Chinese space station Tiangong-2 is about to burn up over the Pacific
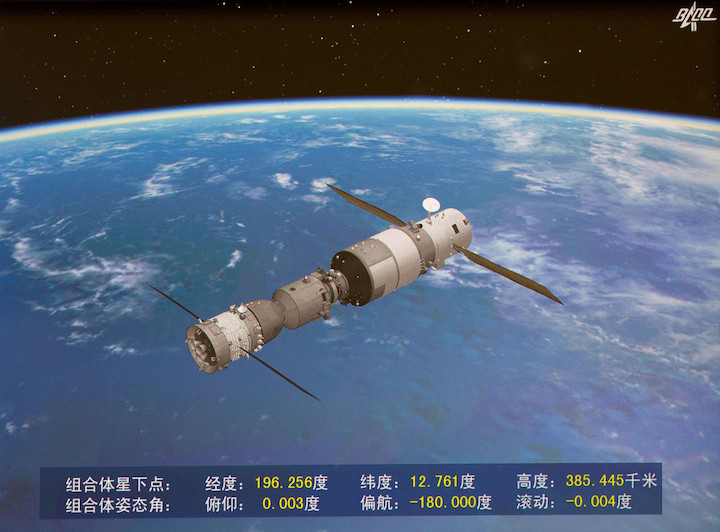

The final hours for China’s Tiangong-2 space station are at hand, as the eight-ton piece of hardware will fall to earth, or rather sea, some time in the next 20 hours or so in a controlled deorbit maneuver. But unlike with its predecessor, it isn’t a mystery where this particular piece of space debris is going to fall.
Tiangong-2 is a small space station that was put into orbit in 2016 to test a number of China’s orbital technologies; it was originally planned to stay up there for two years, but as many a well-engineered piece of space kit has done, it greatly exceeded its expected lifespan and has been operational for more than a thousand days now.
Chinese Taikonauts have visited the station to perform experiments, test tools, perform orbital refueling and all that sort of thing. But it’s not nearly as well equipped as the International Space Station, nor as spacious — and that’s saying something — so they only stayed a month, and even that must have been pretty grueling.
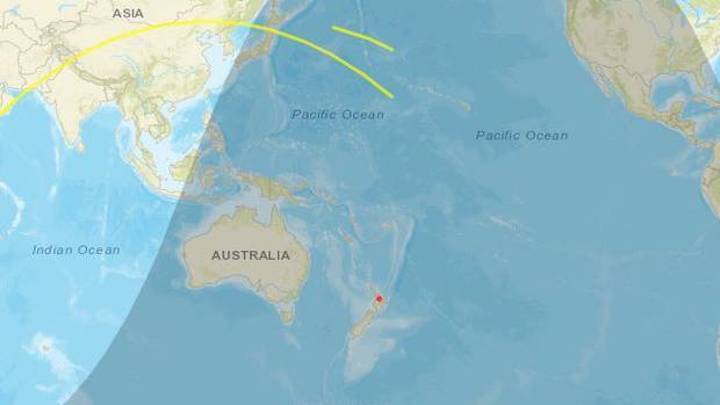
The time has come, however, for Tiangong-2 to be deorbited and, naturally, destroyed in the process. The China National Space Administration indicated that the 18-meter-wide station and solar panels will mostly burn up during reentry, but that a small amount of debris may fall “in a safe area in the South Pacific,” specifying a rather large area that does technically include quite a bit of New Zealand (160-190°W long by 30-45°S lat).
They did not specify when exactly it would be coming down, except that it would be during July 19 Beijing time (it’s already morning there at the time of publishing). It should produce a visible streak but not anything you’ll see if you aren’t looking for it. This visualization from The Aerospace Company shows how the previous, very similar station would break up:
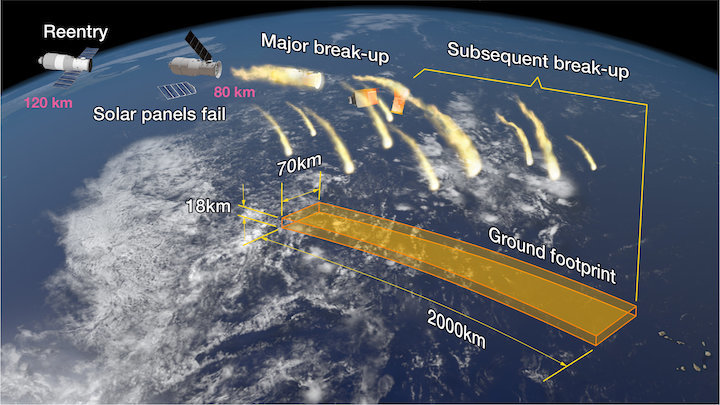
That’s much better than Tiangong-1, which stopped responding to its operators after several years and as such could not be deliberately guided into a safe reentry path. Instead it just slowly drifted down until people were pretty sure it would be reentering sometime in the following few days — and it did.
There was never any real danger that the bus-sized station would land on anyone, but it’s just fundamentally a little unnerving not knowing where the thing would be coming down.
This isn’t the last Tiangong; Tiangong-3 is planned for a 2020 launch, and will further inform the Chinese engineers and astronauts in their development of a more full-featured space station planned for a couple years down the line.
Controlled deorbit is the responsible thing to do, not to mention just plain polite, and the CNSA is doing the right thing here. All the same, Kiwis should probably carry umbrellas tomorrow.
Quelle: TC
+++