26.09.2020

SpaceX’s first orbital Starship engine just breathed fire
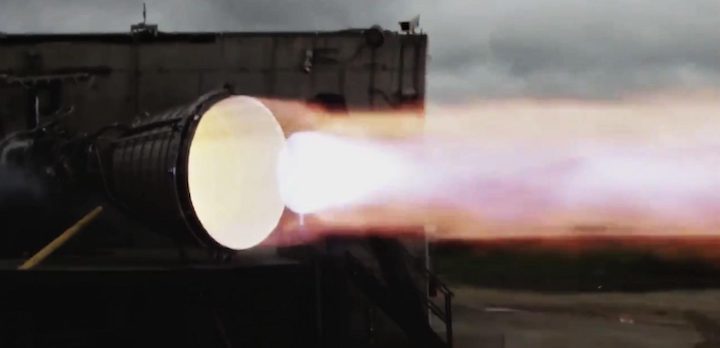
Less than three weeks after shipping to Texas, SpaceX says that Starship’s first Raptor Vacuum engine has completed a “full duration test fire” on the march towards orbital test flights.
Known as Raptor Vacuum or RVac, the engine is almost entirely based off of its sea level-optimized cousin, taking all of the complex turbomachinery and combustion chambers that represent the bulk of a rocket engine. Things start to diverge below the throat of the combustion chamber (the narrow part of the central hourglass-like curve), where SpaceX has expanded Raptor’s existing bell nozzle by a factor of five or more.
SpaceX’s reusable Starship spacecraft will use a mix of three sea level Raptors and three Raptor Vacuum engines to give it the thrust it needs to reach orbit and ensure efficient operations both in atmosphere and vacuum.
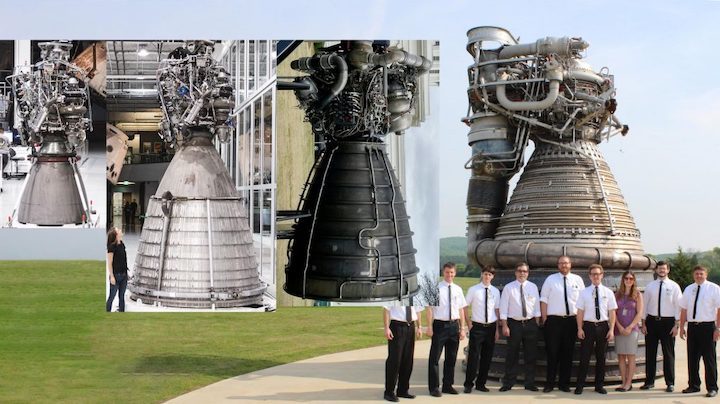
Raptor Vacuum (roughly) to scale alongside Raptor Sea Level, a Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME), and a Saturn V F-1.(Teslarati)
In simple terms, a rocket engine can benefit from a vacuum-optimized nozzle because the added surface area (more or less) gives the extremely high-pressure gases exiting its combustion chamber even more footholds to push against. Rocket nozzles are at their most efficient when the engine’s exhaust gas finishes expanding to match ambient pressure at the exact moment it exits the bell. Logically, at sea level on Earth, the ambient air pressure is quite high, meaning that rocket exhaust doesn’t have to expand as much to equalize.

In the vacuum of space, however, exhaust gases must expand far more to reach the same pressure as its surroundings. For rocket propulsion, that extra expansion can be exploited to make a more efficient engine, squeezing extra energy out of the same propellant and in a perfect vacuum, the most efficient nozzle would technically be infinite. Engineering and physical infinities don’t exactly get along, unfortunately, so vacuum rocket engineers are forced to settle on a nozzle size at a scale that humans can feasibly manufacture.
In theory, Starship doesn’t need Raptor Vacuum engines to be a functioning orbital spacecraft and CEO Elon Musk himself floated a design with seven sea-level engines just two years ago. Since then, the SpaceX CEO revealed that Raptor was making such good progress that the company undid the removal of vacuum-optimized engines from Starship’s baseline design.

It’s unclear exactly what SpaceX means when it says that Raptor Vacuum SN1 completed a “full duration test fire.” For Starship, a full-duration orbital insertion burn – beginning immediately after Super Heavy booster separate – would likely be no shorter than five or six minutes. Even for SpaceX, going from shipping the very first engine (Raptor Vacuum) produced to a successful several-minute static fire in less than three weeks’ time would be an almost inconceivable feat of engineering. The feat would imply that SpaceX is already extremely comfortable with several-minute Raptor burns – perhaps the single biggest hurdle standing between Starship and orbit.
More likely, “full duration test fire” simply refers to the fact that the pathfinder Raptor Vacuum engine managed to ignite, burn, and shut down on schedule – avoiding a premature shutdown, in other words. For an engine as large and complex as Raptor, even that downgraded interpretation would represent an impressive achievement.
Quelle: TESLARATI
----
Update: 2.10.2020
.
SpaceX’s first high-altitude Starship fitted with flaps and rolled to the launch pad

After a four-day delay, SpaceX has successfully installed the first high-altitude Starship at its Boca Chica launch pad not long after the rocket was outfitted with large flaps.
Technically the second time a Starship was outfitted with flaps, Starship serial number 8 had the bottom half of its aerodynamic control surfaces installed on September 23rd – exactly one year after Starship Mk1’s flaps were first installed. Starship Mk1’s flaps were likely meant to be functional but SpaceX never appeared to activate them and Mk1’s main body (tank section) was destroyed during a November 2019 pressure test, failing far before the necessary pressures for flight tests. As such, barring a surprise or two, Starship SN8 will very likely become the first flightworthy prototype to have functional flaps installed.
That remains to be seen, though, and will be put to the test over the next few weeks. If all goes according to plan, the ship could become the first to attempt a high-altitude, 15 km (9.3 mile) launch and landing testing, likely also becoming the first Starship to break the sound barrier.
Starship SN8’s first steps toward testing began on September 26th when SpaceX loaded the rocket onto a self-propelled mobile transporter (SPMT) and rolled it to the company’s dedicated Boca Chica launch and test facilities. Shortly after arrival, a crane and load spreader was attached to the rocket to lift it onto one of the pad’s test stands (Stand A). That lift never came and the crane eventually detached and retracted, kicking off what would become an unusual four-day delay.
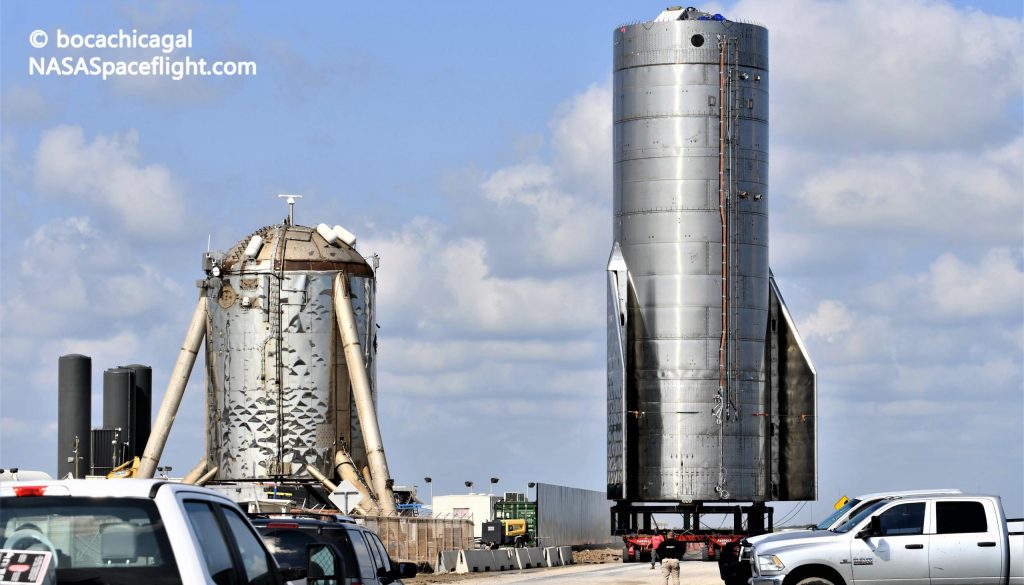

It’s believed that the relatively high winds on the Boca Chica coast were to blame, creating conditions that were too hazardous to risk the precise, hands-on work required to lift and manipulate a ~70 metric ton (~150,000 lb) rocket. While undeniably heavy, an empty Starship’s huge surface area effectively turns it into a giant sail, catching and amplifying wind gusts. Attaching a Starship to a launch mount’s hold-down clamps likely demands millimeter precision, making installation and high winds obviously incompatible (or at least inadvisable).
Finally, around midnight on September 30th, winds died down in Boca Chica and SpaceX fired up a waiting crane and lifted Starship SN8 onto the launch mount. Soon after, technicians began the process of installing the mount’s temporary hydraulic ram – used to mechanically simulate engine thrust – to the rocket’s ‘thrust puck’.
Like every Starship prototype since Mk1, Starship SN8’s first major challenge will involve passing an acceptance test known as a “cryogenic proof.” After being pressurized with ambient-temperature nitrogen gas to check for leaks, SN8 will be fully filled with liquid nitrogen while the hydraulic ram subjects its thrust puck and engine section to stresses similar to the thrust of three Raptor engines. Together, three Raptors are capable of producing more than 600 metric tons (1.3 million lbf) of thrust. For reference, four Raptors would effectively match the thrust of an entire Falcon 9 booster with all nine Merlin 1Ds at full throttle.
If SN8 reaches the necessary pressure and survives the stress of its cryo proof(s), it will likely become the first Starship to attempt a triple-Raptor static fire – a first for the engine, too. Starship SN8’s first cryo proof attempt is scheduled no earlier than 9pm-6am CDT (UTC-5) on Sunday, October 4th with backup windows on the 5th and 6th. The first static fire attempt – possibly beginning with one Raptor or jumping straight to three – could happen several days after a successful cryo proof.
According to Elon Musk, SpaceX will static fire SN8 twice before attempting its 15 km (~50,000 ft) launch debut. More likely than not, SpaceX will attempt a triple-engine static fire with the Starship as-is, install SN8’s nosecone and forward flaps, and attempt a second static fire while only drawing propellant from tbe rocket’s smaller header tanks (one of which is located in the tip of its nose). Only time (or Elon tweets) will tell.
Quelle: TESLARATI
----
Update: 10.10.2020
.
SpaceX’s first high-altitude Starship prototype just “passed cryo proof” testing

SpaceX CEO Elon Musk says that the first high-altitude Starship prototype – known as SN8 – just “passed cryo proof” testing in South Texas, potentially setting the ship up for a ~15 km (9.5 mile) flight test in the near future.
Meanwhile, NASA astronaut Bob Hines recently overflew SpaceX’s Boca Chica, Texas Starship factory with several compatriots, offering an excellent aerial view of the company’s bustling facilities in the midst of Starship SN8’s critical cryo proof test campaign.
Hines managed to catch the Moon alongside one of the T-38 trainer jets NASA astronauts routinely use for training and travel, serving as a reminder that SpaceX won $135 million to build a Lunar Starshipthat might someday return humans to Earth’s lone companion. Likely with or without NASA’s involvement, the Starship prototype production and test program SpaceX is deep in the midst of will directly determine if and when the company visits – and lands on – the Moon and Mars.

A spectacular aerial view of SpaceX’s Boca Chica, Texas Starship factory, captured by one of the NASA astronauts that might one day ride Starship to the Moon. (Bob Hines – NASA)
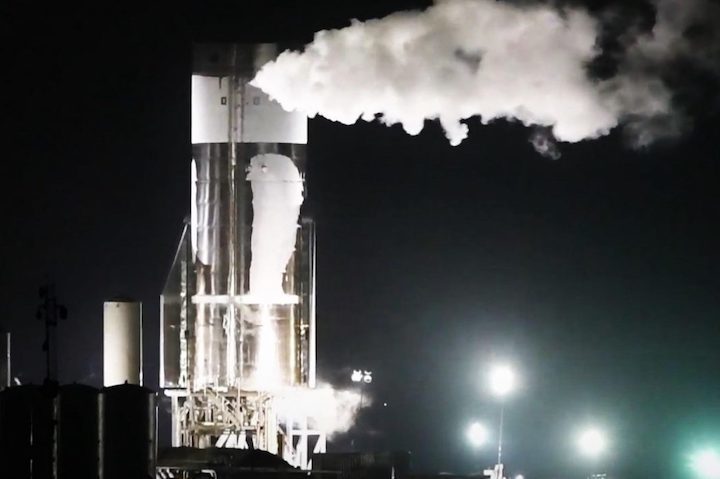
Over the last three days, SpaceX has gradually put Starship SN8 – the first prototype meant for high-altitude flight testing – through its paces, beginning with a seemingly aborted “cryo proof” test on October 5/6. During the first attempt, SpaceX appeared to pressurize the rocket tank section with cold nitrogen gas and perhaps a small volume of liquid nitrogen before reopening the highway. Starship SN8 also actuated its large aft flaps under its own power for the first time on October 4th and SpaceX has performed several more actuation tests in the days since.
24 hours later, SpaceX tried again, this time successfully loading Starship SN8’s liquid oxygen and methane propellant tanks with perhaps a thousand metric tons (2.2 million pounds) of liquid nitrogen – used to simulate the ultra-cold temperatures of cryogenic propellant without the risk of a catastrophic fire or explosion. After cryo load, SpaceX reportedly attempted to pressurize the rocket’s tanks to their limits but the test was stopped somewhat short when Starship SN8 sprung “a small leak…near the engine mounts” after reaching pressures of 7 bar (~100 psi).
Precisely as Musk predicted, SpaceX apparently managed to fix the minor leak in less than 24 hours and began the third round of Starship SN8 cryo proof testing late on October 7th. Once again, the rocket was fully loaded with liquid nitrogen and spent some 2-3 hours under cryogenic stress as SpaceX likely stress the thrust structure (“thrust puck”) by simulating the thrust of Raptor engines with hydraulic rams. Nothing out of the ordinary happened and Musk has yet to comment on the test, suggesting that things went largely as planned.
Intriguingly, SpaceX then geared up for a fourth night of cryogenic testing on October 8/9. It’s not entirely surprising that the company would want to test the first Starship built primarily with a new steel alloy as thoroughly as possible. If SN8’s fourth night of testing produces satisfactory results and SpaceX is less than concerned with the leak discovered during the second round of testing, the company could be ready to install three engines and attempt the first multi-Raptor static fire test ever.
Update: SpaceX CEO Elon Musk says that Starship SN8 “passed cryo proof” testing, most likely setting the rocket up for the first triple-Raptor static fire test ever attempted. If SN8 passes static fire testing, it will most likely be outfitted with a nosecone and forward flaps and attempt another three-engine static fire using smaller ‘header’ propellant tanks, ultimately preparing it to support the first high-altitude flight test of a Starship prototype if all goes according to plan.
Check out Teslarati’s newsletters for prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket launch and recovery processes.
Quelle: TESLARATI
----
Update: 13.10.2020
.
SN8 receiving Raptors as prelude to advanced Starship testing
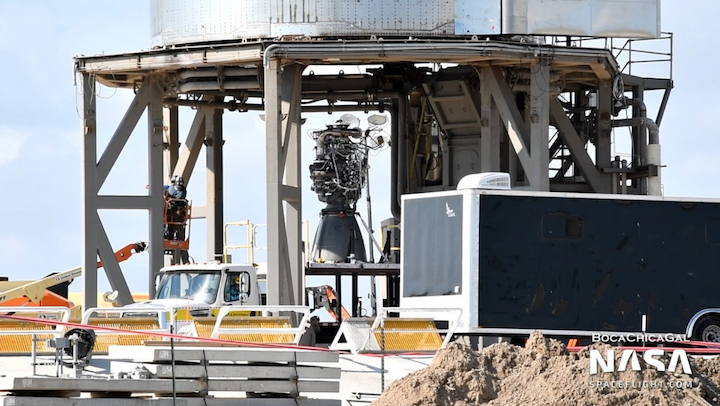

Installation of the three Raptors that will power Starship SN8’s unique test flight began on Sunday at SpaceX Boca Chica. The brand new engines will be the focal point of a test program that will involve at least two Static Fire tests ahead of a test flight to 50,000 feet.
Starship SN8:
SN8 underwent a total of three cryo proofing tests during the week. The first was deemed acceptable per the test parameters, but a small leak “opened up near the engine mounts, possibly due to differential shrinking,” according to SpaceX Chief Designer and CEO Elon Musk.
The repair was completed in time for a second test the following night, which appeared to show SN8 fully loaded with LN2 (Liquid Nitrogen), but without any reference as to how it went from Elon. Roadblocks were then called for the third time, pointing to another test 24 hours later.
This time the test concluded with Elon noting cryo proofing was a success.
With this milestone complete, the Thrust Rams were removed from underneath SN8 to make room for installing the three Raptor engines.
These rams are used to mechanically simulate the forces of engine thrust on the Thrust Puck in the vehicle’s aft.
With Raptor installation beginning on Sunday, Starship testing is now entering a new phase that will include numerous firsts.
Once the Raptors are installed, Starship SN8 is expected to undergo an extensive test program, opening with fueling tests, a spin prime test, and preburner tests, before the first Static Fire test.
That opening Static Fire test will be the first time three Raptors have been fired up simultaneously.
