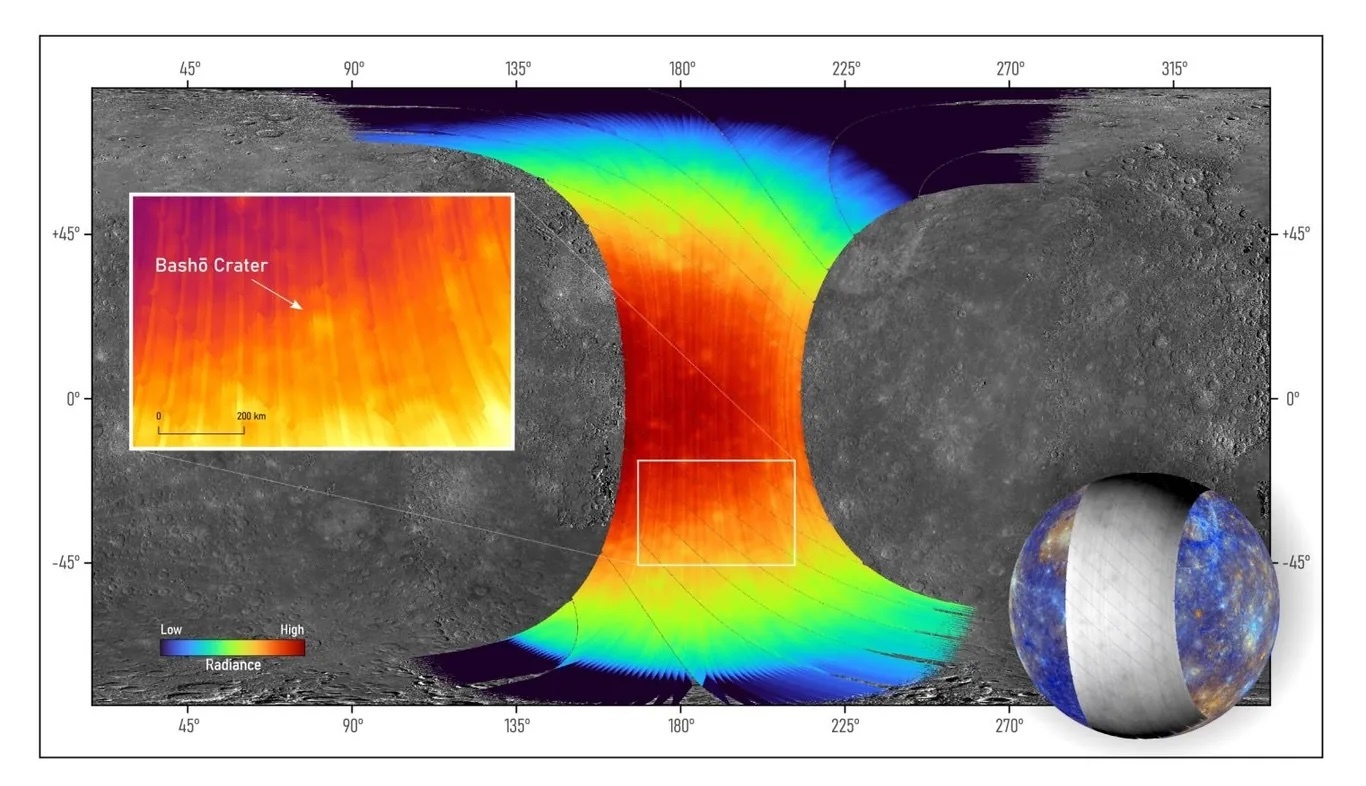
Die Aufnahmen mit dem thermalen Infrarotspektrometer Mertis zeigen die Beschaffenheit des "Bashō"-Einschlagskraters. (Quelle: Mertis / DLR / University of Münster)
Die Daten zeigen den Wissenschaftlern die Unterschiede bei der Oberflächentemperatur und bei der Zusammensetzung der kraterreichen Oberfläche des Merkurs. Die ersten Aufnahmen zeigen Temperaturen von bis zu 420 Grad Celsius auf der von der Sonne beschienenen Seite des Planeten. Hinzu kommen unterschiedliche Signaturen von Einschlagskratern.
Einschlagskrater besteht aus dunklem und sehr hellem Material
Besonders interessant seien Aufnahmen des Einschlagskraters "Bashō", der bereits von anderen Sonden beobachtet wurde. Die jetzt gemachten Bilder zeigen, dass der Krater "sowohl sehr dunkles als auch sehr helles Material aufweist", heißt es. Es gebe eine "Anomalie in der Strahlungsintensität im mittleren Infrarot, die die besonderen Eigenschaften des Kraters" bestätigten.
Der Merkur sei ein "Planet der Extreme", sagt Harald Hiesinger von der Uni Münster. Über den Himmelskörper sei im Vergleich zu anderen Planeten bislang wenig bekannt. Dabei könne der Merkur mehr über die Entstehung des Sonnensystems verraten.
Wassereis trotz der Nähe zur Sonne
Wie bereits bekannt war, tritt auf dem Merkur an den Polen trotz der Nähe von nur 58 bis 69 Millionen Kilometern zur Sonne vermutlich Wassereis auf. Daten einer anderen Sonde hatten im vergangenen August vermuten lassen, dass im Inneren des Planeten eine kilometerdicke Schicht aus Diamanten existieren könnte.
Die weiteren Vorbeiflüge von "BepiColombo" am Merkur sollen mehr Details über die Beschaffenheit des Planeten liefern. Im November 2026 soll die Sonde in eine Merkur-Umlaufbahn einschwenken.
Dann soll sich "BepiColombo" der Oberfläche des Merkurs bis auf 460 Kilometer nähern und Daten mit einer Auflösung von bis zu 500 Metern liefern. "Dann kann MERTIS sein volles Potential ausschöpfen", sagt Wissenschaftler Hiesinger.
Quelle: t-online.de
----
Update: 8.01.2025
.
BepiColombo to swing by Mercury for the sixth time
On 8 January 2025, the ESA/JAXA BepiColombo mission will fly just 295 km above Mercury's surface, with a closest approach scheduled for 06:59 CET (05:59 UTC). It will use this opportunity to photograph Mercury, make unique measurements of the planet’s environment, and fine-tune science instrument operations before the main mission begins. This sixth and final flyby will reduce the spacecraft’s speed and change its direction, readying it for entering orbit around the tiny planet in late 2026.
BepiColombo is more than six years into its eight-year journey to planet Mercury. In total, it is using nine planetary flybys to help steer itself into orbit around the small rocky planet: one at Earth, two at Venus, and six at Mercury. Making the most of this sixth close approach to the small rocky planet, BepiColombo's cameras and various scientific instruments will investigate Mercury's surface and surroundings.
BepiColombo will approach on the night side of the planet. Its monitoring cameras will get the most interesting views of Mercury’s surface as the spacecraft comes around to the planet's sunlit side, from about 07:06 CET, seven minutes after the closest approach. We expect to release the first images on 9 January, with other scientific data to follow.
“We can't wait to see what BepiColombo will reveal during this sixth and final flyby of Mercury. While we're still two years away from the mission's main science phase, we expect this encounter to provide us with beautiful images and important scientific insights into the least-explored terrestrial planet,” says Geraint Jones, ESA's BepiColombo Project Scientist.

Warming up for Mercury's shadow
While Mercury's sunlit side is scorching, the first part of the upcoming flyby will be spent on Mercury's cold, dark night side. While in Mercury's shadow, BepiColombo will not receive any direct sunlight for more than 23 minutes and will rely only on its batteries.
Mission operators at the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) are gearing up for this critical moment of the flyby. One day ahead of the eclipse, they will warm up the spacecraft and only stop the heating a few minutes before BepiColombo enters Mercury's shadow. This operation will help save battery power by ensuring that the spacecraft does not need to use its heaters during the eclipse.
"This is the first time BepiColombo stays in the shadow of Mercury for so long. We have fully charged its batteries and raised the temperature of all components. From ESA's mission control centre, we will keep a close watch on the battery status and the temperature of all systems during the flyby," says Ignacio Clerigo, BepiColombo's Spacecraft Operations Manager.
The Italian Spring Accelerometer (ISA) will record the accelerations felt by the spacecraft as it experiences not only the gravitational pull of the planet, but also the change in solar radiation and temperature as the spacecraft enters and exits Mercury's shadow. ISA will also record any movements and vibrations of the spacecraft caused by the motion of, for example, the spacecraft's solar arrays.
Key views of Mercury's shadowy north pole
Excitingly, BepiColombo's route takes it right over Mercury's north pole. This allows the spacecraft to peer down into craters whose insides never get touched by the Sun. Despite temperatures reaching 450 °C on Mercury's sunlit surface, the polar ‘permanent shadow regions’ are literally ice-cold.
Data gathered by instruments on NASA’s Messenger spacecraft between 2011 and 2015, plus radar observations from Earth, have provided strong evidence for water ice in some of these craters. Whether there is really water ice on hot Mercury is one of the top five mysteries that BepiColombo has set out to solve.
During this flyby, BepiColombo's monitoring camera 1 (M-CAM 1) should get some nice views of the permanently shadowed Prokofiev, Kandinsky and Tolkien craters.
Other exciting features that BepiColombo's monitoring cameras will see are the deep Stieglitz and Gaudí craters, Mercury's largest impact crater (the more than 1500 km-wide Caloris Basin), and the vast northern plains known as Borealis Planitia.
Below is a simulation of M-CAM 1's views of Mercury during the flyby, using a digital topography model prepared by the Messenger mission team. There is a gap in this model around the poles. BepiColombo's upcoming flyby views, and the mission's polar orbits around Mercury from 2026, will greatly improve the coverage in these regions.


Access the video
More insight into Mercury's surroundings
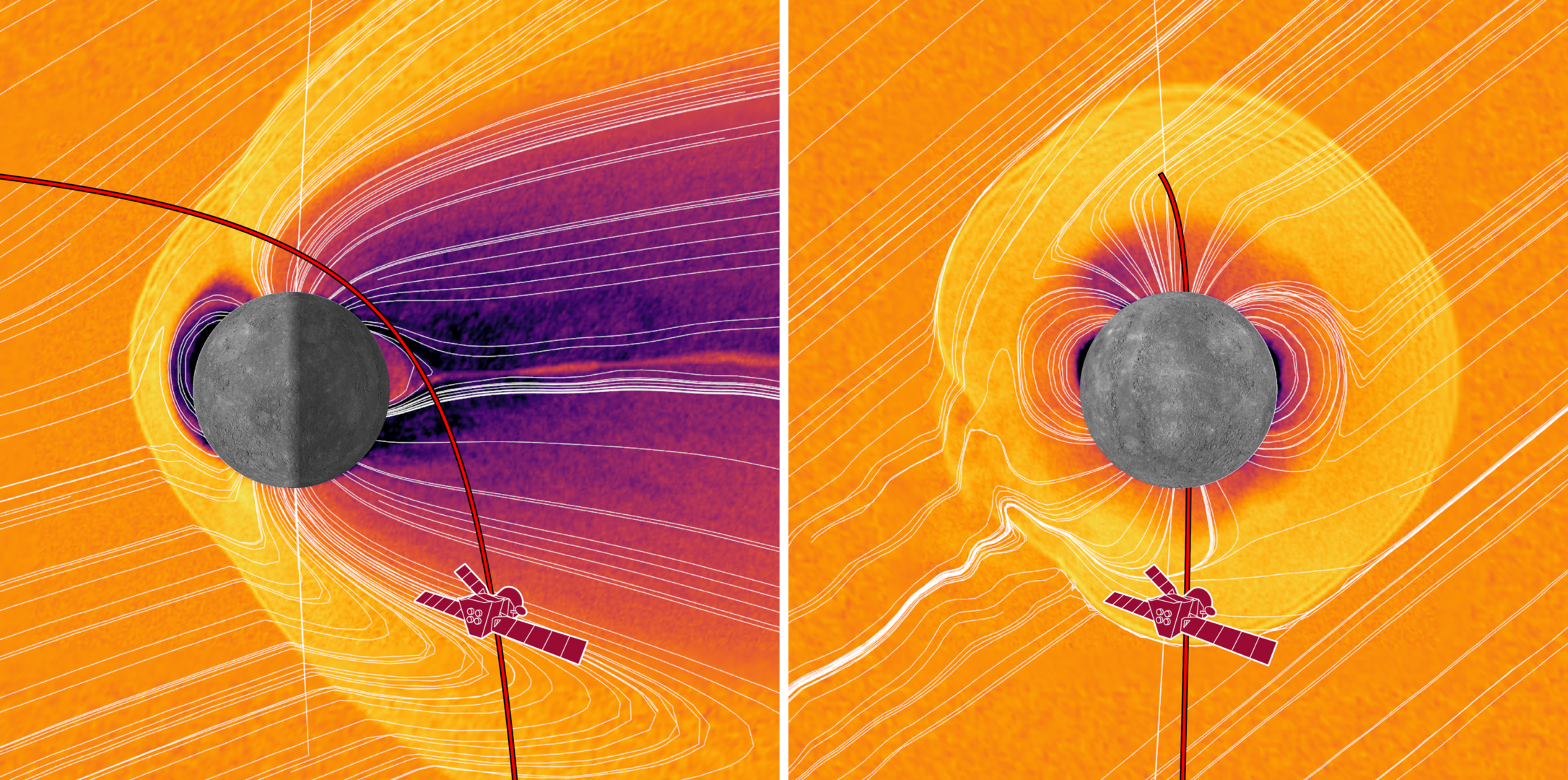
BepiColombo's sixth flyby also takes it on a unique route through Mercury's magnetic and particle environment. The spacecraft will fly through regions around Mercury that haven't been sampled before and parts of which won't be visited by BepiColombo during the main science phase of its mission.
The upcoming flyby route, crossing the equator opposite the Sun on Mercury's night side before flying over the planet’s north pole, makes it particularly interesting. In darkness, the spacecraft will pass through regions where charged particles can flow from the planet’s magnetic tail towards its surface. At the poles, in regions called the cusps, planetary magnetic field lines also funnel particles coming from the Sun down to Mercury's surface. The spacecraft will pass through the northern cusp.

Two particle analysers (SERENA and MPPE) will 'taste’ the particles in these fascinating regions, parts of which won’t be visited when orbiting the planet. Meanwhile, two magnetometers (MPO-MAG and MMO-MGF) will sense Mercury's magnetic field, while a dust monitor (MDM) will measure larger dust particles. (Read more about BepiColombo's science instruments on ESA's Mercury Planetary Orbiter and JAXA's Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter.)
This will build on measurements taken during BepiColombo's earlier Mercury flybys, as well as by NASA's Messenger mission.
About BepiColombo
Launched on 20 October 2018, BepiColombo is a joint mission between the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), executed under ESA leadership. It is Europe's first mission to Mercury.

The mission comprises two scientific orbiters: ESA’s Mercury Planetary Orbiter (MPO) and JAXA’s Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter (Mio). The European Mercury Transfer Module (MTM) carries the orbiters to Mercury.
After arrival at Mercury in late 2026, the spacecraft will separate and the two orbiters will manoeuvre to their dedicated polar orbits around the planet. Starting science operations in early 2027, both orbiters will gather data during a one-year nominal mission, with a possible one-year extension.
Quelle: ESA
----
Update: 10.01.2025
.
Top three images from BepiColombo's sixth Mercury flyby
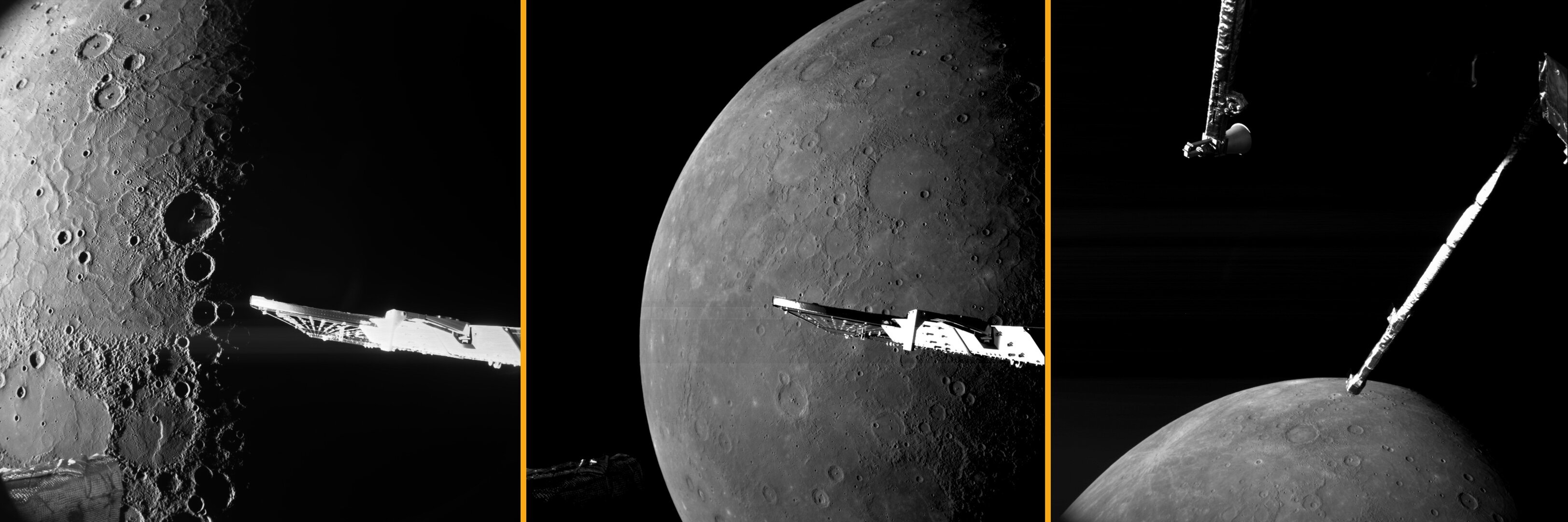

On 8 January 2025, the ESA/JAXA BepiColombo mission flew past Mercury for the sixth time, successfully completing the final ‘gravity assist manoeuvre’ needed to steer it into orbit around the planet in late 2026. The spacecraft flew just a few hundred kilometres above the planet's north pole. Close-up images expose possibly icy craters whose floors are in permanent shadow, and the vast sunlit northern plains.
At 06:59 CET, BepiColombo flew just 295 km above Mercury's surface on the planet's cold, dark night side. Around seven minutes later, it passed directly over the Mercury's north pole before getting clear views of the planet's sunlit north.
European Space Agency (ESA) Director General Josef Aschbacher revealed the first image during his Annual Press Briefing on 9 January. As during BepiColombo's previous flybys, the spacecraft's monitoring cameras (M-CAMs) did not disappoint.
This flyby also marks the last time that the mission's M-CAMs get up-close views of Mercury, as the spacecraft module they are attached to will separate from the mission's two orbiters – ESA’s Mercury Planetary Orbiter and JAXA’s Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter – before they enter orbit around Mercury in late 2026.
Celebrating the M-CAMs' final hurrah, let's explore the best three images from BepiColombo's sixth close encounter with the little planet, and what they reveal about mysterious Mercury.

Peering into Mercury's darkest craters
After flying through Mercury's shadow, BepiColombo's monitoring camera 1 (M-CAM 1) got the first close views of Mercury's surface. Flying over the ‘terminator’ – the boundary between day and night – the spacecraft got a unique opportunity to peer directly down into the forever-shadowed craters at planet's north pole.
The rims of craters Prokofiev, Kandinsky, Tolkien and Gordimer cast permanent shadows on their floors. This makes these unlit craters some of the coldest places in the Solar System, despite Mercury being the closest planet to the Sun!
Excitingly, there is existing evidence that these dark craters contain frozen water. Whether there is really water on Mercury is one of the key Mercury mysteries that BepiColombo will investigate once it is in orbit around the planet.
A surface shaped by impacts and lava
To the left of Mercury's north pole in M-CAM 1's view lie the vast volcanic plains known as Borealis Planitia. These are Mercury’s largest expanse of ‘smooth plains' and were formed by the widespread eruption of runny lava 3.7 billion years ago.
This lava flooded existing craters, such as the Henri and Lismer craters highlighted in the image. The wrinkles in the surface were formed over billions of years following the solidification of the lava, probably in response to the planet contracting as its interior cooled down.
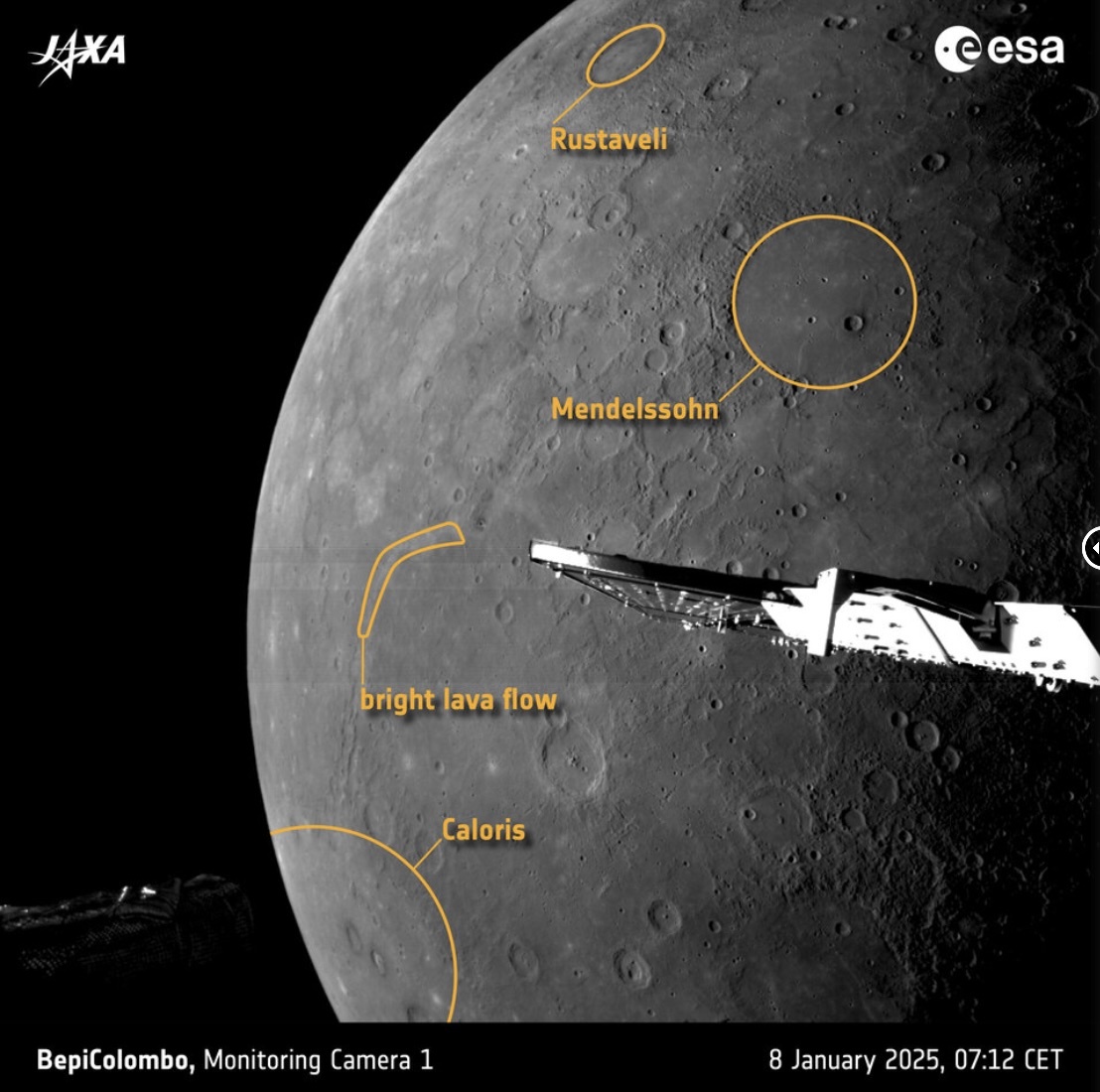
Another M-CAM 1 image, taken just five minutes after the first, shows that these plains extend over a large part of Mercury's surface. Prominently visible is the Mendelssohn crater, whose outer rim is barely visible above its flooded interior. Just a handful of smaller, more recent impact craters dent the smooth surface.
Further out, but still within the Borealis Planitia, the Rustaveli crater suffered a similar fate.
On the bottom left of the image lies the massive Caloris basin, Mercury's largest impact crater, which spans more than 1500 km. The impact that created this basin scarred Mercury's surface up to thousands of kilometres away, as evidenced by the linear troughs radiating out from it.
Above a particularly large trough, a boomerang-shaped curve brightens the surface. This bright lava flow appears to connect to a deep trough below it. It appears similar in colour to both the lava on the floor of the Caloris basin and the lava of Borealis Planitia further north. Yet another mystery that BepiColombo hopes to solve is which way this lava moved: into the Caloris basin, or out of it?
On Mercury, a bright surface is a young surface
While M-CAM's images might not always make it appear so, Mercury is a remarkably dark planet. At a first glance the cratered planet may resemble the Moon, but its cratered surface only reflects about two-thirds as much light.
On this dark planet, younger features on the surface tend to appear brighter. Scientists don't yet know what exactly Mercury is made of, but it is clear that material brought up from beneath the outer surface gradually becomes darker with age.
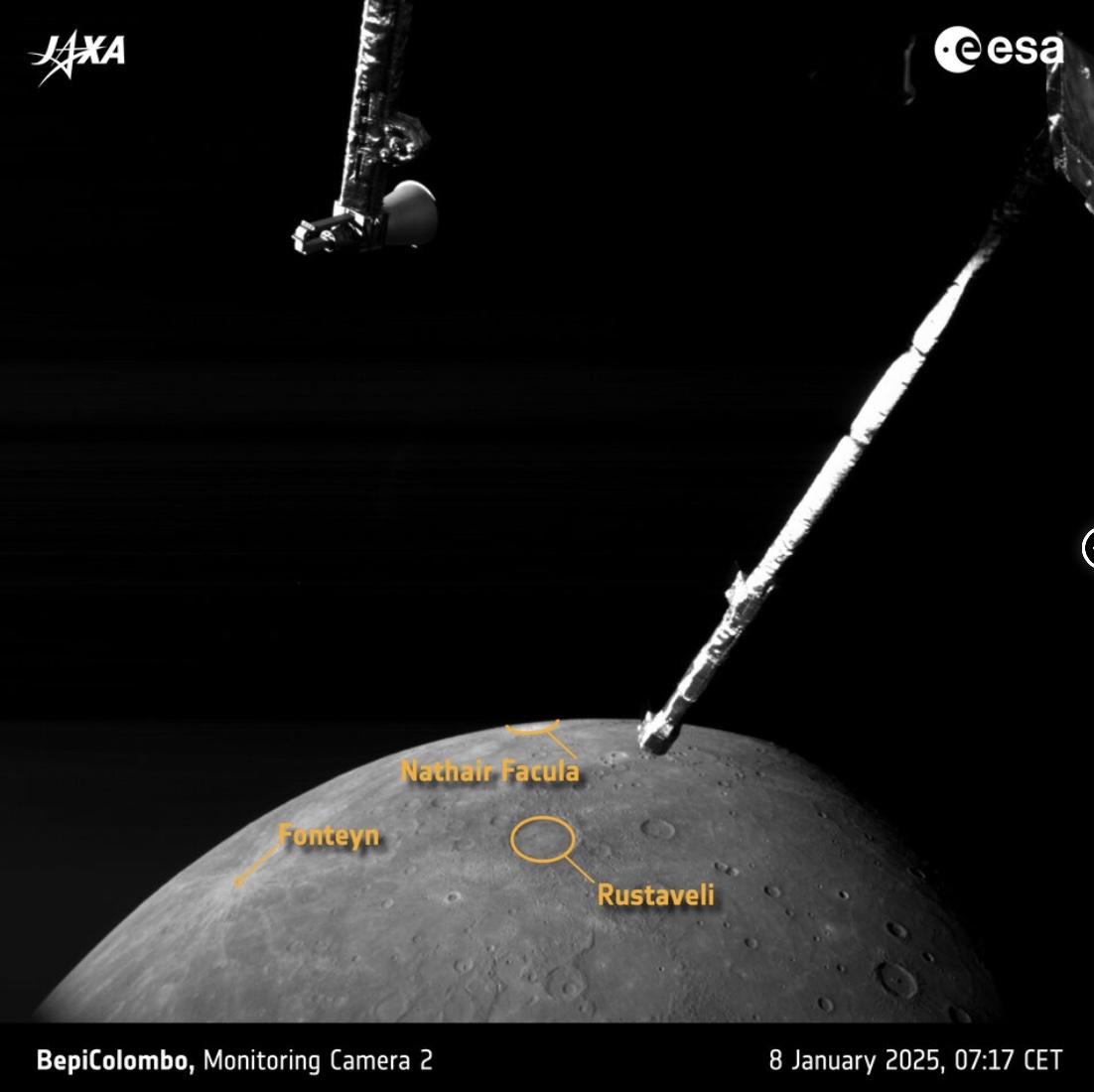
BepiColombo's third image selected from this flyby, taken by M-CAM 2, shows spectacular examples of the two things that bring bright material to the surface: volcanic activity and large impacts.
The bright patch near the planet's upper edge in this image is the Nathair Facula, the aftermath of the largest volcanic explosion on Mercury. At its centre is a volcanic vent of around 40 km across that has been the site of at least three major eruptions. The explosive volcanic deposit is at least 300 km in diameter.
And to the left lies the relatively young Fonteyn crater, which formed a ‘mere’ 300 million years ago. Its youth is apparent from the brightness of the impact debris that radiates out from it.
Throughout its mission, several BepiColombo instruments will measure the composition of both old and new parts of the planet's surface. This will teach us about what Mercury is made of, and how the planet formed.
Finishing in style
"This is the first time that we performed two flyby campaigns back-to-back. This flyby happens a bit more than a month after the previous one," says Frank Budnik, BepiColombo Flight Dynamics Manager. “Based on our preliminary assessment, everything proceeded smoothly and flawlessly.”
“BepiColombo's main mission phase may only start two years from now, but all six of its flybys of Mercury have given us invaluable new information about the little-explored planet. In the next few weeks, the BepiColombo team will work hard to unravel as many of Mercury's mysteries with the data from this flyby as we can,” concludes Geraint Jones, BepiColombo's Project Scientist at ESA.

About BepiColombo
Launched on 20 October 2018, BepiColombo is a joint mission between the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), executed under ESA leadership. It is Europe's first mission to Mercury.
The mission comprises two scientific orbiters: ESA’s Mercury Planetary Orbiter (MPO) and JAXA’s Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter (Mio). The European Mercury Transfer Module(MTM) carries the orbiters to Mercury.
After arrival at Mercury in late 2026, the spacecraft will separate and the two orbiters will manoeuvre to their dedicated polar orbits around the planet. Starting science operations in early 2027, both orbiters will gather data during a one-year nominal mission, with a possible one-year extension.
All M-CAM images will be made publicly available in the Planetary Science Archive.
Quelle: ESA
----
Update: 15.03.2025
.
FIRST THERMAL IMAGES OF MERCURY FROM BEPICOLOMBO
The European BepiColombo mission made a detailed heat map of a large swath of Mercury’s surface during its most recent flyby.
At the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference in Texas, members of the BepiColombo science team revealed on March 12th the first views of Mercury from the spacecraft’s thermal camera. It’s the first time Mercury has ever been imaged from a spacecraft in the thermal infrared, and the rich detail in the planetwide swath has whetted scientists’ appetites for what BepiColombo will achieve once it finally enters orbit in November 2026.
When BepiColombo launched, the team that built the Mercury Radiometer and Thermal Infrared Spectrometer (MERTIS) didn’t expect to receive any Mercury data until after orbit insertion. The main reason: BepiColombo is a stack of four spacecraft, and during the mission’s cruise phase the Mercury Planetary Orbiter (MPO)’s remote sensing instrument deck is blocked by the bulk of the Mercury Transfer Module (MTM), a solar-electric propulsion craft that is powering BepiColombo’s cruise. However, unlike the other MPO cameras, MERTIS has a second, side-looking “space port” that isn’t blocked by the MTM.
MERTIS’ space port is intended for taking calibration data of black space. It’s pointed out the same side of the spacecraft as its radiators. That side of the spacecraft was never supposed to be pointed at Mercury’s sweltering surface, and the MERTIS instrument software didn’t include any capability to perform planetary imaging out the space port. After launch, however, ESA permitted the MERTIS team to upgrade the software, which “required a complete reprogramming of instrument observation sequences and procedures,” team member Harald Hiesinger (University of Münster, Germany) said.
All of BepiColombo’s originally planned five Mercury flybys were supposed to happen at distances less than 300 kilometers (190 miles). With Mercury’s hot surface so nearby, spacecraft safety required the radiators — and the MERTIS space port — to be pointed away from the planet, precluding imaging. But a thruster anomaly discovered in 2024 required ESA to insert an extra, distant flyby before its final gravity assist on January 8, 2025.
The fifth flyby happened on December 1, 2024, at an altitude of more than 37,000 kilometers, a distance at which the planet’s heat wouldn’t overwhelm the spacecraft’s cooling systems. MERTIS gazed at Mercury through its space port as the spacecraft floated past, acquiring a pole-to-pole swath of data across the planet’s sunlit face.
Unsurprisingly, an uncorrected view of the thermal data shows that Mercury is hottest where the Sun’s heat is fiercest, with equatorial temperatures reaching a blistering 693 kelvins (788°F). Reassuringly, MERTIS’s two channels measured the same temperature. But within that obvious bullseye pattern are subtle hints of variation across Mercury’s surface.

Courtesy of Harald Hiesinger, Universität Münster, and the MERTIS team
Take out the bullseye pattern, and lots of subtle details appear, many associated with craters. Many factors could influence the details of thermal brightness: topography, shadowing, grain size, surface roughness, and mineral composition. It’s not yet possible to say for sure, because the MERTIS team must first calibrate their instrument, reducing the effects of pixel-to-pixel sensitivity variations. Plus, the space port images are slightly contaminated by some stray Mercuryshine reflecting off the spacecraft radiators. That glow won’t be an issue once the MTM separates from the MPO and MERTIS can use its planetary port to view Mercury.

Courtesy of Harald Hiesinger, Universität Münster, and the MERTIS team
Just this one flyby yielded 1.4 million MERTIS spectra. The unusual viewing geometry means these data aren’t ideal for science, but they are proof positive of MERTIS’s sensitivity, and a little taste of what’s to come during BepiColombo’s orbital mission.
Quelle: Sky&Telescope
