14.11.2018
NASA has certified SpaceX’s Falcon 9 (likely F9 v1.2) to launch the space agency’s most valuable and critical scientific spacecraft, opening up the floor for SpaceX to routinely compete for missions comparable to Hubble Space Telescope, the Curiosity Mars rover (Mars Science Laboratory), Cassini (a Saturn orbiter), and James Webb Space Telescope, among many others.
As SpaceX nears the Falcon family’s 35th consecutive launch success, this certification serves as a pragmatic endorsement of the years of work the company has put into optimizing Falcon 9 for performance and reliability.
Although Falcon 9 is capable of extremely impressive performance beyond Earth orbit, that performance only becomes truly competitive with ULA’s Atlas V rocket when Falcon 9 is launched as a fully expendable vehicle. Regardless, both Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy are all but guaranteed to cost far less than a comparably capable Atlas V, even assuming no recovery attempt is made. Given the rarity of such valuable NASA launches, typically no more than two annually at best, SpaceX would undoubtedly be more than happy to expend as much hardware as necessary to give NASA a competitive offer for the performance it needs.
“LSP Category 3 certification is a major achievement for the Falcon 9 team and represents another key milestone in our close partnership with NASA. We are honored to have the opportunity to provide cost-effective and reliable launch services to the country’s most critical scientific payloads.” – Gwynne Shotwell, COO and President of SpaceX
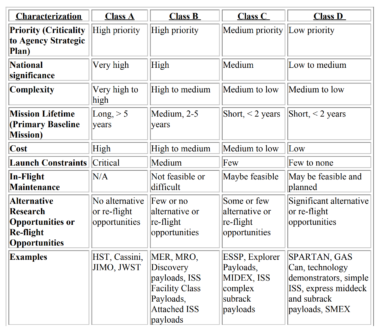
Still, the fact remains that most – if not all – of NASA’s high-value “Class A or B” missions end up being extremely heavy spacecraft, either as a result of large and expensive scientific instruments, a need for lots of extra onboard propellant, or some combination of the two. Saturnian orbiter Cassini, launched in 1997, weighed a full ~5700 kg (~12,600 lbs) and had to make its way from Earth to Saturn, a journey of many hundreds of millions of miles. Hubble, placed in a medium Earth orbit, weighed 11,100 kg (24,500 lbs) at liftoff. The Curiosity rover – including cruise stage, reentry hardware, and rocket crane – weighed ~3900 kg (~8600 lbs) at launch.
PAVING THE WAY FOR FALCON HEAVY
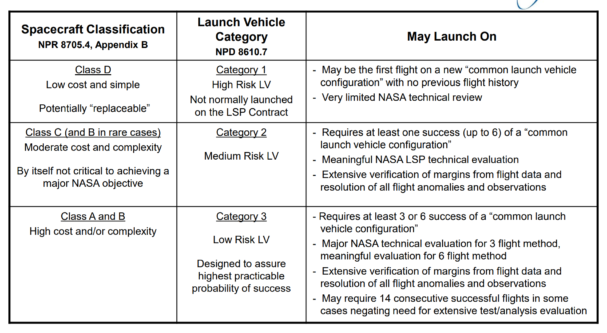
Falcon 9 routinely launches payloads as heavy as that but only to comparatively low-energy orbits around Earth – to launch the same massive payloads beyond Earth orbit requires far more energy and thus rocket performance. Perhaps the most encouraging part of this NASA certification is the demonstration that NASA’s trust in SpaceX rockets has grown to the point that Falcon Heavy certification is likely just a matter of time. In order to qualify for “LSP Category 3” certification, any given rocket must launch anywhere from 3-6 times depending on what the certification board feels is necessary.
SpaceX has at least two Falcon Heavy launches scheduled for 2019. Combined with the rocket’s nearly flawless February 2018 launch debut, those two launches – commsat Arabsat 6A and the Air Force’s STP-2 mission – could satisfy NASA LSP and allow the agency to certify Falcon Heavy for flagship science missions. If/when that occurs, SpaceX will be able to offer NASA all the performance they will conceivably need for the foreseeable future, ensuring that NASA will be able to compete most future launch contracts. At worst, a ULA victory would force the company to significantly lower their prices.

Quelle: TESLARATI