12.07.2018
Launched on 13 October 2017, Sentinel-5P is the first Copernicus satellite dedicated to monitoring our atmosphere. It is part of the fleet of Sentinel missions that ESA develops for the European Union’s environmental monitoring Copernicus programme managed by the European Commission.
Philippe Brunet, Director of Space Policy, Copernicus and Defence at the European Commission, welcomed the release and accuracy of the new data, which has shone a light on air pollution on a global scale.
“These first data are another milestone for our Copernicus programme. They show how Sentinel-5P is set to make a real difference in monitoring air quality and highlight European Union’s contribution to combatting the global issue of air pollution.”
As poor air quality continues to prematurely claim the lives of millions of people every year, it is more important than ever that we find better and more accurate ways of monitoring the air we breathe.
Thanks to its Tropomi instrument – the most advanced multispectral imaging spectrometer to date – Sentinel-5P can zoom down to the surface of Earth and deliver highly detailed and accurate data about the atmosphere.
With a resolution of up to 7 x 3.5 km, it can even detect air pollution over individual cities.
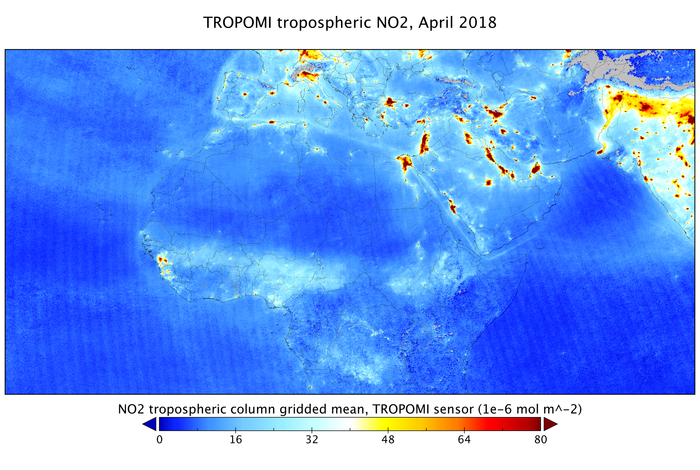
Nitrogen dioxide from Sentinel-5P
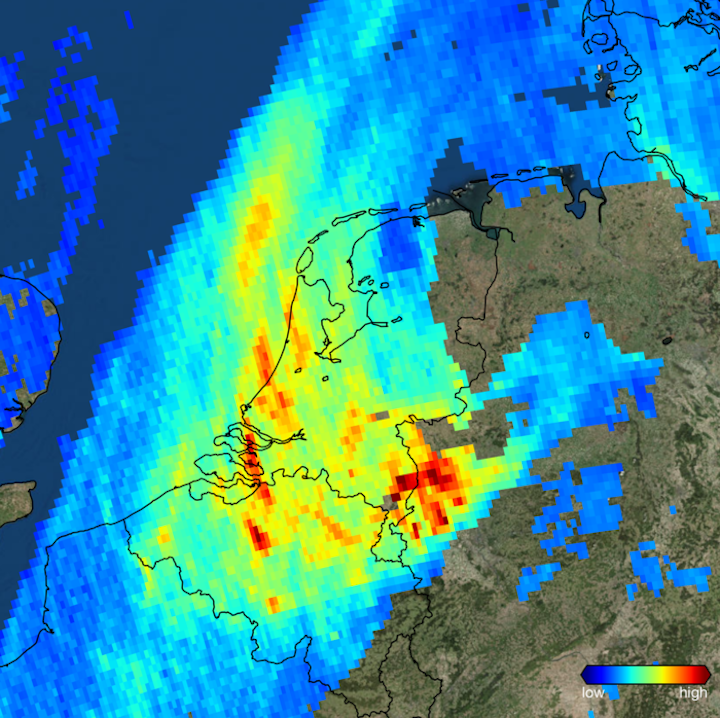
The Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite imaged high levels of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide over the Netherlands and the Ruhr area in west Germany on 7 November 2017. Launched on 13 October 2017, Sentinel-5P is the first Copernicus mission dedicated to monitoring our atmosphere. This new satellite carries the state-of-the-art Tropomi instrument to map a multitude of trace gases and aerosols that affect the air we breathe and our climate. This is one of the first images delivered by this new mission.
This higher spatial resolution is key to what makes the data produced by Sentinel-5P so useful. Tropomi also has the capacity to locate where pollutants are being emitted, effectively identifying pollution hotspots.
Initial data have highlighted air pollution as emitted by big cities and ship lanes through measurements of nitrogen dioxide over Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and India.
These new data also show the transport of carbon monoxide from India to China, and the closing of the ozone hole during 2017.
Harry Förster from the Netherlands Space Office explains, “Sentinel-5P further enhances existing and initiates new European applications in this area because the very high resolution of Tropomi is simply unprecedented.
“In combination with the improved sensitivity of the detectors we now have a spectrometer that is about 10 times better than its predecessor.
Josef Aschbacher, ESA’s Director of Earth Observation Programmes, added, “I am proud that we now have a state-of-the-art measuring instrument that allows us to capture high-quality data on the atmosphere worldwide, and to do this more accurately than ever before.
Claus Zehner, ESA’s Sentinel-5P mission manager, affirmed, “We often hear about climate change and the depletion of the ozone layer when we consider why we need to monitor the atmosphere.
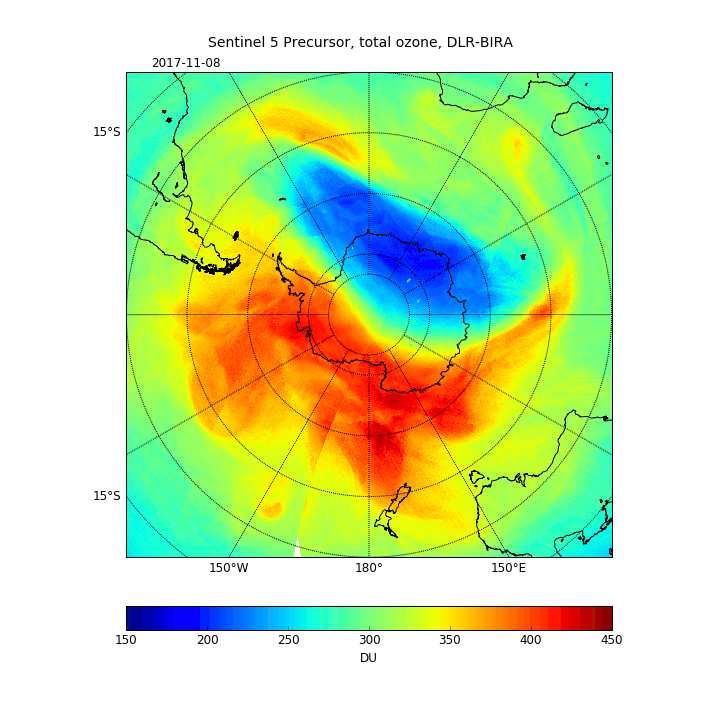
Closing of the ozone hole
“But air quality is also a huge global problem. It affects the health of humans and affects agriculture and the economy in general.”
Having completed its commissioning phase, Copernicus Sentinel-5P data is now available to all, free of charge.
From policy makers and environmental agencies to scientists, users have access to data that ultimately help to better forecast and mitigate air quality problems.
Copernicus Sentinel-5P will also contribute to services such as volcanic ash monitoring for aviation safety and warnings of high level UV radiation.
Quelle: ESA
