.
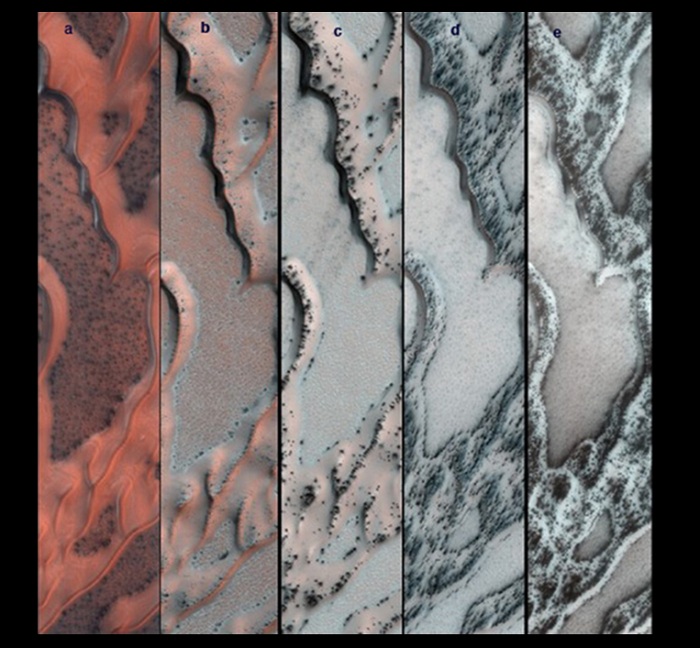
Seasonal Changes on Far-Northern Mars
The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter snapped this series of false-color pictures of sand dunes in the north polar region of Mars. The area covered in each of the five panels is about 0.8 mile (1.3 kilometers) wide.
The progression begins at left (Panel A) in early spring, when the ground is covered by a seasonal layer of carbon dioxide ice (dry ice) about 2 feet thick. As spring progresses the ice cracks (Panel B), releasing dark sand from the dune below. When pressurized gas trapped below the ice layer is released, it carries along sand and dust to the top of the ice layer, where it is dropped in fan-shaped deposits downhill and downwind (panels C and D). The final panel shows more and more of the dark dunes as the overlying layer of seasonal ice evaporates back into the atmosphere.
The location in this series of images is at 80 degrees north latitude, 122.5 degrees east longitude.
-
PASADENA, Calif. -- Researchers using NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter see seasonal changes on far-northern Martian sand dunes caused by warming of a winter blanket of frozen carbon dioxide.
Earth has no naturally frozen carbon dioxide, though pieces of manufactured carbon-dioxide ice, called "dry ice," sublime directly from solid to gas on Earth, just as the vast blankets of dry ice do on Mars. A driving factor in the springtime changes where seasonal coverings of dry ice form on Mars is that thawing occurs at the underside of the ice sheet, where it is in contact with dark ground being warmed by early-spring sunshine through translucent ice. The trapped gas builds up pressure and breaks out in various ways.
Transient grooves form on dunes when gas trapped under the ice blanket finds an escape point and whooshes out, carrying out sand with it. The expelled sand forms dark fans or streaks on top of the ice layer at first, but this evidence disappears with the seasonal ice, and summer winds erase most of the grooves in the dunes before the next winter. The grooves are smaller features than the gullies that earlier research linked to carbon-dioxide sublimation on steeper dune slopes.
The findings reinforce growing appreciation that Mars today, however different from its former self, is still a dynamic world, and however similar to Earth in some respects, displays some quite unearthly processes.
"It's an amazingly dynamic process," said Candice Hansen of the Planetary Science Institute, Tucson. She is lead author of the first of the three new reports. "We had this old paradigm that all the action on Mars was billions of years ago. Thanks to the ability to monitor changes with the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, one of the new paradigms is that Mars has many active processes today."
With three Martian years (six Earth years) of data in hand from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera, the researchers report on the sequence and variety of seasonal changes. The spring changes include outbursts of gas carrying sand, polygonal cracking of the winter ice blanketing the dunes, sandfalls down the faces of the dunes, and dark fans of sand propelled out onto the ice.
"It is a challenge to catch when and how those changes happen, they are so fast," said Ganna Portyankina of the University of Bern in Switzerland, lead author of the second report. "That's why only now we start to see the bigger picture that both hemispheres actually tell us similar stories."
The seasonal dry-ice sheets overlie different types of terrain in the two hemispheres. In the south, diverse terrains include the flat, erodible ground where the spiders form, but in the north, a broad band of sand dunes encircles the permanent north polar ice cap.
Another difference is in brightening on parts of the ice-covered dunes. This brightening in the north results from the presence of water-ice frost, while in the south, similar brightening is caused by fresh carbon dioxide. The third paper of the Icarus set, by Antoine Pommerol of the University of Bern and co-authors, reports distribution of the water frost using the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM). The light water frost is blown around by spring winds.
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates the HiRISE camera, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colo. The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, Md., provided and operates CRISM. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, built the orbiter.-
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona
