Perseverance is officially headed into a new phase of scientific investigation on the Jezero Crater rim!
26.08.2024
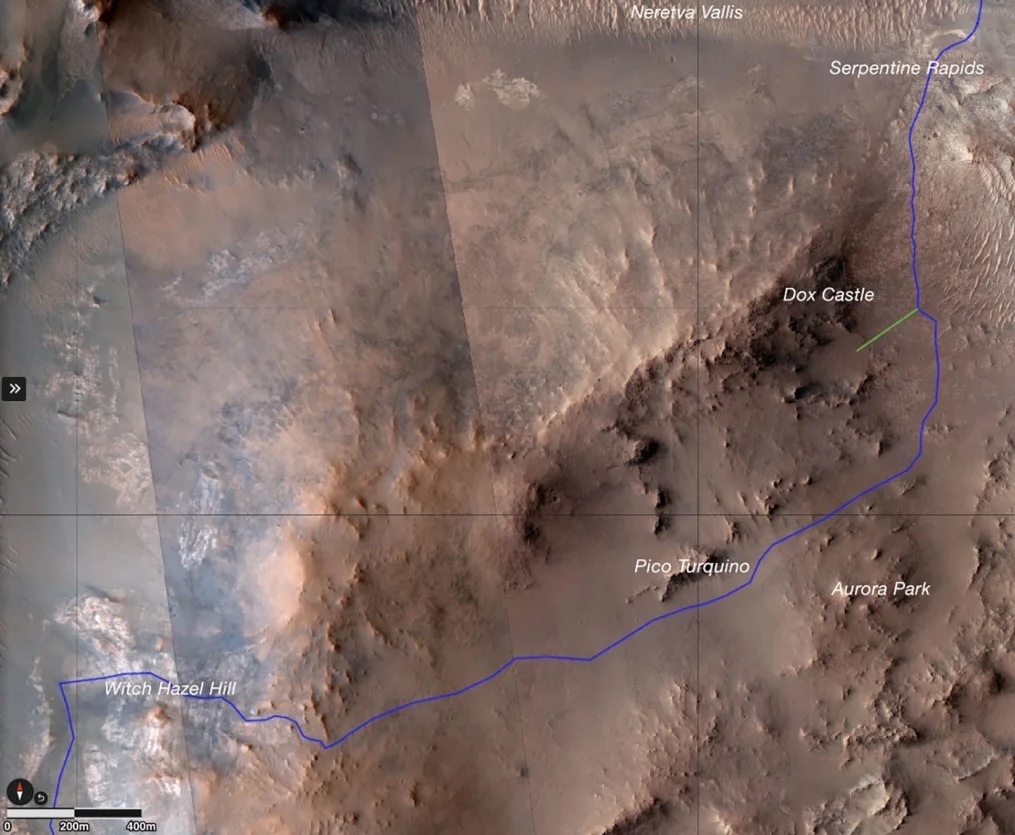
Perseverance rover is making a steep ascent to reach unexplored Martian territory
NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona
The Perseverance rover has begun a long climb up the steep rim of Jezero Crater on a quest to discover some of the most ancient rocks on Mars — and the potential for environments that may have once hosted life on the red planet.
Landing in Jezero Crater 3 1⁄2 years ago, the robotic explorer has since explored the site of an ancient lake and river delta and collected numerous rock samples. But its latest scientific journey could rewrite the way astronomers understand Mars.
“Perseverance has completed four science campaigns, collected 22 rock cores, and traveled over 18 unpaved miles (29 kilometers),” said Art Thompson, Perseverance project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, in a statement. “As we start the Crater Rim Campaign, our rover is in excellent condition, and the team is raring to see what’s on the roof of this place.”
The rover will use its auto-navigation capabilities, which allows Perseverance to function like a self-driving car, to follow a route planned by the vehicle’s engineers. The route will enable the rover to avoid hazards on the challenging climb. Perseverance will gain about 1,000 feet (300 meters) in elevation when it summits the rim toward the end of 2024.
This ascent is something scientists have been looking forward to for years, long before Perseverance landed on Mars.
About 4 billion years ago, some kind of object slammed into Mars and created Jezero Crater, and the impact kicked up huge blocks of rock that became trapped in the crater rim.
“We should be able to access and sample some of the oldest rocks on Mars in the crater rim,” said Briony Horgan, co-investigator on the Perseverance rover mission and professor of planetary science at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana.
“We think these include everything from ancient sedimentary rocks that could preserve the earliest habitable environments on Mars, to the building blocks of the planet that formed the earliest crust at the dawn of the solar system.”
The crater rim will provide a window into the earliest period of Mars’ history — and could reveal evidence of hot springs that might have supported ancient microbial life, Horgan said.
Turning back Martian time
The impact that created Jezero Crater also generated a lot of heat, partly from the energy of the object that slammed into Mars. Some of the heat also came from hotter rock that existed beneath the Martian surface, as the planet was still cooling after forming half a billion years earlier. The impact churned up those rocks from below the Martian surface.
If groundwater or surface water was present on Mars at the time, which scientists believe likely, there would have been hydrothermal systems, said Ken Farley, Perseverance project scientist and professor of geochemistry at the California Institute of Technology.
With hydrothermal systems, hot water likely circulated through cracks on rocks and may have created the right environment for microbial life to thrive.
So far, Perseverance has investigated the site of the ancient lake bed and river delta, where life could have existed. The crater rim site of Pico Turquino, as the hydrothermal rocks are called, provides another, different possibility.
“In the scheme of the overall objectives of the mission, looking for evidence of possible life on Mars is very high up there, so we want to investigate as many potentially habitable environments as Mars will offer us,” Farley said.
The science team is also eager to reach Witch Hazel Hill, a large outcrop of black-and-white layered rock that extends for hundreds of meters. These layers of rock may preserve information about Mars’ climate billions of years ago. The rover should arrive there in six to nine months.
The movement of plate tectonics and other erosive processes have erased some of Earth’s earliest rocks, but ancient rocks encoded with the history of Mars still exist on the red planet.
The solar system formed 4.55 billion years ago, and the science team expects to find and study Martian rocks that are 4.2 billion years old, Farley said.
Ascending the crater
During the long drive up the crater wall, Perseverance could encounter slopes angled nearly 23 degrees. Typically, the team avoids any route that will tilt the rover more than 30 degrees. But the rover is well-prepared for the climb and isn’t in any danger, Farley said.
“Climbing up the crater rim, even though it would be a bit of an arduous journey for us humans, from a rover standpoint it actually won’t be that big of a deal,” said Steven Lee, Perseverance deputy project manager.
But the rover’s rate of progress may slow if it feels its wheels slipping on the Martian terrain or encounters big boulders during the climb.
Perseverance can watch the terrain as it drives, and if its wheels slip too much, the rover will stop and “call home for Mommy, wait to be told what to do and we’ll figure it out on the ground,” Lee said.
The rover remains in excellent condition, with “no showstoppers in any way to say we can’t continue operating this vehicle for many more years,” Lee said.
By the time the rover climbs to the top of the rim, it will have traveled tens of kilometers more and captured tons of new images for the mission team to analyze.
“It’s a unique perspective for those of us who get to work day-to-day on the project,” Lee said. ” Pretty soon you start to get a sense of Mars as a place. My memories of Perseverance’s traverses are a lot like memories of a hike. I can actually think of what Mars is like from the landing site all the way to where we are today.”
And the rover’s perspective above the 28-mile-wide (45-kilometer-wide) crater will provide some beautiful vistas.
“We will definitely get some amazing views looking back where we came from in Jezero and out into the plains beyond,” Horgan said.
The biggest challenge will be for the science team as it determines which rocks to study up close as well as the ones from which to collect samples. With so many intriguing school bus-size piles of rock, the team will have to learn as much as it can while keeping the rover moving.
“We’ll have all of this stuff just thrown out in front of us,” Farley said, “so I think it’ll be a very different kind of exploration.”
The team anticipates that Perseverance will spend at least a few years beyond the crater rim collecting samples.
Meanwhile, the question looms as to how those samples, along with the ones Perseverance collected within the crater, will return to Earth as NASA reassesses the Mars Sample Return program. The agency is evaluating different proposals and is expected to announce a decision in the fall.
The decision could determine how long and how far the rover drives since the vehicle may be responsible for delivering samples to a spacecraft to carry back to Earth.
“This part of the mission is essential for creating a sample collection that is the collection of everybody’s dreams,” Farley said. “For now, we’re just going to pursue our crater rim investigation. And then when the time comes, we’ll do whatever we need to do to support Mars Sample Return.”
Quelle: CNN
----
Update: 29.08.2024
.
Perseverance Kicks off the Crater Rim Campaign!
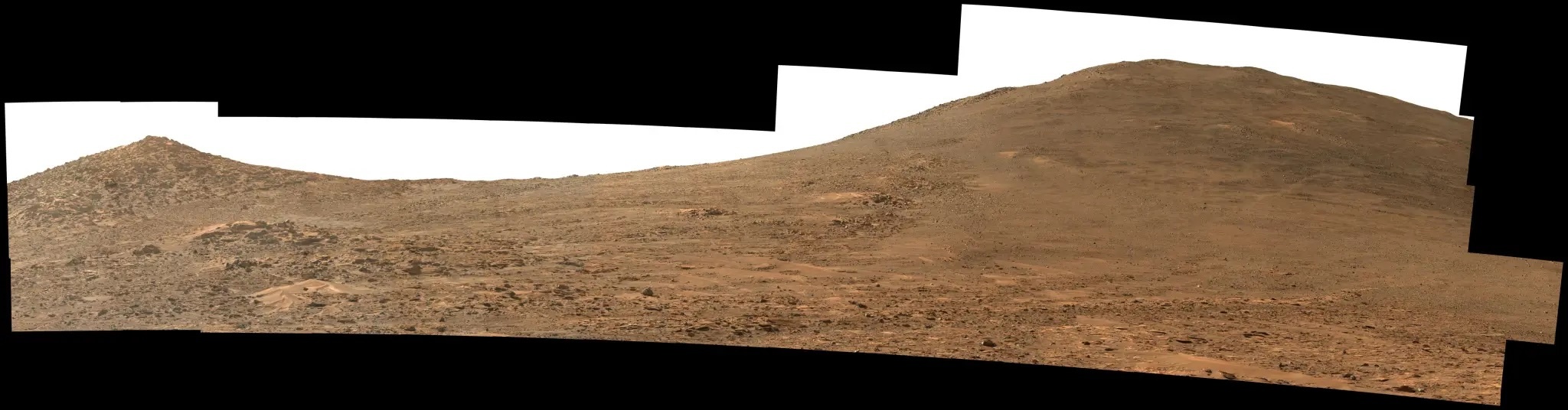

For the last 2 months, the Perseverance rover has been exploring the Neretva Vallis region of Jezero Crater, where rocks with interesting popcorn-like textures and “leopard spot” patterns have fascinated us all. Now, the rover has begun its long ascent up the crater rim, and is officially kicking off a new phase of exploration for the mission.
Strategic (longer-term) planning is particularly important for the Mars 2020 mission given the crucial role Perseverance plays in collecting samples for Mars Sample Return, and the Mars 2020 team undertakes this planning in the form of campaigns. Perseverance has now completed four such campaigns— the Crater Floor, Delta Front, Upper Fan and Margin Unit campaigns respectively— making the Crater Rim Campaign next in line. Given its broad scope and the wide diversity of rocks we expect to encounter and sample along the way, it may be the most ambitious campaign the team has attempted so far.
The team also has less information from orbiter data to go on compared to previous campaigns, because this area of the crater rim does not have the high-resolution, hyperspectral imaging of CRISM that helped inform much of our geological unit distinctions inside the crater. This means that Mastcam-Z multispectral and SuperCam long-distance imaging will be particularly useful for understanding broadscale mineralogical distinctions between rocks as we traverse the crater rim. Such imaging has already proved extremely useful in the Neretva Vallis area, where at Alsap Butte we observed rocks that appeared similar to each other in initial imaging, but actually display an Andy-Warhol-esque array of color in multispectral products, indicative of varied mineral signatures.
Our next stop is Dox Castle where Perseverance will investigate the contact between the Margin Unit and the Crater rim, as well as rubbly material that may be our first encounter with deposits generated during the impact that created Jezero crater itself. Later in the campaign, we will investigate other light-toned outcrops that may or may not be similar to those encountered at Bright Angel, as well as rocks thought to be part of the regionally extensive olivine-carbonate-bearing unit, and whose relationship to both Séítah and the Margin Unit remains an interesting story to unravel. Throughout this next phase of exploration, comparing and contrasting the rocks we see on the rim to both each other and those previously explored in the mission will be an important part of our scientific investigations.
The whole Mars 2020 science team is incredibly excited to be embarking on the next phase of Perseverance’s adventure, and we expect these results, and the samples we collect along the way, to inform our understanding of not just Jezero itself, but the planet Mars as a whole. We can’t wait to share what we find!
Reaching New Heights to Unravel Deep Martian History!
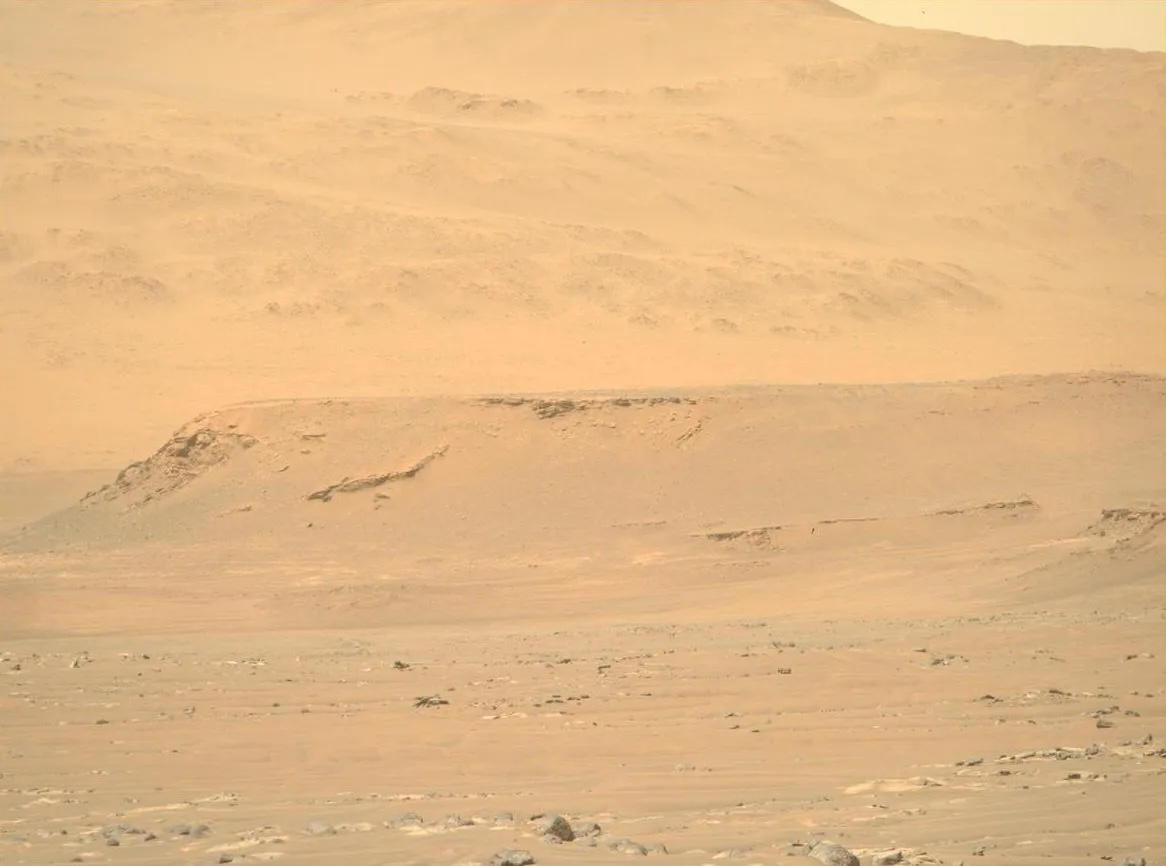

The Perseverance rover is reaching new heights as it ascends the rim of Jezero crater (over 300 meters in elevation higher than the original landing site)! The rover is now enroute to its first campaign science stop Dox Castle (image in the far ground) a region of interest for its potential to host ancient Mars’ bedrock in the exposed rocks on the rim.
Impact craters like Jezero may be the key to piecing together the early geologic history of Mars, as they provide a window into the history of the ancient crust by excavating and depositing deep crustal materials above the surface. Crater rims act as keepers of ancient Martian history, uplifting and exposing the stratigraphy of these impacted materials. Additionally, extreme heat from the impact can encourage the circulation of fluids through fractures similar to hydrothermal vents, which have implications for early habitability and may be preserved in the exposed rim bedrock. With the Perseverance rover we have the potential to explore some of the oldest exposed rocks on the planet.
Exploring such diverse terrains takes a lot of initial planning! The team has been preparing for the Crater Rim Campaign these last few months by working together to map out the types of materials Perseverance may encounter during its traverse up and through the rim. Using orbital images from the High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) instrument, the science team divided the rim area into 36 map quadrants, carefully mapping different rock units based on the morphologies, tones, and textures they observed in the orbital images. Mapping specialists then connected units across the quads to turn 36 miniature maps into one big geologic map of the crater rim. This resource is being used by the team to plan strategic routes to scientific areas of interest on the rim.
On Earth, geologic maps are made using a combination of orbital images and mapping in the field. Planetary scientists don’t typically get to check their map in the field, but we have the unique opportunity to validate our map using our very own robot geologist! Dox Castle will be our first chance to do rim science - and we’re excited to search for evidence of the transition between the margin and rim materials to start piecing together the stratigraphic history of the rocks that make up the rim of Jezero crater.
Quelle: NASA
----
Update: 27.09.2024
.
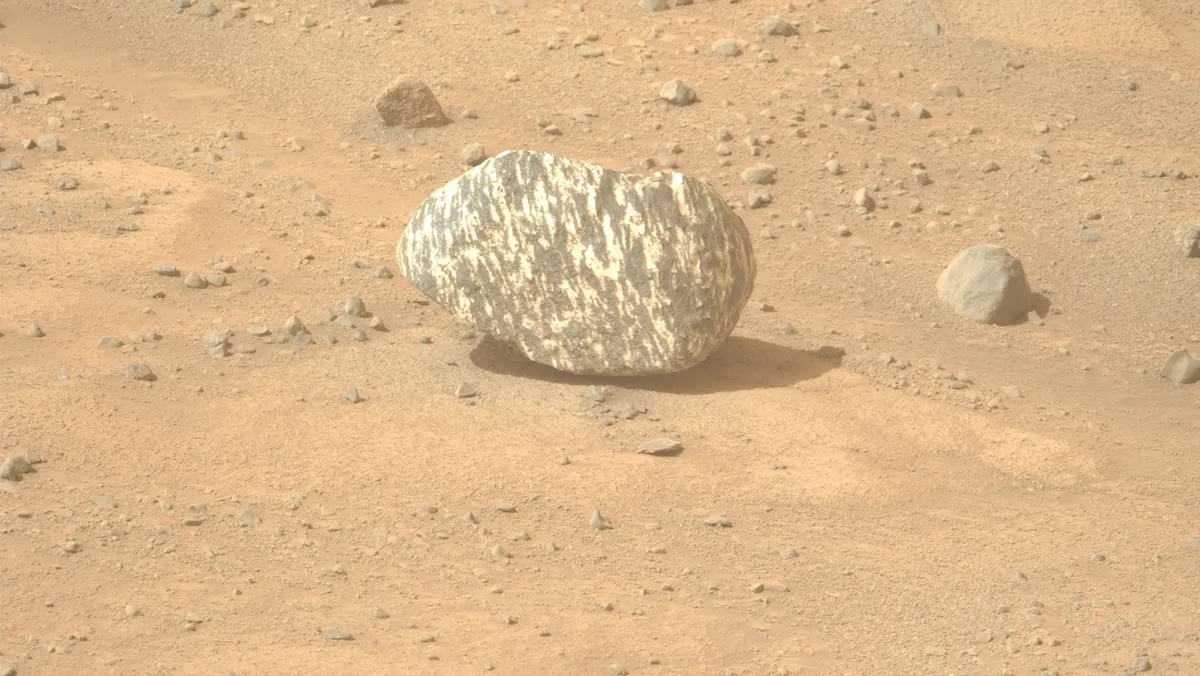
Weird striped rock 'unlike any seen on Mars' found by Perseverance rover. Here's why NASA's excited



