15.06.2019
A small near-Earth object might be a historic piece of space hardware: the Apollo 10 lunar module, dubbed "Snoopy."
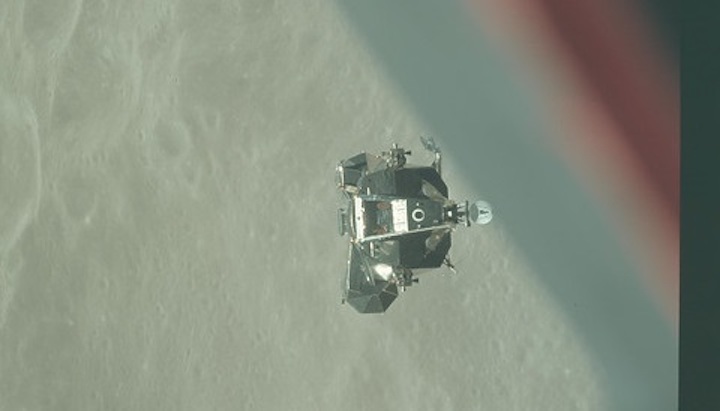

The Snoopy lunar module, closing in on the Charlie Brown command module.
NASA / Project Apollo Archive
On May 23, 1969, astronauts aboard Apollo 10 jettisoned the Snoopy lunar module and headed for Earth. That's the last time humans set eyes on Snoopy — now, astronomers may have rediscovered this fascinating artifact of space history.
Fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society astronomer Nick Howesshared the possible discovery recently at Cheltenham Science Festival. Howes, who began the search for Snoopy in 2011, said in a recent Sky News report that he is 98% certain that the object in question is, in fact, Snoopy. However, it will require follow-up observations to conclusively prove (or disprove) this conclusion.
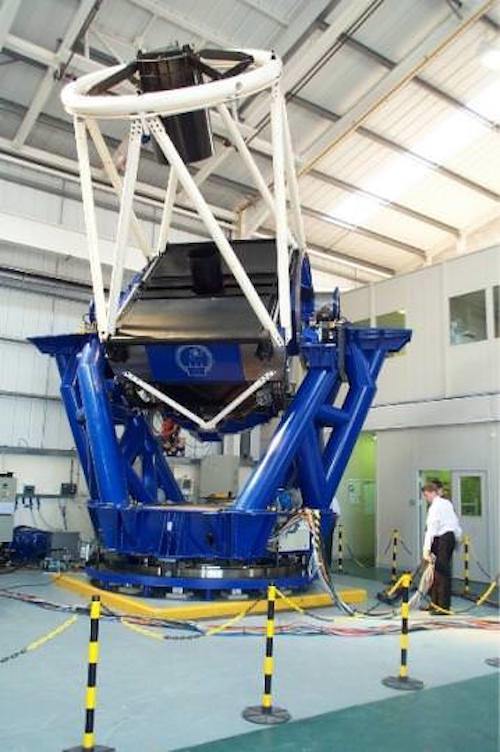

The 2-meter Faulkes Telescope South at Siding Spring Observatory.
Nick Howes / LCOGT
Astronomers started the hunt in 2011 using the Faulkes North Telescope in Hawai'i, the Faulkes South Telescope in Australia, and data from the Catalina Sky Survey, located outside of Tucson, Arizona. The break came last year during observations taken at the Mt Lemmon and other survey observatories, with the discovery of the small Earth-crossing asteroid 2018 AV2. Orbiting the Sun once every 382 days, 2018 AV2 spends most of its time trailing Earth in its orbit around the Sun. Two factors grabbed astronomers' attention: its low orbital inclination (less than 1°) relative to the ecliptic, and its low speed, less than a kilometer per second relative to Earth's orbital velocity.
Other factors also led to the conclusion that 2018 AV2 is likely to be Snoopy. It's already listed as an artificial object on the International Astronomical Union Minor Planet Center's Distant Artificial Objects page. According to Howes, the object's brightness also corresponded to "a size in the right ballpark." In addition, Howes says he had received mail "from a trusted astronomer at the Arizona Sky Survey indicating that JPL teams had also worked on it, and it looked like it was in the right place in 1969."
Apollo 10: Prelude to History
Often forgotten between the dramatic Apollo 8 mission around the Moon and the first crewed Moon landing of Apollo 11, Apollo 10 was still a vital mission. After Apollo 9 tested the lunar module in space for the first time in Earth orbit, Apollo 10 acted as a dress rehearsal for the Moon landing. The astronauts flew the lunar module down to within 14.5 kilometers (9 miles) of the lunar surface. The module was named "Snoopy" after the Peanuts comics strip character, while the corresponding command module was named Charlie Brown.
Snoopy's trajectory was unique among the Apollo missions. Unlike in the five missions that landed on the Moon, the Snoopy lunar module was ultimately jettisoned into an orbit around the Sun.
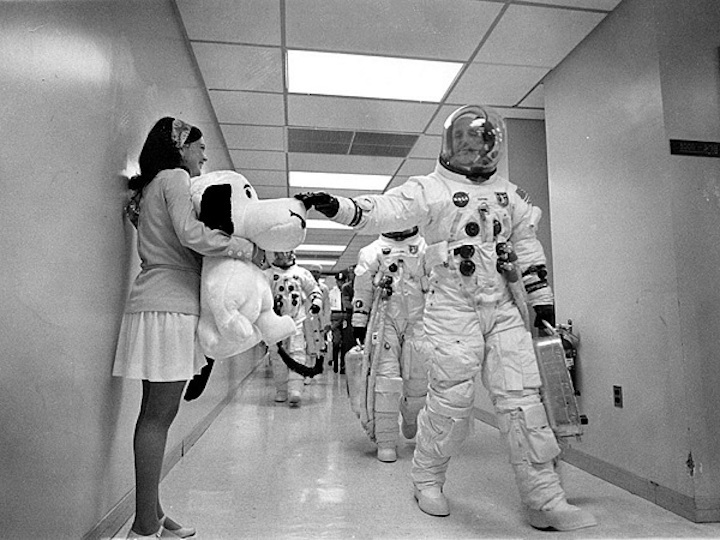

Apollo 10 astronauts (Commander Tom Stafford is patting Snoopy's nose) preparing for departure.
NASA
False Alarms
There have been several false finds over the years in the hunt to recover Snoopy. Around 2015 astronomers were convinced that the small near-Earth asteroid WT1190F was in fact the lost lunar module. WT1190F struck Earth in the Indian Ocean near Sri Lanka on November 13, 2015, and is now thought to have been the trans-lunar injection stage from the 1998 Lunar Prospector mission.
In 2006 one of the first temporary mini-moons of the Earth was discovered, 2006 RH120. As the ranks of near-Earth asteroids has grown in the years since, astronomers have realized that small asteroids are occasionally captured by the Earth-Moon system, following complex orbits around the pair before being ejected back out into solar orbit. These objects may be confused with discarded Space Age hardware, which often follows the same path. For example, asteroid J002E3 was spotted back in 2002, but astronomers soon realized that its spectra matched paint used by NASA in the late 1960s. The object turned out to be a third-stage booster from Apollo 12. Another asteroid, 2013 QW1, turned out to be an upper stage booster from China's Chang'e 2 Moon mission.
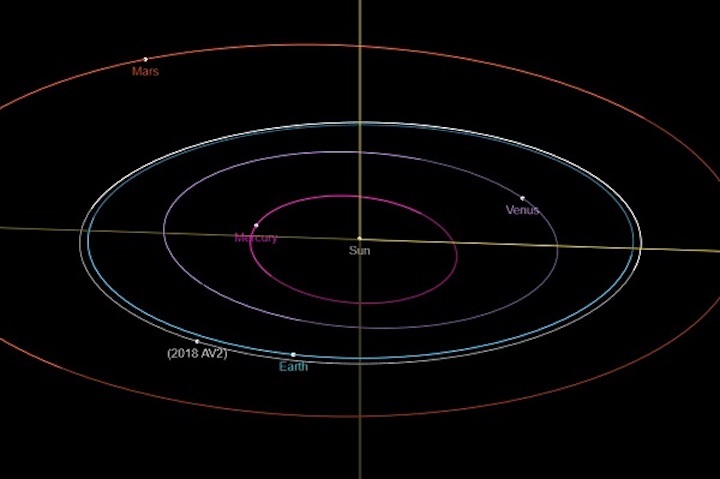
The orbit of 2018 AV2.
NASA / JPL
Unfortunately, 2018 AV2 is currently 0.374 astronomical units (34.7 million miles) from Earth, making it a faint +29.5 magnitude object. Its next close approach won't come until July 10, 2037, when it will pass 4 million miles from Earth, equivalent to 16 times the Earth-Moon distance.
However, it would theoretically be possible to observe the object now: Howes notes that a Falcon Heavy or Delta IV rocket could traverse the current distance in a year. Another possibility would be to send a small CubeSat along with a future SLS launch, with the purpose of flying by the object to make observations.
Spectral analysis, a radar profile, and other observations would go a long ways towards confirming or rejecting the object's identity. After all, hollow metallic artificial objects react differently to solar heating and radiative pressure (known as the Yarkovsky effect) than solid space rocks.
Certainly, Snoopy is one of the more curious objects man-made objects in solar orbit. Elon Musk's Tesla Roadster, which SpaceX launched into solar orbit via its inaugural Falcon Heavy flight in 2018, probably wins for "most curious." Howes notes that Musk is a big fan of the Apollo program, so maybe a salvage isn't totally out of the question. The module has suffered from a half-century of continuous ultraviolet radiation exposure, but it should be relatively intact.
"There's clearly a lot from humankind's first foray in to deep space still out there," says Howes, "and whilst the scientific argument to retrieve them is marginal, I think with Snoopy you have a unique, one-off remnant of our greatest technical achievement . . . One I'd love to show close-up images of to [Apollo 10 astronauts] Tom Stafford and the family of Gene Cernan one day."
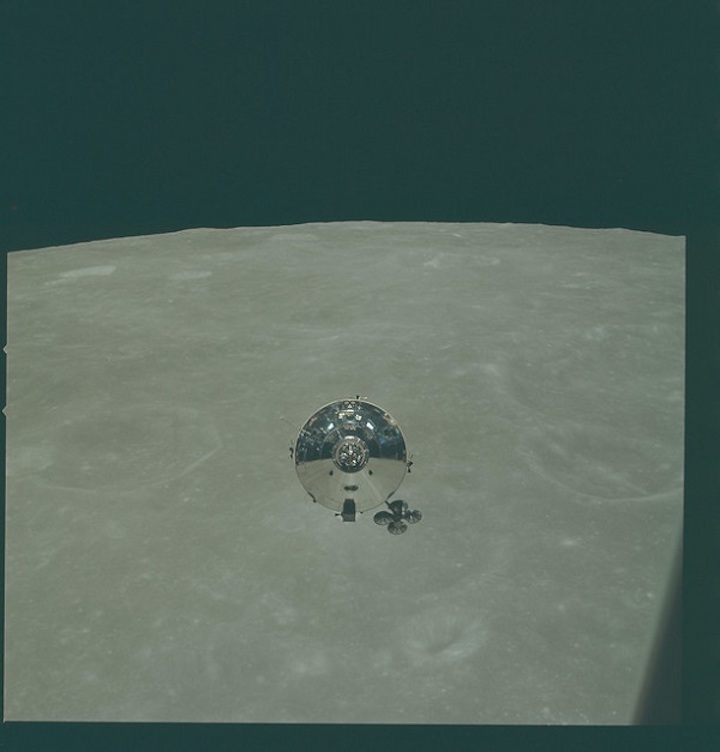

Looking out the lunar module window at Charlie Brown.
NASA / Apollo Image Archives.
For now though, it's an interesting idea to consider as we approach the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 moon landing, that a part of the precursor mission that made it all possible is still out there, silently orbiting the Sun.
Qwelle: Sky&Telescope
