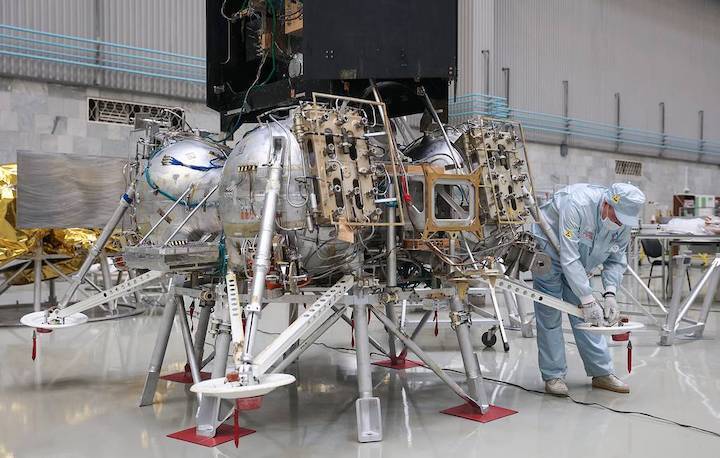
"The production of the final types of instruments will begin somewhere at the end of this year," he said.
In February, work was completed to test the electric interfaces of devices for switching on/off, selecting and issuing commands and obtaining data, he said.
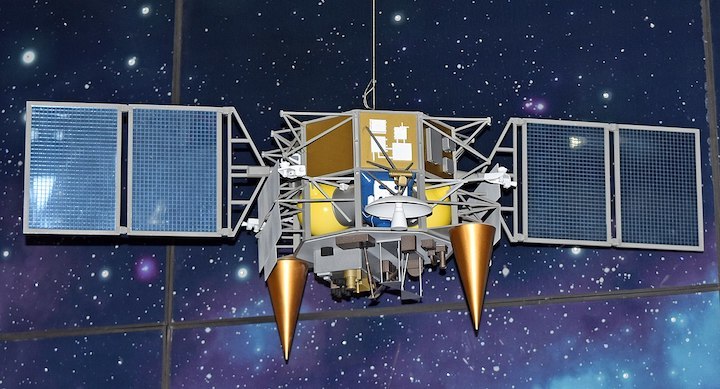
The Luna-26 lunar orbital probe is expected to scan almost the entire surface of the Earth’s natural satellite from the orbit. The Luna-26 orbiter will also carry equipment to create a 3D map. The space vehicle is expected to be launched in 2024.
Russia’s State Space Corporation Roscosmos also plans to launch the Luna-25 probe in 2021 and the Luna-27 space vehicle in 2025. Roscosmos Chief Dmitry Rogozin earlier said that Russia’s integrated space program whose beginning was scheduled for 2020 would include heavy rovers for drilling the Moon’s surface, collecting soil samples and delivering them to Earth.