.
NASA, ESA Telescopes Find Evidence for Asteroid Belt Around Vega
WASHINGTON -- Astronomers have discovered what appears to be a large asteroid belt around the star Vega, the second brightest star in northern night skies. The scientists used data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the European Space Agency's (ESA) Herschel Space Observatory, in which NASA plays an important role.
The discovery of an asteroid belt-like band of debris around Vega makes the star similar to another observed star called Fomalhaut. The data are consistent with both stars having inner, warm belts and outer, cool belts separated by a gap. This architecture is similar to the asteroid and Kuiper belts in our own solar system.
What is maintaining the gap between the warm and cool belts around Vega and Fomalhaut? The results strongly suggest the answer is multiple planets. Our solar system's asteroid belt, which lies between Mars and Jupiter, is maintained by the gravity of the terrestrial planets and the giant planets, and the outer Kuiper belt is sculpted by the giant planets.
"Our findings echo recent results showing multiple-planet systems are common beyond our sun," said Kate Su, an astronomer at the Steward Observatory at the University of Arizona. Su presented the results Tuesday at the American Astronomical Society meeting in Long Beach, Calif., and is lead author of a paper on the findings accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal.
Vega and Fomalhaut are similar in other ways. Both are about twice the mass of our sun and burn a hotter, bluer color in visible light. Both stars are relatively nearby at about 25 light-years away. The stars are thought to be around 400 million years old, but Vega could be closer to its 600 millionth birthday. Fomalhaut has a single candidate planet orbiting it, Fomalhaut b, which orbits at the inner edge of its cometary belt.
The Herschel and Spitzer telescopes detected infrared light emitted by warm and cold dust in discrete bands around Vega and Fomalhaut, discovering the new asteroid belt around Vega and confirming the existence of the other belts around both stars. Comets and the collisions of rocky chunks replenish the dust in these bands. The inner belts in these systems cannot be seen in visible light because the glare of their stars outshines them.
Both the inner and outer belts contain far more material than our own asteroid and Kuiper belts. The reason is twofold: the star systems are far younger than our own, which has had hundreds of millions more years to clean house, and the systems likely formed from an initially more massive cloud of gas and dust than our solar system.
The gap between the inner and outer debris belts for Vega and Fomalhaut also proportionally corresponds to the distance between our sun's asteroid and Kuiper belts. This distance works out to a ratio of about 1:10, with the outer belt 10 times farther away from its host star than the inner belt. As for the large gap between the two belts, it is likely there are several undetected planets, Jupiter-sized or smaller, creating a dust-free zone between the two belts. A good comparison star system is HR 8799, which has four known planets that sweep up the space between two similar disks of debris.
"Overall, the large gap between the warm and the cold belts is a signpost that points to multiple planets likely orbiting around Vega and Fomalhaut," said Su.
If unseen planets do in fact orbit Vega and Fomalhaut, these bodies will not likely stay hidden.
"Upcoming new facilities such as NASA's James Webb Space Telescope should be able to find the planets," said paper co-author Karl Stapelfeldt, chief of the Exoplanets and Stellar Astrophysics Laboratory at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
-
NASA's Hubble Reveals Rogue Planetary Orbit for Fomalhaut B
WASHINGTON -- Newly released NASA Hubble Space Telescope images of a vast debris disk encircling the nearby star Fomalhaut and a mysterious planet circling it may provide forensic evidence of a titanic planetary disruption in the system.
Astronomers are surprised to find the debris belt is wider than previously known, spanning a section of space from 14 to nearly 20 billion miles from the star. Even more surprisingly, the latest Hubble images have allowed a team of astronomers to calculate the planet follows an unusual elliptical orbit that carries it on a potentially destructive path through the vast dust ring.
The planet, called Fomalhaut b, swings as close to its star as 4.6 billion miles, and the outermost point of its orbit is 27 billion miles away from the star. The orbit was recalculated from the newest Hubble observation made last year.
"We are shocked. This is not what we expected," said Paul Kalas of the University of California at Berkeley and the SETI Institute in Mountain View, Calif.
The Fomalhaut team led by Kalas considers this circumstantial evidence there may be other planet-like bodies in the system that gravitationally disturbed Fomalhaut b to place it in such a highly eccentric orbit. The team presented its finding Tuesday at the 221st meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Long Beach, Calif.
Among several scenarios to explain Fomalhaut b's 2,000-year-long orbit is the hypothesis that an as yet undiscovered planet gravitationally ejected Fomalhaut b from a position closer to the star, and sent it flying in an orbit that extends beyond the dust belt.
"Hot Jupiters get tossed through scattering events, where one planet goes in and one gets thrown out," said co-investigator Mark Clampin of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "This could be the planet that gets thrown out."
Hubble also found the dust and ice belt encircling the star Fomalhaut has an apparent gap slicing across the belt. This might have been carved by another undetected planet. Hubble's exquisite view of the dust belt shows irregularities that strongly motivate a search for other planets in the system.
If its orbit lies in the same plane with the dust belt, then Fomalhaut b will intersect the belt around 2032 on the outbound leg of its orbit. During the crossing, icy and rocky debris in the belt could crash into the planet's atmosphere and create the type of cosmic fireworks seen when Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 crashed into Jupiter. Most of the fireworks from collisions will be seen in infrared light. However, if Fomalhaut b is not co-planar with the belt, the only thing to be seen will be a gradual dimming of Fomalhaut b as it travels farther from the star.
Kalas hypothesized that Fomalhaut b's extreme orbit is a major clue in explaining why the planet is unusually bright in visible light, but very dim in infrared light. It is possible the planet's optical brightness originates from a ring or shroud of dust around the planet, which reflects starlight. The dust would be rapidly produced by satellites orbiting the planet, which would suffer extreme erosion by impacts and gravitational stirring when Fomalhaut b enters into the planetary system after a millennium of deep freeze beyond the main belt. An analogy can be found by looking at Saturn, which has a tenuous, but very large dust ring produced when meteoroids hit the outer moon Phoebe.
The team has also considered a different scenario where a hypothetical second dwarf planet suffered a catastrophic collision with Fomalhaut b. The collision scenario would explain why the star Fomalhaut has a narrow outer belt linked to an extreme planet. But in this case the belt is young, less than 10,000 years old, and it is difficult to produce energetic collisions far from the star in such young systems.
Fomalhaut is a special system because it looks like scientists may have a snapshot of what our solar system was doing 4 billion years ago. The planetary architecture is being redrawn, the comet belts are evolving, and planets may be gaining and losing their moons. Astronomers will continue monitoring Fomalhaut b for decades to come because they may have a chance to observe a planet entering an icy debris belt that is like the Kuiper Belt at the fringe of our own solar system.
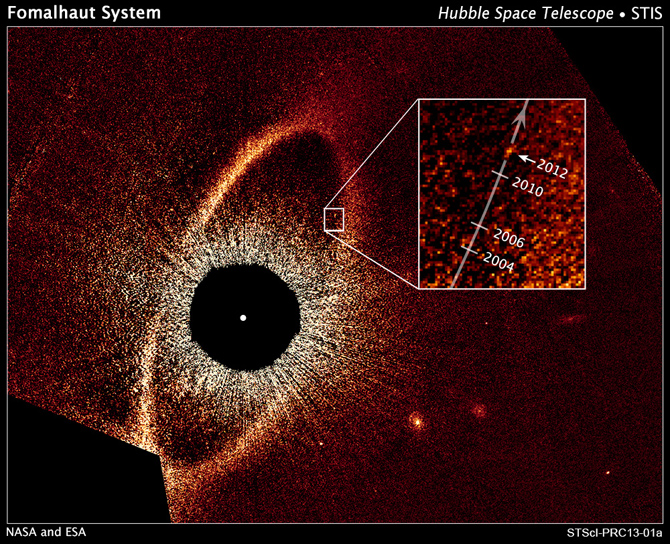
This false-color composite image, taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, reveals the orbital motion of the planet Fomalhaut b. Based on these observations, astronomers calculated that the planet is in a 2,000-year-long, highly elliptical orbit. The planet will appear to cross a vast belt of debris around the star roughly 20 years from now. If the planet's orbit lies in the same plane with the belt, icy and rocky debris in the belt could crash into the planet's atmosphere and produce various phenomena. The black circle at the center of the image blocks out the light from the bright star, allowing reflected light from the belt and planet to be photographed. The Hubble images were taken with the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph in 2010 and 2012. Credit: NASA, ESA, and P. Kalas (University of California, Berkeley and SETI Institute)
-
Newly released NASA Hubble Space Telescope images of a vast debris disk encircling the nearby star Fomalhaut and a mysterious planet circling it may provide forensic evidence of a titanic planetary disruption in the system.
Astronomers are surprised to find the debris belt is wider than previously known, spanning a section of space from 14 to nearly 20 billion miles from the star. Even more surprisingly, the latest Hubble images have allowed a team of astronomers to calculate the planet follows an unusual elliptical orbit that carries it on a potentially destructive path through the vast dust ring.
The planet, called Fomalhaut b, swings as close to its star as 4.6 billion miles, and the outermost point of its orbit is 27 billion miles away from the star. The orbit was recalculated from the newest Hubble observation made last year.
"We are shocked. This is not what we expected," said Paul Kalas of the University of California at Berkeley and the SETI Institute in Mountain View, Calif.
The Fomalhaut team led by Kalas considers this circumstantial evidence there may be other planet-like bodies in the system that gravitationally disturbed Fomalhaut b to place it in such a highly eccentric orbit. The team presented its finding Tuesday at the 221st meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Long Beach, Calif.
Among several scenarios to explain Fomalhaut b's 2,000-year-long orbit is the hypothesis that an as yet undiscovered planet gravitationally ejected Fomalhaut b from a position closer to the star, and sent it flying in an orbit that extends beyond the dust belt.
"Hot Jupiters get tossed through scattering events, where one planet goes in and one gets thrown out," said co-investigator Mark Clampin of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "This could be the planet that gets thrown out."
Hubble also found the dust and ice belt encircling the star Fomalhaut has an apparent gap slicing across the belt. This might have been carved by another undetected planet. Hubble's exquisite view of the dust belt shows irregularities that strongly motivate a search for other planets in the system.
If its orbit lies in the same plane with the dust belt, then Fomalhaut b will intersect the belt around 2032 on the outbound leg of its orbit. During the crossing, icy and rocky debris in the belt could crash into the planet's atmosphere and create the type of cosmic fireworks seen when Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 crashed into Jupiter. Most of the fireworks from collisions will be seen in infrared light. However, if Fomalhaut b is not co-planar with the belt, the only thing to be seen will be a gradual dimming of Fomalhaut b as it travels farther from the star.
Kalas hypothesized that Fomalhaut b's extreme orbit is a major clue in explaining why the planet is unusually bright in visible light, but very dim in infrared light. It is possible the planet's optical brightness originates from a ring or shroud of dust around the planet, which reflects starlight. The dust would be rapidly produced by satellites orbiting the planet, which would suffer extreme erosion by impacts and gravitational stirring when Fomalhaut b enters into the planetary system after a millennium of deep freeze beyond the main belt. An analogy can be found by looking at Saturn, which has a tenuous, but very large dust ring produced when meteoroids hit the outer moon Phoebe.
The team has also considered a different scenario where a hypothetical second dwarf planet suffered a catastrophic collision with Fomalhaut b. The collision scenario would explain why the star Fomalhaut has a narrow outer belt linked to an extreme planet. But in this case the belt is young, less than 10,000 years old, and it is difficult to produce energetic collisions far from the star in such young systems.
Fomalhaut is a special system because it looks like scientists may have a snapshot of what our solar system was doing 4 billion years ago. The planetary architecture is being redrawn, the comet belts are evolving, and planets may be gaining and losing their moons. Astronomers will continue monitoring Fomalhaut b for decades to come because they may have a chance to observe a planet entering an icy debris belt that is like the Kuiper Belt at the fringe of our own solar system.
-
Quelle: NASA
6735 Views
