22.04.2023
The futuristic space station will feature a greenhouse and a centrifuge to relieve side effects of weightlessness.
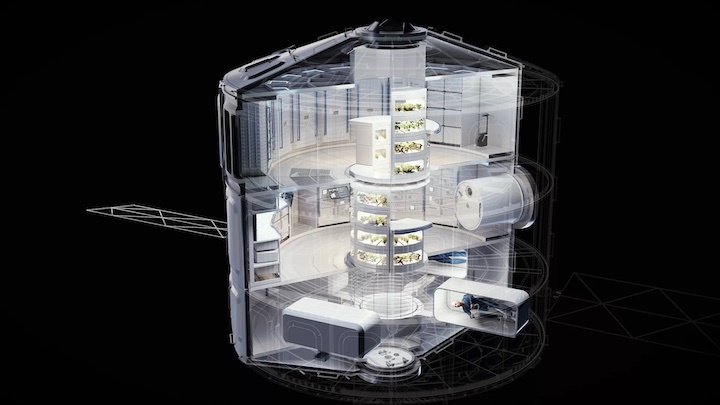
Airbus' new Loop space habitat has a centrifuge and an in-built greenhouse. (Image credit: Airbus)
The European aerospace giant Airbus has unveiled a new concept space habitat that will be more spacious and comfortable than existing space stations.
The multi-purpose orbital module called Loop features three customizable decks that are connected via a tunnel surrounded by an integrated greenhouse. The orbital habitat is designed for a four-person crew but could be adjusted to accommodate up to eight spacefarers, Airbus said in a statement(opens in new tab).
At 26 feet wide (8 meters), LOOP is designed to fit into the fairing of the upcoming generation of superheavy launchers, such as SpaceX's Starship, and could thus be deployed with one launch and be habitable immediately after reaching orbit, Airbus said.
In its basic configuration, LOOP features a habitation deck, a science deck and a centrifuge deck producing artificial gravity, where inhabitants could receive temporary relief from zero-gravity conditions. It is well known that the human body quickly deteriorates in the absence of gravity, with muscles and bones wasting away from disuse. The absence of gravity also confuses the human nervous system and spatial orientation, which frequently leads to queasiness during the first days of an orbital stay.
"The Airbus LOOP is designed to make long-term stays in space comfortable and enjoyable for its inhabitants, while supporting efficient and sustainable operations at the same time," Airbus said in the statement. "It builds on everything that has been learnt over the decades and fully exploits the potential of tomorrow’s technologies in order to best support humanity’s future in space: in low-Earth or lunar orbit, or on long-term missions to Mars."
The concept space habitat, which according to Airbus offers more internal space to its occupants than existing space stations, could be ready to fly in the early 2030s after the end of life of the International Space Station.
Airbus previously led the consortia that built the European Columbus module of the International Space Station and the Automated Transfer Vehicle that served as a cargo carrier for the orbiting lab. The firm is currently in charge of the construction of the Orion Service Modules, built to propel the crew capsule of NASA's Artemis exploration program to the moon.
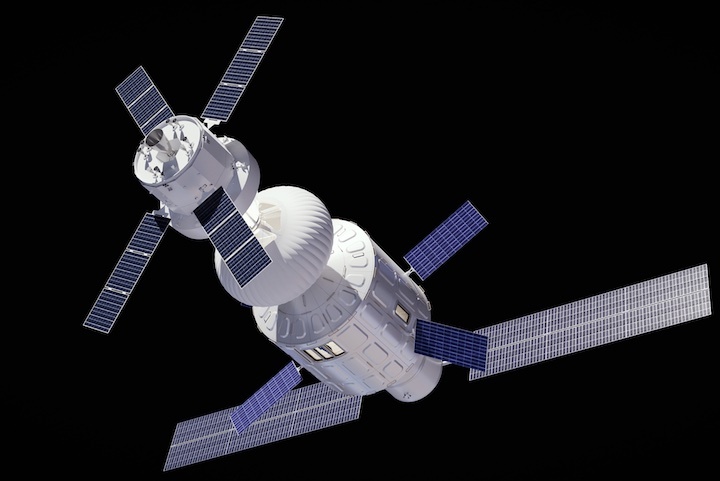

Airbus' Loop futuristic space station from the outside.(Image credit: Airbus)
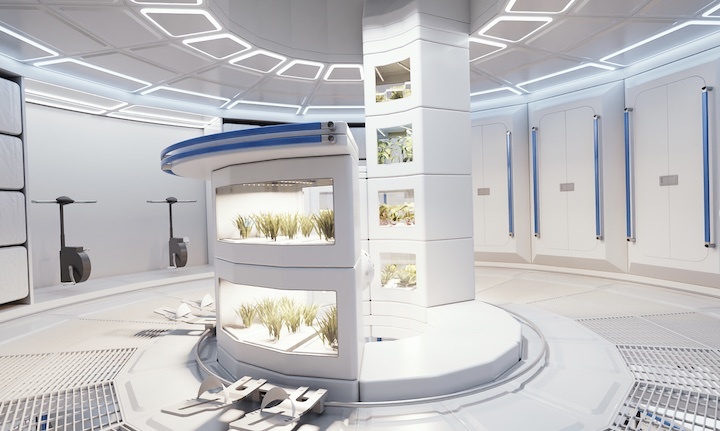

Airbus' Loop futuristic space station from the outside.(Image credit: Airbus)
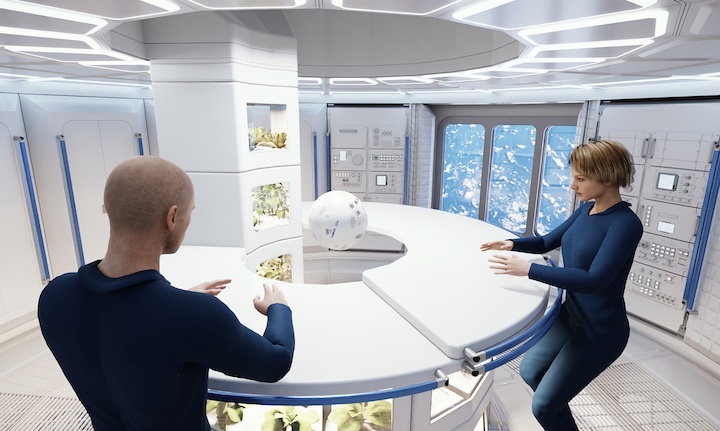

Airbus' Loop futuristic space station from the outside.(Image credit: Airbus)
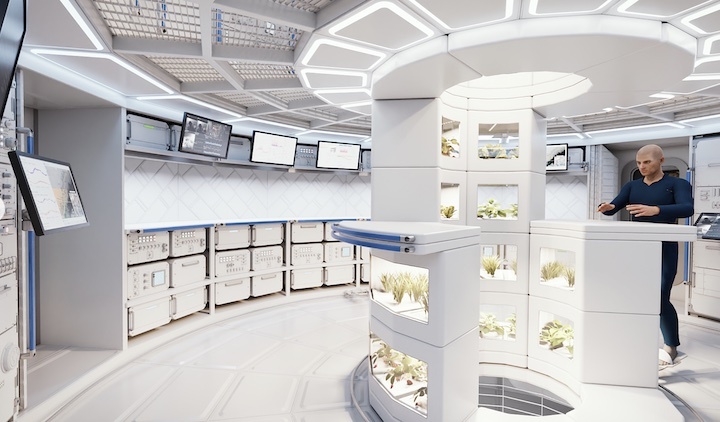

Airbus' Loop futuristic space station from the outside.(Image credit: Airbus)
Quelle: SC
