21.12.2022

SpaceX preparing to start Starlink Gen2 launches this month
TAMPA, Fla. — SpaceX could start launching second-generation Starlink satellites in the coming weeks to add more capacity to its increasingly congested broadband network.
In Dec. 16 regulatory filings with the Federal Communications Commission, SpaceX said it “anticipates that it will begin launching Gen2 satellites before the end of December 2022.”
The company is asking the FCC for a 60-day special temporary authority (STA) to connect existing user terminals to the upcoming satellites in non-geostationary orbit (NGSO). If granted, the STA would allow SpaceX to start providing Gen2 services while waiting for the FCC to process its application for longer-term approval.
Granting the STA would enable users “to access the increased capacity for low-latency broadband services from SpaceX’s upgraded, next-generation NGSO system as soon as its satellites are deployed,” SpaceX told the FCC.
Starlink has more than one million “active subscribers,” SpaceX tweeted Dec. 19, up from 250,000 the company said it had in March.
The network has come under strain amid its growing popularity, according to analysis from Ooklashowing how median Starlink download speeds have continued to fall in the United States and Canada.
SpaceX has launched more than 3,600 Starlink satellites to date with Falcon 9 rockets. Of those, around 3,300 of the 4,408 Gen1 satellites authorized by the FCC are estimated to still be in orbit.
On Dec. 1, the FCC granted Starlink partial approval to operate 7,500 of the nearly 30,000 satellites in its proposed Gen2 constellation.
In addition to adding more capacity for existing Starlink customers, SpaceX is hoping to use Gen2 to add new capabilities, including direct-to-smartphone services.
The FCC continues to review SpaceX’s overall proposal to expand the Gen2 constellation significantly.
The regulator also deferred a decision on SpaceX’s plans to add small radio frequency beacons to Gen2 satellites that, according to the company, will improve their safety by providing specialized telemetry, tracking and command (TT&C) functions.
SpaceX provided more details about the beacons in a separate regulatory filing, which detailed how they could be used to track and maintain contact with Gen 2 satellites during orbit raising and poor space weather conditions.
The beacons would be capable of broadcasting a telemetry tracking message once every 100 seconds on average, SpaceX said.
“Once the satellites reach their intended orbit, the beacons will be shut off, only to transmit again if commanded in the unlikely event of an emergency,” SpaceX senior director of satellite policy David Goldman told the FCC in a Dec. 15 letter.
“Such capability will enable SpaceX to continue to lead the industry in space stewardship by formally including a redundant backup TT&C system on its already-advanced Gen2 satellites.”
SpaceX has plans to use Falcon 9 rockets and its upcoming Starship heavy-launch vehicle to deploy Gen2. The company has previously outlined intentions to launch Gen2 satellites at least once a week, with plans to increase this cadence.
Quelle: SN
+++
SpaceX might launch first Starlink Gen2 satellites next week
SpaceX has told the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) that it plans to begin launching its first next-generation Starlink Gen2 satellites before the end of 2022.
The FCC only just granted SpaceX partial approval of its Starlink Gen2 constellation, which has been under review since May 2020, in late November 2022. Just a week or two later, in several filings asking the FCC to expedite Special Temporary Authority (STA) requests that would allow it to fully test and communicate with its first next-generation satellite prototypes, SpaceX said [PDF] that it “anticipates that it will begin launching Gen2 satellites before the end of December 2022.”
In most of the main STA requests filed in early December, SpaceX appears to be asking the FCC to add Starlink Gen2 satellites as approved points of communication for user terminals and ground stations that are already licensed. Those include its new high-performance dishes, newer base-model dishes (both fixed and in motion), and first-generation (round) dishes. While the FCC’s recent actions on Starlink do not raise confidence in its consistency, objectivity, and rationality, these requests should be shoe-ins.
SpaceX also wants permission to activate Very High Frequency (VHF) beacons that are meant to be installed on all Starlink Gen2 satellites. Those beacons would serve as a backup to existing telemetry, tracking, and command (TT&C) antennas and decrease the odds of a total loss of control by ensuring that SpaceX can remain in contact with Gen2 satellites regardless of their orientation – an ability that would obviously improve the safety of Starlink orbital operations.
Given how unusually long it took the FCC to review SpaceX’s Starlink Gen2 applications and how arbitrarily strict it was with its partial Gen2 license grant, it’s hard to say if the FCC will grant these STA requests or how long it will take if it does. SpaceX finds itself in a strange position where the FCC has given it permission to begin launching up to 7500 Starlink Gen2 satellites, but has not granted SpaceX permission to use those satellites to communicate with user terminals.
To the FCC’s credit, a constellation operator has never been ready to launch satellites less than one month after launches were approved, and it’s likely that the processes to ensure those satellites can be properly used after launch are ongoing. Additionally, because of the FCC’s arbitrary license restrictions, SpaceX is not allowed to launch or operate any Starlink Gen2 satellites outside of a narrow range of altitudes (475-580 km). After launch, Starlink Gen2 satellites will likely take around two or three months to reach those operational orbits, only after which can SpaceX begin using them in earnest. As long as the FCC approves most of SpaceX’s December 2022 STA requests, the disruption to Starlink Gen2 deployment and on-orbit testing should thus be limited.
NEXT WEEK?
While SpaceX’s schedule targets can often be easily dismissed for future projects, there is evidence that SpaceX will actually attempt to launch the first Starlink Gen2 satellites before the end of the year. Earlier this month, SpaceX received permission to communicate with a Falcon 9 rocket for a mission called Starlink 5-1. One of five orbital ‘shells’ that make up SpaceX’s first-generation Starlink constellation does technically have zero satellites and is awaiting its first launch. But that shell (Group 5) is polar, meaning that its satellites will orbit around Earth’s poles, and the STA license the FCC granted indicates that this launch will be to a more equatorial inclination, which would not make sense for a Group 5 launch.
It’s thus possible that SpaceX decided to repurpose the STA for its first Starlink Gen2 launch, which the company cannot currently launch to an inclination other than 53 degrees – roughly the same trajectory indicated by the document. Starlink Gen1 has two 53-degree shells, Group 1 and Group 4, and both are nearly complete and would likely be called Starlink 1-XX or 4-XX in FCC filings. Combined with SpaceX stating in its VHF beacon STA request that initial Starlink Gen2 launches will start in “late December 2022,” and unofficial manifests indicating that SpaceX has a Starlink launch scheduled as early as December 28th, it certainly appears that first Gen2 satellites will reach orbit later this year.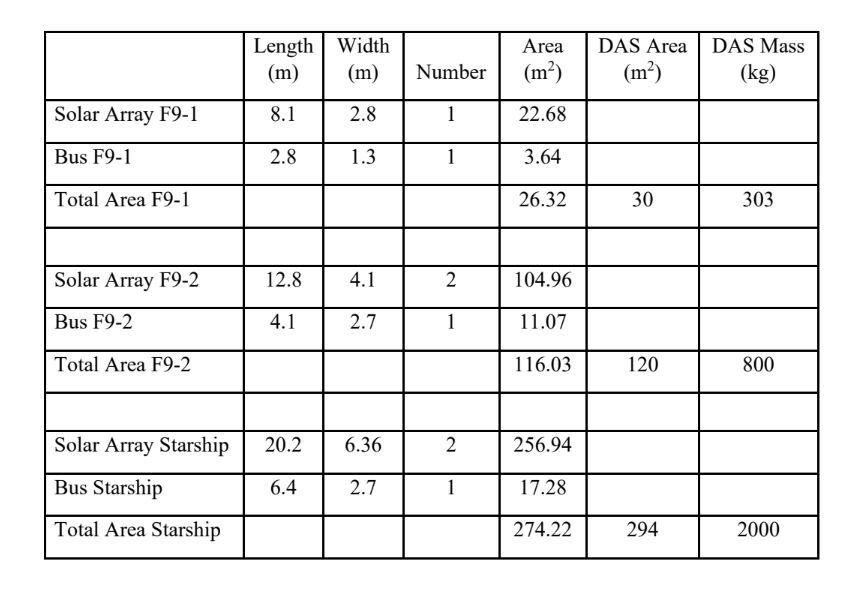
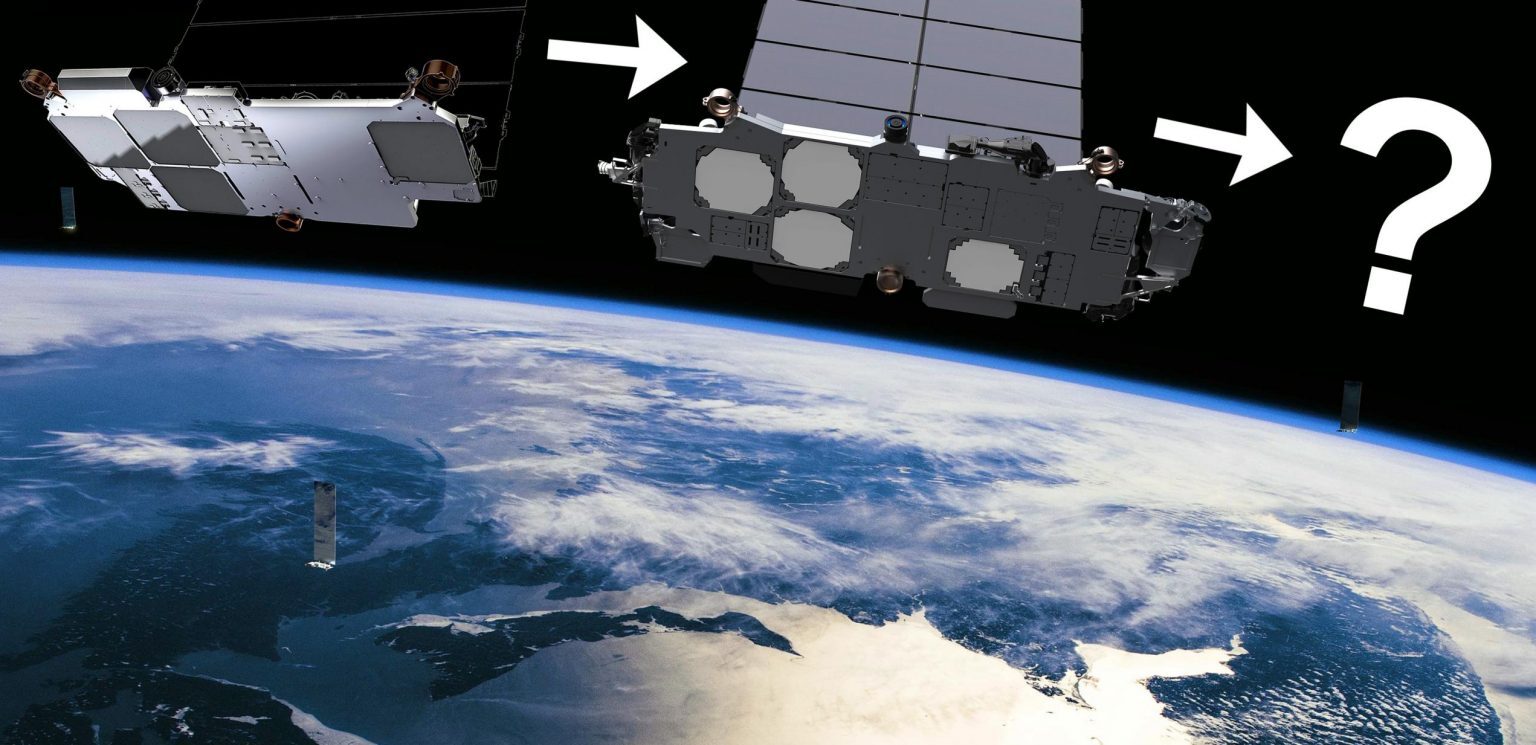
More likely than not, they will be Starlink “V2 Mini” satellites – a downsized variant created to maximize the efficiency of Falcon 9 Starlink Gen2/V2 launches while SpaceX’s next-generation Starship rocket remains stuck on the ground. The Starship-optimized Starlink V2 satellites SpaceX initially hoped would be the only version reportedly weigh about 1.25 tons (~2750 lb) and measure roughly 6.5 by 2.7 meters (21 x 9 ft). According to an October 2022 FCC filing, Starlink V2 Mini satellites will still be several times larger than today’s Starlink V1.5 satellites, weighing up to 800 kilograms (~1750 lb) and measuring 4.1 by 2.7 meters (13.5 x 9 ft).
SpaceX says Starlink V2 Mini satellites will also have a pair of massive solar arrays with a total array of 120 square meters (~1300 sq ft). Assuming V2 Mini satellites are roughly as power-efficient as V1.5 satellites and use similarly efficient solar arrays, that indicates that could offer around 3-4 times more usable bandwidth per satellite. Assuming SpaceX has again found a way to use all of Falcon 9’s available performance, each rocket should be able to carry up to 21 Starlink V2 Mini satellites to low Earth orbit.
Quelle: TESLARATI
----
Update: 28.12.2022 / 7:00 MEZ
.
SpaceX’s first “next-gen” Starlink satellites are suspiciously familiar
In a strange twist, SpaceX says that its next Starlink mission will launch 54 satellites into low Earth orbit (LEO), implying that they’re roughly the same size as the V1.5 satellites it’s already launching – not the larger V2 or V2 Mini satellites discussed in recent FCC filings.
However, the data SpaceX provided also shows that those 54 satellites are headed to an orbit that only matches the company’s next-generation Starlink Gen2 (V2) constellation. While SpaceX quietly indicated that a V1.5-sized satellite was an option for early Gen2 launches in a supplemental October 2022 filing [PDF] with the FCC, it’s still unclear why SpaceX would prioritize launching V1.5-sized V2 satellites while its V1 constellation remains unfinished.
Adding to the confusion, in November 2021, CEO Elon Musk strongly implied that the inefficiencies of smaller Starlink V1.x satellites were so significant that they could risk bankrupting SpaceX if the company couldn’t start launching larger V2 satellites on its next-generation Starship rocket by the end of 2022. What, then, is the purpose of SpaceX’s imminent “Starlink G5-1” launch?
The name alone is confusing. Using the same shorthand as past Starlink V1 launches, “G5-1” refers to the first launch of “Group 5” of a constellation. “Group” here is synonymous with “shell,” which describes a set of satellites that share the same orbital inclination (the angle at which the orbit crosses the equator) and a similar orbital altitude. Of SpaceX’s three approved constellations, only one has five shells, and that shell can only exist at 97.6 degrees, not 43 degrees. SpaceX’s Gen2 constellation technically has nine planned shells, but the FCC has only partially approved three of those shells, one of which is at 43 degrees.
Ignoring the obtuse name, one possibility is that aspects of Starlink V2 satellite upgrades are not explicitly tied to the much larger size of those satellites and can be applied to SpaceX’s first-generation Starlink constellation without requiring a modified FCC license. If SpaceX wanted to add larger satellites to its V1 constellation or change the frequency bands they use, it would almost certainly have to seek a modified license from the FCC, which could take months.
There is no evidence SpaceX has done so, and any attempt would produce public documentation. The 43-degree inclination SpaceX’s mysterious “Starlink G5-1” launch is targeting also rules out any involvement in its V1 constellation, which only has approval for satellites between 53 and 97.6 degrees.
Aside from the unlikely possibility that details about the Starlink 5-1 mission are somehow incorrect or an artifact of a messy launch licensing process, there is at least one other unlikely explanation. In October 2018, the FCC granted SpaceX permission to launch a very low earth orbit (VLEO) constellation of 7518 Starlink satellites with dimensions similar to satellites that make up the 4408-satellite constellation the company is currently launching. More than four years later, SpaceX has yet to begin launching its approved VLEO constellation.
In November 2022, SpaceX told the FCC it intended to combine its Starlink VLEO and Starlink Gen2 constellations by adding V-band antennas to some of the almost 33,000 Gen2 satellites it hoped to launch – a move that would reduce the total number of Starlink satellites SpaceX needs to launch. Around the turn of the month, the FCC partially granted SpaceX’s Starlink Gen2 license, adding unprecedentedly strict requirements and only permitting the launch of 7500 of 33,000 planned Gen2 satellites to a limited set of inclinations (33, 43, and 53 degrees).
Perhaps, then, the uncertainty created by the FCC’s strange partial Gen2 grant made SpaceX change its mind about a dedicated Starlink VLEO constellation. However, without a license modification, SpaceX’s VLEO constellation is stuck with the same smaller (and potentially bankruptcy-inducing) satellites that its CEO believes make the first Starlink V1 constellation unsustainable. SpaceX also has less than two years until its VLEO constellation crosses its first deployment milestone, at which point the company will need to have launched half of it (3759 satellites) to avoid penalties from the FCC – up to and including the revocation of its license.
Despite the numerous reasons it wouldn’t make sense for Starlink 5-1 to be SpaceX’s first Starlink VLEO launch, almost 2500 of SpaceX’s approved VLEO satellites were intended to operate in a 336-kilometer (~209 mi) orbit inclined by 42 degrees – oddly similar to the 338-kilometer (~210 mi), 43-degree orbit SpaceX appears to be targeting with Starlink 5-1.
A surprise VLEO launch is a very unlikely explanation, but it’s only marginally stranger than the alternatives: that Starlink 5-1 is a V1-sized V2 launch with no prior mention or warning, a V1 launch to an orbit that would explicitly violate SpaceX’s Starlink V1 FCC license, or a paperwork error that has propagated so far that SpaceX distributed incorrect orbit information (which could threaten other satellites and rockets) less than two days before liftoff.
Thankfully, there is one last explanation – raised after this article was published – that appears to be much more likely. In response to a tweet summarizing these claims, astrophysicist Jonathan McDowell noted that SpaceX had, in fact, mentioned a third smaller Starlink V2 satellite variant in an October 2022 FCC filing that fell mostly under the radar. In that filing, SpaceX told that FCC it was developing three variants, not two. The smallest variant was said to weigh 303 kilograms and featured dimensions seemingly identical to SpaceX’s existing V1.5 satellites, which are estimated to weigh around 307 kilograms. SpaceX also stated that initial Falcon 9 launches will carry “approximately twenty to sixty satellites,” again confirming that V2 satellites could be about the same size and shape as V1.5 satellites.
SpaceX’s decision to develop a V1.5-sized version of V2 satellites makes little sense in the context of Musk’s implicit claims that problems inherent to its smaller V1 satellites threaten the company’s solvency. It’s clearer than ever that the SpaceX CEO may have been stretching the truth of the matter to craft an existential threat that might encourage employees to work longer hours. Still, developing and launching a V1.5-sized V2 satellite variant and beginning to launch those satellites while SpaceX’s Starlink Gen1 is more than 25% incomplete is confusing at best.
Regardless of what it’s carrying or why, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is scheduled to launch Starlink 5-1 out of Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) no earlier than 4:40 am EST (09:40 UTC) on Wednesday, December 28th.
Quelle: TESLARATI
+++
Update: 16:00 MEZ
.
















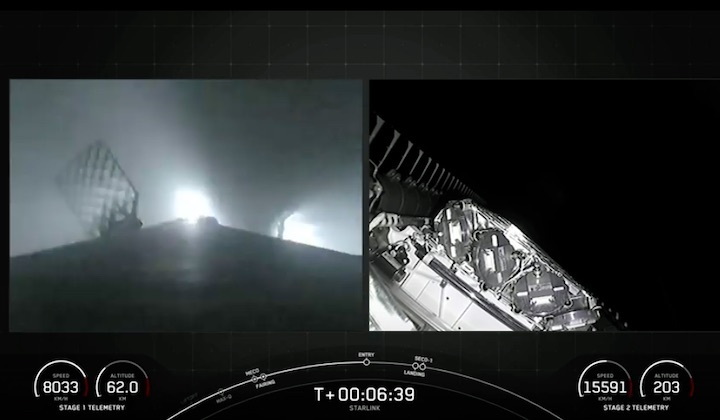






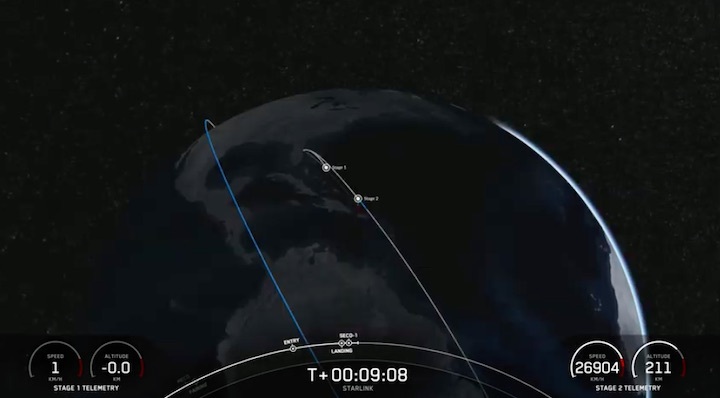
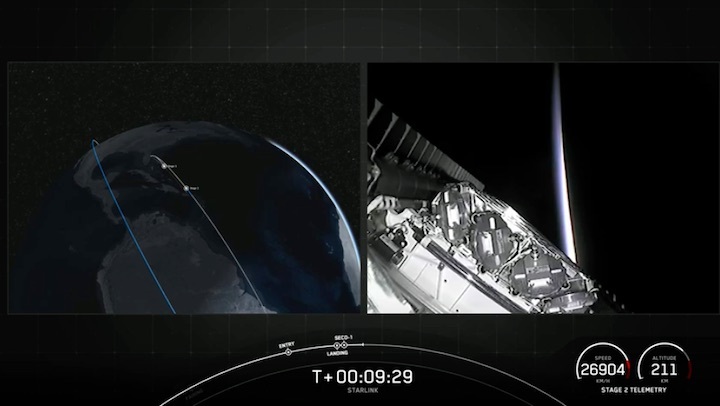
Quelle: SpaceX
