.
![]()
Tracking clouds on Venus
.
The most detailed record of cloud motion in the atmosphere of Venus chronicled by ESA’s Venus Express has revealed that the planet’s winds have steadily been getting faster over the last six years.
Venus is well known for its curious super-rotating atmosphere, which whips around the planet once every four Earth days. This is in stark contrast to the rotation of the planet itself – the length of the day – which takes a comparatively laborious 243 Earth days.
By tracking the movements of distinct cloud features in the cloud tops some 70 km above the planet’s surface over a period of 10 venusian years (6 Earth years), scientists have been able to monitor patterns in the long-term global wind speeds.
When Venus Express arrived at the planet in 2006, average cloud-top wind speeds between latitudes 50º on either side of the equator were clocked at roughly 300 km/h. The results of two separate studies have revealed that these already remarkably rapid winds are becoming even faster, increasing to 400 km/h over the course of the mission.
“This is an enormous increase in the already high wind speeds known in the atmosphere. Such a large variation has never before been observed on Venus, and we do not yet understand why this occurred,” says Igor Khatuntsev from the Space Research Institute in Moscow and lead author of the Russian-led paper to be published in the journal Icarus.
.
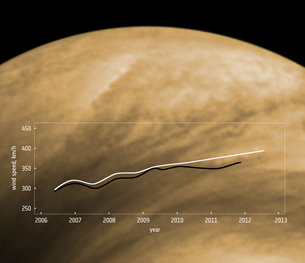
Increasing wind speeds on Venus
.
Dr Khatuntsev’s team determined the wind speeds by measuring how cloud features in images moved between frames: over 45 000 features were painstakingly tracked by hand and more than 350 000 further features were tracked automatically using a computer programme.
In a complementary study, a Japanese-led team used their own automated cloud tracking method to derive the cloud motions: their results are to be published in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
On top of this long-term increase in the average wind speed, however, both studies have also revealed regular variations linked to the local time of day and the altitude of the Sun above the horizon, and to the rotation period of Venus.
One regular oscillation occurs roughly every 4.8 days near the equator and is thought to be connected to atmospheric waves at lower altitudes.
But the research also unveiled some harder-to-explain curiosities.
“Our analysis of cloud motions at low latitudes in the southern hemisphere showed that over the six years of study the velocity of the winds changed by up 70 km/h over a time scale of 255 Earth days – slightly longer than a year on Venus,” says Toru Kouyama from the Information Technology Research Institute in Ibaraki, Japan.
Quelle:ESA
5967 Views
